The nervous system is an organ system that coordinates our actions by transmitting signals between different parts of our bodies. Central to the functioning of the nervous system is an extensive network of specialized cells called neurons. Neurons send signals along thin fibers called axons and communicate with other cells by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters at cell-cell junctions called synapses .
Major elements in neuron-to-neuron communication
Electrical impulses travel along the axon of a neuron. When this signal reaches a synapse, it provokes release of neurotransmitter molecules, which bind to receptor molecules located in the the target cell.
In most animals, including humans, the nervous system consists of two parts: central and peripheral. The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and retina. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and neurons that communicate either between subdivisions of the PNS or connect the PNS to the CNS .
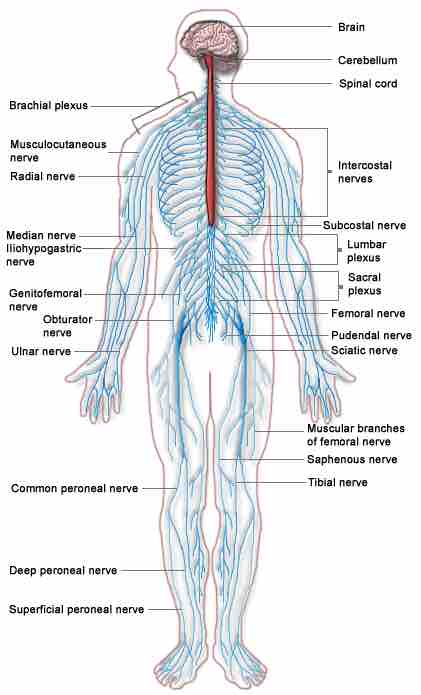
The Human Nervous System
The major organs and nerves of the human nervous system.
The nervous system has three broad functions: sensory input, information processing, and motor output . In the PNS, sensory receptor neurons respond to physical stimuli in our environment, like touch or temperature, and send signals that inform the CNS of the state of the body and the external environment. This sensory information is then processed by the CNS, predominantly by the brain. After information is processed, signals return to the PNS by way of motor neurons to muscles and glands, which respond with a motor output. Central neurons, which in humans greatly outnumber the sensory and motor neurons, make all of their input and output connections with other neurons. The connections of these neurons form neural circuits that are responsible for our perceptions of the world and determine our behavior. Along with neurons, the nervous system relies on the function of other specialized cells called glial cells, or glia, that provide structural and metabolic support to the nervous system.
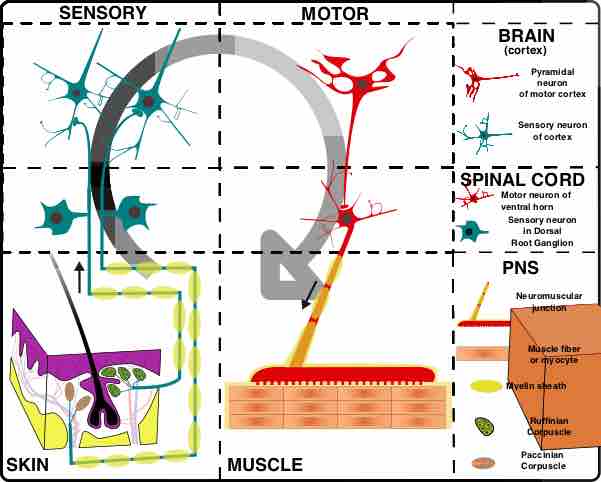
The organization of the nervous system
Gross organization of the nervous system, with the peripheral nervous system, the spinal, and the cortical levels.