The Kidneys
The kidneys are the primary functional organ of the renal system. They are essential in homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and the regulation of blood pressure (by maintaining salt and water balance). They serve the body as a natural filter of the blood and remove wastes that are excreted through the urine.
They are also responsible for the reabsorption of water, glucose, and amino acids, and will maintain the balance of these molecules in the body. In addition, the kidneys produce hormones including calcitriol, erythropoietin, and the enzyme renin, which are involved in renal and hemotological physiological processes.
Anatomical Location
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped, brown organs about the size of your fist. They are covered by the renal capsule, which is a tough capsule of fibrous connective tissue. Adhering to the surface of each kidney are two layers of fat to help cushion them.
The asymmetry within the abdominal cavity caused by the liver typically results in the right kidney being slightly lower than the left, and left kidney being located slightly more medial than the right. The right kidney sits just below the diaphragm and posterior to the liver, the left below the diaphragm and posterior to the spleen.
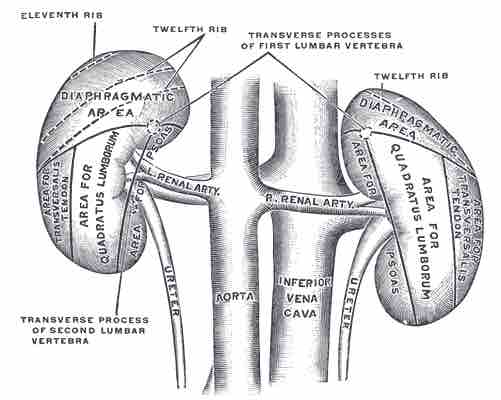
The kidneys
Human kidneys viewed from behind with the spine removed.
Resting on top of each kidney is an adrenal gland (adrenal meaning on top of renal), which are involved in some renal system processes despite being a primarily endocrine organ. The upper parts of the kidneys are partially protected by lower ribs, and each whole kidney and adrenal gland are surrounded by two layers of fat (the perirenal and pararenal fat) and the renal fascia.
The kidneys are located at the rear wall of the abdominal cavity just above the waistline and are protected by the ribcage. They are considered retroperitoneal, which means that they lie behind the peritoneum, the membrane lining of the abdominal cavity.
There are a number of important external structures connecting the kidneys to the rest of the body. The renal artery branches off from the lower part of the aorta and provides the blood supply to the kidneys. Renal veins take blood away from the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. The ureters are structures that come out of the kidneys, bringing urine downward into the bladder.