Chapter 11
Gender Stratification and Inequality
By Boundless
Gender socialization is the process by which males and females are informed about the norms and behaviors associated with their sex.

Social constructivists propose that there is no inherent truth to gender; it is constructed by social expectations and gender performance.

Gender identity is one's sense of one's own gender. It is the result of socialization, but it also has a biological basis.

Gender roles refer to the set of social and behavioral norms that are considered to be appropriate for people of a specific sex.

Gender roles vary widely across different cultural contexts.

Gender roles are taught from infancy through primary socialization, or the type of socialization that occurs in childhood and adolescence.

Adolescence is a transitional stage of biological, cognitive and social development that prepares individuals for taking on adult roles.

Masculine and feminine individuals generally differ in how they communicate with others.

The functionalist perspective of gender roles suggests that gender roles exist to maximize social efficiency.

Conflict theory suggests that men, as the dominant gender, subordinate women in order to maintain power and privilege in society.

From a symbolic interactionist perspective, gender is produced and reinforced through daily interactions and the use of symbols.

Feminist theory analyzes gender stratification through the intersection of gender, race, and class.

While women are succeeding in a number of professions, they continue to face significant barriers to entry and participation.
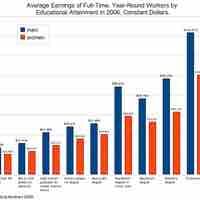
Women are frequently treated unequally at work, often through sexual harassment and/or wage discrimination.

Social expectations that women manage childcare contribute to the gender pay gap and other limitations in professional life for women.

Women have historically been disadvantaged in education, and learning has often been segregated along gender lines.

Women have had to fight for equal treatment in politics in the United States by winning the right to vote and a seat at the political table.

Despite legal protections, job discrimination against women still exists in the workplace.

Gender discrimination in health care manifests itself primarily as the difference that men and women pay for their insurance premium.

The definition of rape and its effects on victims have evolved historically alongside ideas about gender and sexuality.
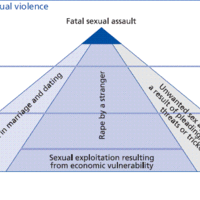
Sexual violence is any sexual act or sexual advance directed at one individual without their consent.

Sexual harassment is intimidation, bullying, teasing, or coercion of a sexual nature.