Chapter 7
Human Resource Management
By Boundless

Human resource management's mission is to coordinate people within an organization to achieve the organization's goals.

Human resource planning identifies the competencies an organization needs to fulfill its goals and acquires the appropriate people.

Discrimination—treating specific groups of people unequally—is unethical behavior and is prohibited by several pieces of U.S. legislation.
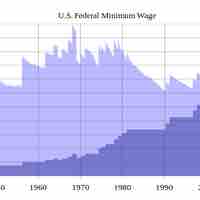
Labor laws encompass various types of government mandates that define the relationship between an employee and employer.

Unionization is the process of workers forming a union, which is an organization to further the workers' shared interests.

Collective bargaining is negotiation between unions and employers to come to an agreement on the conditions of employment.

Compensation and benefits is the subdiscipline of human resources that deals with employees' remuneration.

Occupational safety and health (OSH) is used to protect people in the workplace and create human resource policies that adhere to the law.

Recruitment is the process of identifying an organizational gap and attracting, evaluating, and hiring employees to fill that role.

Selection is the process—based on filtering techniques that ensure added value—of choosing a qualified candidate for a position.
Orientation tactics exist to provide new employees enough information to adjust, resulting in satisfaction and effectiveness in their role.

A core function of human resource management is development—training efforts to improve personal, group, or organizational effectiveness.

Career-path management requires human resource management to actively manage employee skills in pursuit of successful professional careers.

Performance evaluation is the process of assessing an employee's job performance and productivity over a specified period of time.
Effective feedback is structured in a way that provides actionable conclusions to motivate employee growth through objective assessments.

Making pay decisions can be a function of HR; payroll surveys and internal measures can help determine what is appropriate.
Human resources professionals assess organizational and employee needs to identify the ideal incentive systems for collaborative success.
Employee benefits are non-wage compensations designed to provide employees with extra economic security.
A promotion is the advancement of an employee's rank, salary, duties, and/or designation within an organization.

Transfers take place in response to goals, needs, talent, or employee requests; HR evaluates and executes transfers.

Organizations must create strong, clear disciplinary policies; all disciplinary actions should be well documented and fairly applied.
Dismissal is the involuntary termination of an employee due to incompetence, poor job performance, or violation of policy.

Managers are increasingly aware of the importance of promoting a healthy work-life balance for employees, which increases job satisfaction.
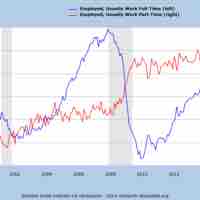
Management must both define and carefully consider the common tradeoffs in employing a part-time or contract-based workforce.
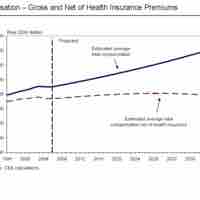
Good compensation helps organizations stay competitive in their industry by retaining high-quality employees.
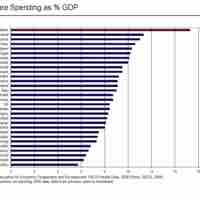
Hiring and retaining employee talent is a critical factor in success, and providing fringe benefits can be an effective tool in this process.
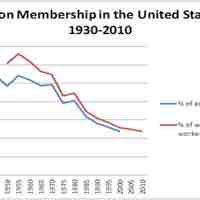
Human resource management must carefully monitor the labor relations and regulations in all of the geographic regions where they hire.