Chapter 15
Government
By Boundless

Political sociology studies the relation between state and society, authority and power, and the methods used to formulate social policy.

Power is frequently defined as the ability to influence the behavior of others with or without resistance.

Authority refers to the use of power that is seen as legitimate or socially approved/recognized.

Max Weber conceived of the state as a monopoly of the legitimate use of physical force.

Traditional authority refers to a form of leadership in which authority derives from tradition or custom.
Rational-legal authority is a form of leadership in which authority is largely tied to legal rationality, legal legitimacy, and bureaucracy.
Charismatic authority is power legitimized by a leader's exceptional personal qualities, which inspire loyalty and obedience from followers.

In the United States, transfers of authority generally occur after presidential elections.
Various schools of thought consider the state to be either a neutral entity separated from society or an immoral partisan instrument.

A state is an organized political community acting under a government. States differ in sovereignty, governance, geography, and interests.

Citizenship carries both rights and responsibilities, as it describes a person with legal rights within a given political order.

Theories explaining the origins and formation of states all revolve around the ability to centralize power in a sustainable way.
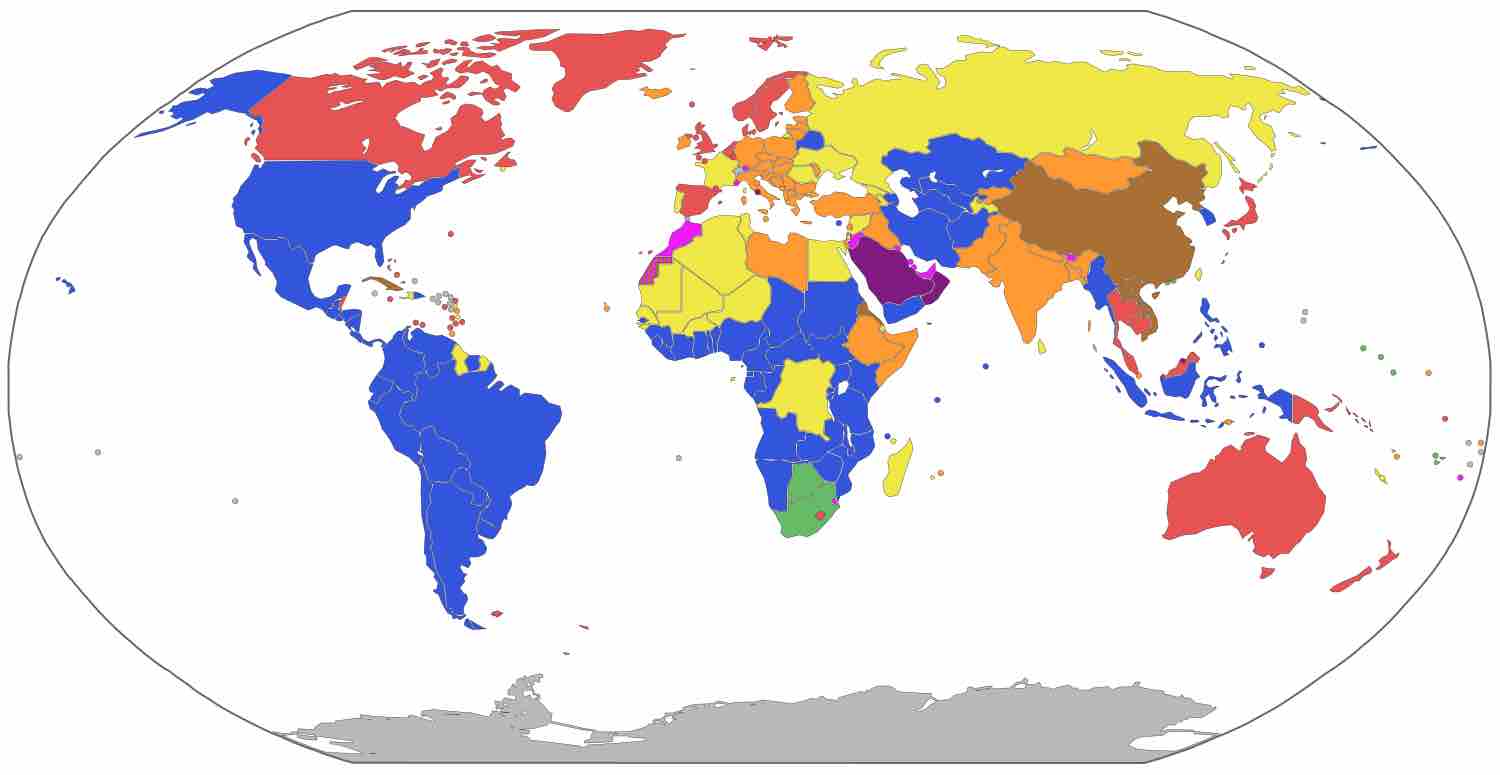
States vary based on who holds power, who elects the empowered, and how authority is maintained.

A monarchy is a form of government in which supreme power is absolutely or nominally lodged with an individual, who is the head of state.
An oligarchy is a form of government in which power effectively rests with a small elite segment of society.

Dictatorships govern without consent of the people and in totalitarian dictatorships the power to govern extends to all aspects of life.
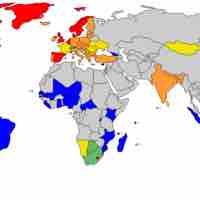
Democracy is a form of government in which sovereignty is held by the majority of citizens within a country or a state.

States are not necessarily the same as nations. New state spaces are redefining borders, and they may not be ruled by national governments.

Democracy is an egalitarian form of government in which all the citizens of a nation together determine policy, laws, and state actions.

Participatory democracy emphasized the broad participation of constituents in the direction and operation of political systems.
Monarchies, in which sovereignty embodied in a single individual, eventually gave way to liberal democracies.
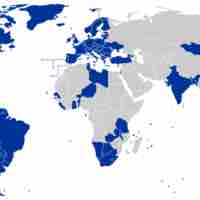
Liberal democracy requires universal suffrage, competitive politics, and the rule of law and is currently the dominant world political ideology.

The United States is a federal constitutional republic in which the federal government shares sovereignty with the state governments.

Women's political participation has increased due to landmark events—women's suffrage and the election of women to public office.

Theories of democracy advocate different degrees of participation by the people with the government.

The public sphere is composed of voluntary associations that promote social capital and social cohesion while enhancing democracy.

The United States is a representative federal democracy driven by elections in which citizens' and lobbyists' diverse interests compete.

Political parties seek to influence government policy by nominating select candidates to hold seats in political offices.

Voter turnout depends on socioeconomic factors such as education, income, gender, age, and race.

Lobbying describes paid activity in which special interest groups argue for specific legislation in decision-making bodies.

Collectively, African Americans are more involved in the American political process than other minority groups.

Hispanics have the ability to be an influential force in politics, a fact that is especially true in areas with high Hispanic populations.
Media are means of transmitting information, which is important for a democracy in which citizens must make their own informed decisions.

There is a correlation between age and political activity/organization.

War is an organized, armed, and often prolonged conflict that is carried on between states, nations, or other parties.

Terrorism is an act of violence intended to create fear, which is then leveraged in order to achieve goals.

Peace is a state of harmony characterized by the lack of violent conflict or war.