Section 4
Democracy
By Boundless

Democracy is an egalitarian form of government in which all the citizens of a nation together determine policy, laws, and state actions.

Participatory democracy emphasized the broad participation of constituents in the direction and operation of political systems.
Monarchies, in which sovereignty embodied in a single individual, eventually gave way to liberal democracies.
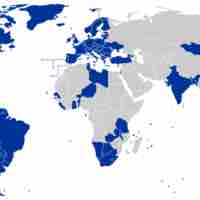
Liberal democracy requires universal suffrage, competitive politics, and the rule of law and is currently the dominant world political ideology.

The United States is a federal constitutional republic in which the federal government shares sovereignty with the state governments.

Women's political participation has increased due to landmark events—women's suffrage and the election of women to public office.

Theories of democracy advocate different degrees of participation by the people with the government.

The public sphere is composed of voluntary associations that promote social capital and social cohesion while enhancing democracy.