Section 6
Wave Behavior and Interaction
By Boundless
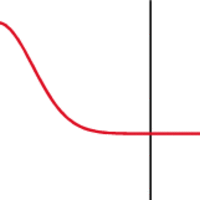
When the medium changes, a wave often experiences partial transmission and partial refection at the interface.
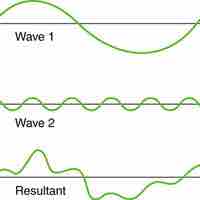
A wave may have a complicated shape that can result from superposition and interference of several waves.
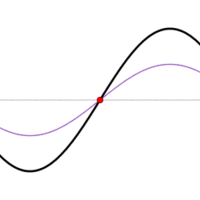
A standing wave is one in which two waves superimpose to produce a wave that varies in amplitude but does not propagate.
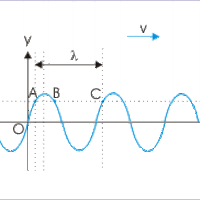
When vibrations in the string are simple harmonic motion, waves are described by harmonic wave functions.
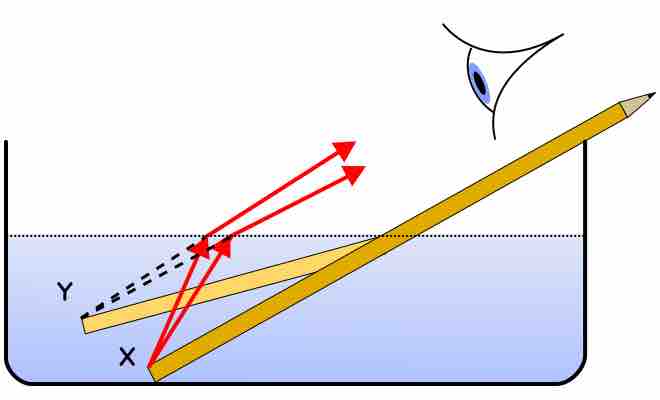
Refraction is a surface phenomenon that occurs as the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its medium.

Diffraction refers to various phenomena such as the bending of waves around obstacles and the spreading out of waves past small openings.
The most general solution of the wave equation

The energy in a wave is proportional to its amplitude squared and the intensity of a wave is defined as power per unit area.