Chapter 10
Race and Ethnicity
By Boundless
The idea of race refers to superficial physical differences that a particular society considers significant.
Racial groups are sociologically, rather than biologically, different; that is to say, there is no "race" gene or set of genes.
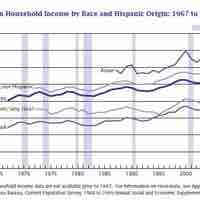
Many governments provide legal definitions of race for purposes of census-taking and calculating budgets for governmental programs.
Most social scientists and biologists believe race is a social construct affecting sociopolitical, legal, and economic contexts.

Racism is the belief that different traits of racial groups are inherent and justify discrimination.
Prejudice refers to a positive or negative evaluation of another person based on their perceived group membership (e.g., race, class, or gender).

Discrimination is the prejudicial treatment of an individual based on his or her membership (or perceived membership) in a certain group.
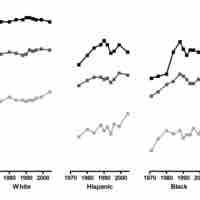
Institutionalized discrimination refers to discrimination embedded in the procedures, policies or objectives of large organizations.

Assimilation describes the process of social, cultural, and political integration of a minority into a dominant culture and society.

Multiculturalism is an ideology that promotes the institutionalization of communities containing multiple cultures.
Segregation is the division of human beings into separate groups based on any number of criteria, such as race, ethnicity, or nationality.
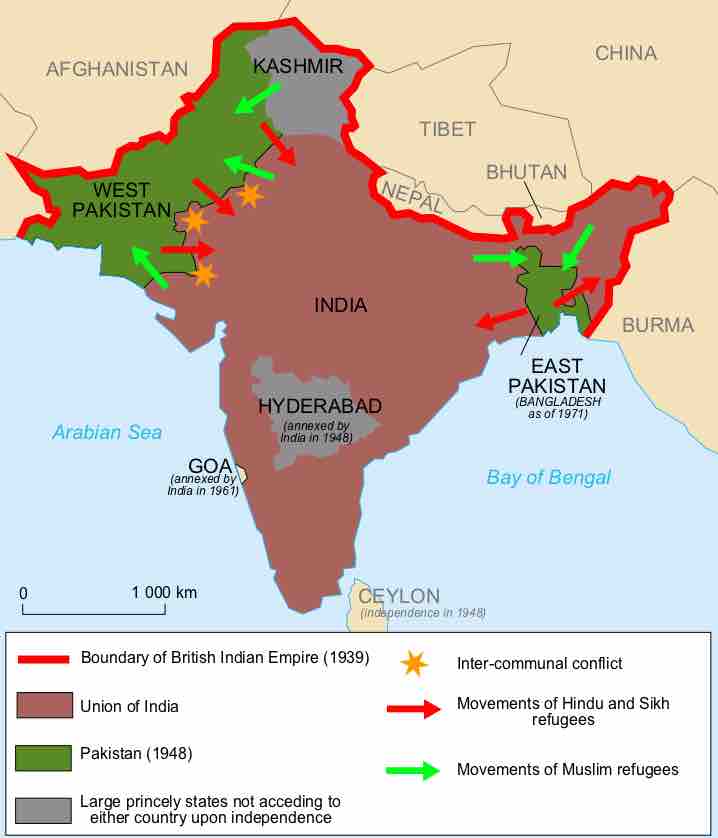
Population transfer is the movement of a large group of people from one region to another by state policy or international authority.

Genocide is "the deliberate and systematic destruction, in whole or in part, of an ethnic, racial, religious, or national group".

According to the functionalist perspective, race and ethnicity are two of the various parts of a cohesive society.
For Karl Marx, class conflict was most prominent; other theorists saw racial and ethnic conflict as more significant.
Race and ethnicity affect the meaning we attach to each other's actions.

One crucial psychological finding is that members of stereotyped groups internalize those stereotypes and may suffer as a result.
The U.S. has a diverse society, and its history is marked by attempts to concentrate power, wealth, and privilege into the hands of whites.
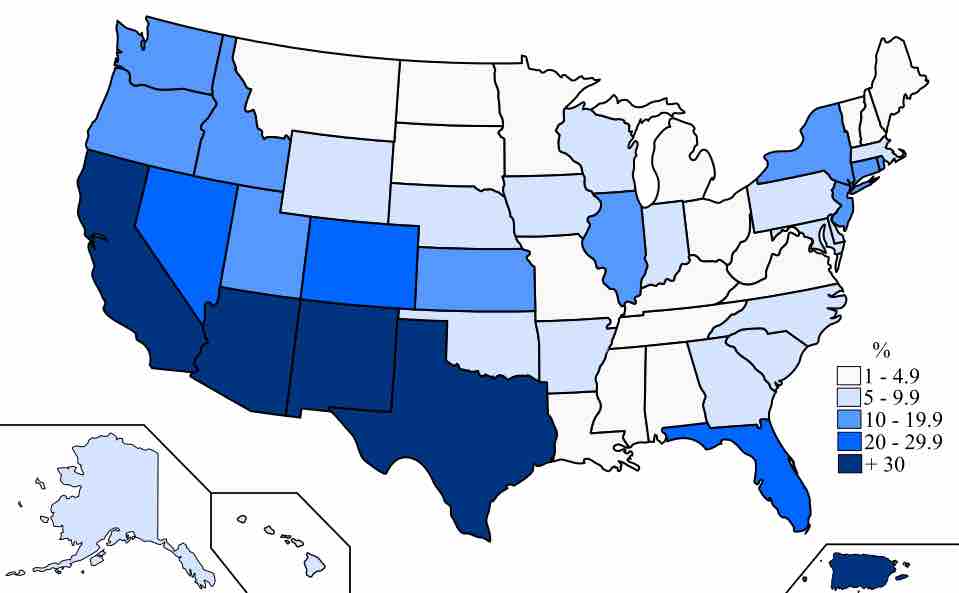
The United States is a diverse country, racially and ethnically.
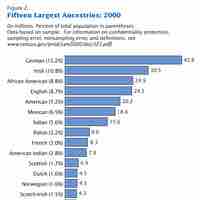
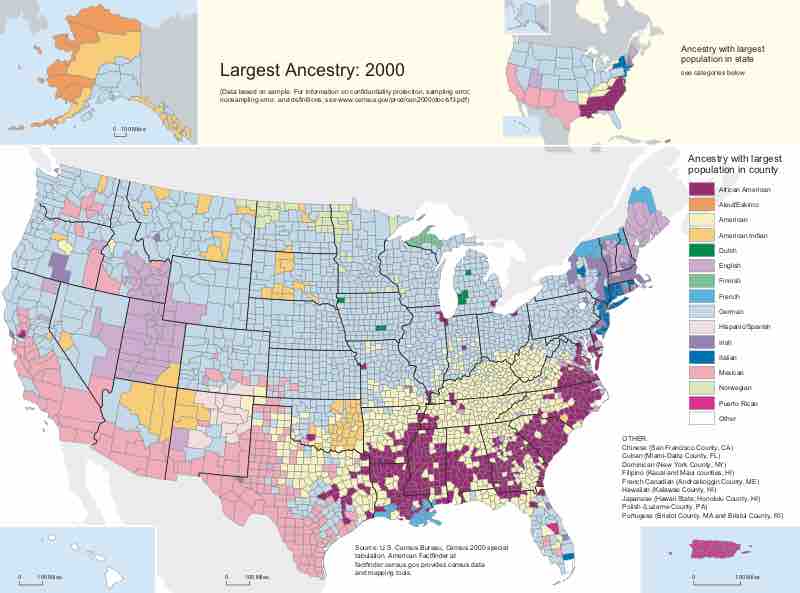
An ethnic group is a group of people who share a common heritage, culture, and/or language; in the U.S., ethnicity often refers to race.
Immigration is the act of foreigners passing or coming into a country for the purpose of permanent residence.

Affirmative action refers refers to policies that take factors such as race, gender, sexual orientation, and religion into consideration.

Multiculturalism is an ideology that promotes the institutionalization of communities containing multiple cultures.

