Concept
Version 12
Created by Boundless
Venous Blood Pressure
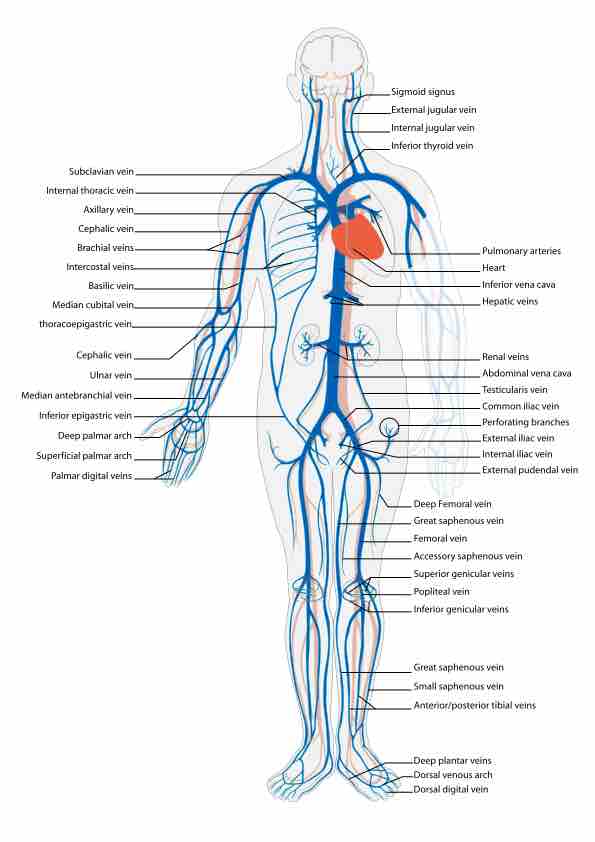
The Human Venous System
Veins (from the Latin vena) are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Veins differ from arteries in structure and function; arteries are more muscular than veins, while veins are often closer to the skin and contain valves to help keep blood flowing toward the heart.
This diagram of the venous system indicates the sigmoid sinus, internal and external jugular vein, inferior thyroid vein, pulmonary arteries, heart, inferior vena cava, hepatic veins, renal veins, abdominal vena cava, testicularis vein, common iliac vein, perforating branches, external and internal iliac vein, external pudendal vein, deep femoral vein, great saphenous vein, femoral vein, accessory saphenous vein, superior genicular vein, popliteal vein, inferior genicular vein, small saphenous vein, anterior and posterior tibial veins, deep plantar veins, dorsal venous arch, dorsal digital vein, palmar digital veins, superficial palmar arch, deep palmar arch, inferior epigastric vein, median antebranchial vein, ulnar vein, cephalic vein, thoracoepigastric vein, median cubital vein, basilic vein, intercostal veins, brachial veins, cephalic vein, axillary vein, internal thoracic vein, and subclavial vein.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: