Chapter 1
Introduction to the Field and Goals of Financial Management
By Boundless

Finance is the study of fund management and asset allocation over time.
Finance, economics, and accounting are business subjects with many similarities and differences; each is a distinct field of study.
The primary role of corporate finance is to determine how best to maximize shareholder value.

Investment and financing decisions boil down to how to spend money and how to borrow money.

Corporate finance utilizes tools and analysis to make sound financial business decisions.

The financial manager is responsible for budgeting, projecting cash flows, and determining how to invest and finance projects.
Finance is relevant to all business functions, the macroeconomy, and personal finances.

Valuation, a goal of financial management, often relies on fundamental analysis of financial statements.

A goal of financial management can be to maximize shareholder wealth by paying dividends and/or causing the market value to increase.

A goal of financial management can be to maximize value without harming stakeholders, the diverse set of parties affected by the business.

Current issues in finance include the economic and regulatory impacts of the financial crisis and the growth of new types of finance.

The financial sector is a large field offering many different types of employment for a broad range of organizations that manage money.
Ethics are the set of moral principles that guide a person's behavior.
Moral reasoning is the process in which an individual tries to determine what is right and what is wrong.
Culture reflects the moral values and ethical norms governing how people should behave and interact with others.
Employees can more easily make ethical decisions that promote a company's values when their personal values match the company's norms.

Ethical decisions involve judgments of facts and situations that are subject to interpretation and other influences.
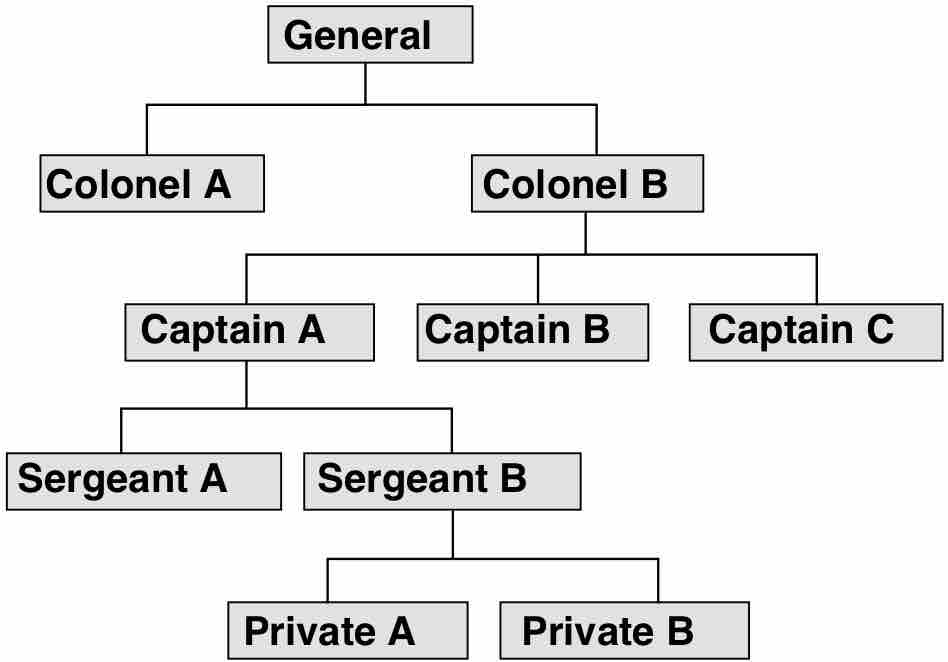
Business organizations can be structured in various ways, both as legal entities and in terms of internal management processes.
The sole proprietorship structure has the benefit of simplicity and control but the drawback of unlimited liability.

The partnership structure has the benefit of simplicity and control but the drawback of personal liability for the partnership's activities.

The corporate structure is less simple to found and maintain but has the advantages of limited liability and perpetual life.

Agency conflicts can occur when the incentives of the agent do not align with those of the principal.
Three parties key to the corporation's functioning are managers, shareholders, and bondholders, each of which can have different interests.

Agency costs mainly occur when ownership is separated, or when managers have objectives other than shareholder value maximization.

The shareholders and bondholders have different rights and returns, leading to potential conflicts of interest.
Cash, the most liquid asset, refers to physical currency such as banknotes and coins.
A debt is an obligation owed by one party (the debtor) to a second party (the creditor).
The capital stock (or stock) of a business entity represents the original capital paid into or invested in the business by its founders.

Financial markets are of many types, including general and specialized; capital and money; and primary and secondary.

One of the main functions of financial markets is to allocate capital, matching those who have capital to those who need it.

Financial markets can provide feedback to management by showing signals of the demand to supply funds to that enterprise.

A market trend is a putative tendency of a financial market to move in a particular direction over time.

