Chapter 1
Introduction to Marketing
By Boundless
Marketing is the creation, communication, and delivery of value as well as the management of customer relationships for a lifetime.

Consumer wants and needs should drive marketing decisions, and no strategy should be pursued until it passes the test of consumer research.

Product, placement, promotion, and price are four elements of the marketing mix crucial to determining a brand's unique selling proposition.

Customer-focused marketing is known as SIVA which provides a demand-centric alternative to the four P's supply side of marketing management.
The act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something of value in return is called the exchange process.
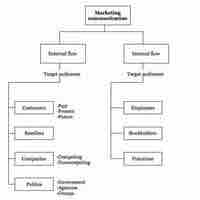
The key to building a strong stakeholder relationship is communicating effectively with all stakeholders.

Since the business environment is constantly changing and customer preferences keep evolving, marketers are required to adapt rapidly.
Marketing by firms compared to marketing by individuals differs greatly in terms of customization level and personal attention.

Marketing adds value to an organization by communicating relevant positioning and building long-term customer relationships.

Production orientation follows the premise that any product of high quality can be readily sold.
A firm employing a product orientation is chiefly concerned with the quality of its product.

As opposed to production or product orientation, a sales orientation focuses primarily on the selling and promotion of a particular product.
A marketing-oriented business starts with the customer, finds out what they want, and then produces it for them.
Holistic marketing incorporates integrated marketing, relationship management, internal marketing and social responsibility to build a unified and shared brand.
Relationship marketing is a form of marketing that shifts focus away from sales transactions to emphasize customer satisfaction.

Business marketing is the practice of organizations facilitating the sale of their products or services to other companies or organizations.

Social marketing is the systematic application of marketing to achieve specific behavioral goals for a social good.
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol, or any other feature that identifies a seller's good or service.
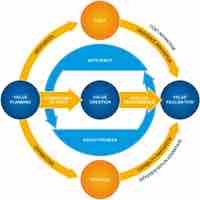
Value-based marketing allows organizations to create and sustain differentiating values that enable them to compete within their markets.
The values of an organization are just as important as the products they sell; having a strong value driven culture is important.
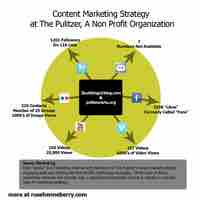
Non-profit marketing focuses on goals in education, youth development, environmental protection, healthcare, poverty and spirituality.

Marketing can play a key role in integrating supply chain processes and promoting collaboration between different stakeholders.

Increased global competition, financial flows and internet technologies are some of the driving forces behind global marketing strategies.

Consumer awareness is the extent to which a brand is recognized by potential customers, and is correctly associated with a particular product.

Adopting socially responsible practices that benefit customers and society is fast becoming a competitive advantage in global business.

The marketing field provides a wide range of careers for professionals in brand management, PR, and communications.

Many firms task their marketing teams to promote a culture of entrepreneurial thinking via initiatives in and outside the organization.

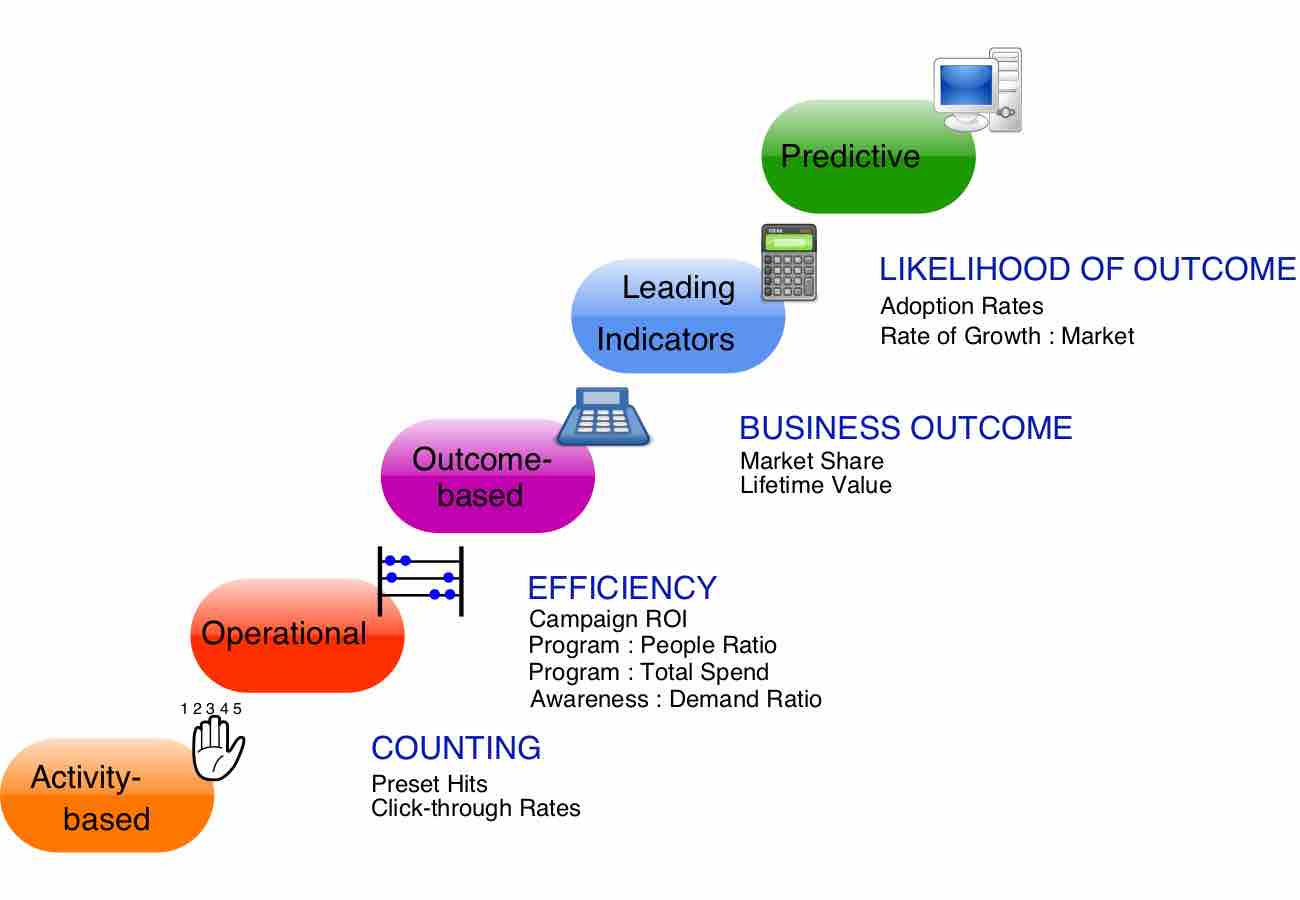
Evaluating marketing performance guides future marketing initiatives and helps a company achieve its goals.
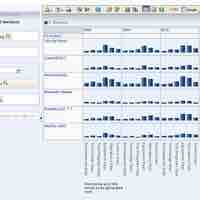
Marketing metrics are numeric data that allow marketers to evaluate their performance against organizational goals.
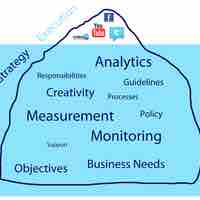
KPIs, ROMI, and Accountable Marketing are all metrics that are used to track marketing performance.