Measuring IT Risk
Information technology (IT) risk involves the business risk associated with the use, ownership, operation, involvement, influence and adoption of IT within an enterprise. IT encompasses not only the negative impact on operations and service delivery, but also the benefit and/or value enabling risk associated with missed opportunities to use technology to enable or enhance the business (including improper management of IT projects). The negative impact can cause destruction or reduction of the organization's value. The benefit and/or enabling risk can result in overspending or late delivery of projects that lead to adverse business results.
Risk is the product of the likelihood of an occurrence times its impact (Risk = Likelihood x Impact). The measure of IT risk can be determined as a product of threat, vulnerability, and asset values (Risk = Threat x Vulnerability x Asset Value).
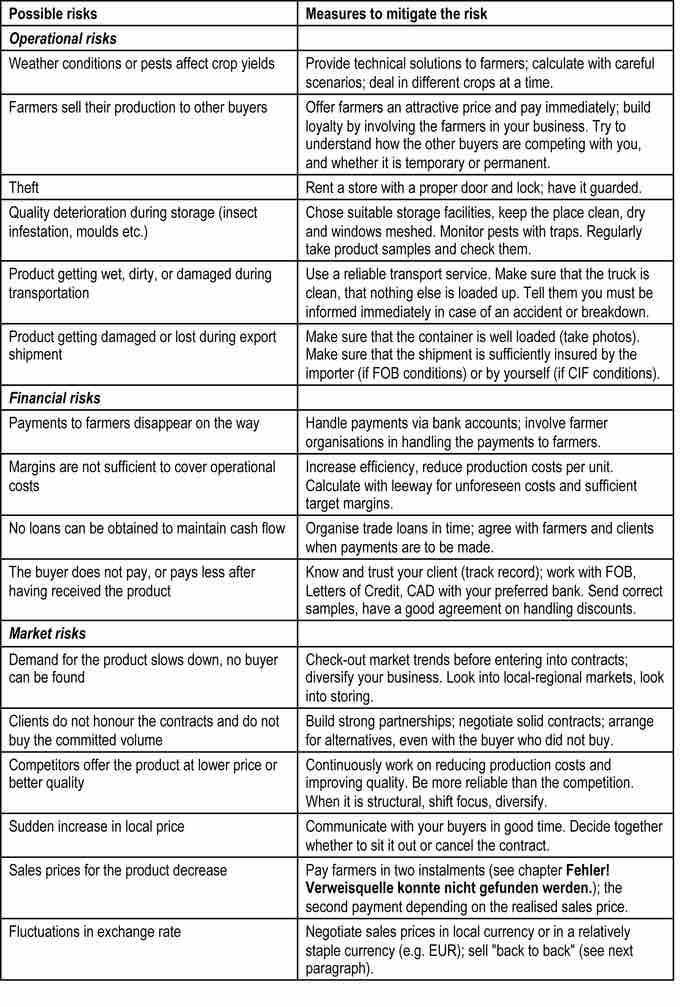
Possible Business Risks
This chart represents a list of the possible risks involved in running an organic business. Risks such as these affect sales, which in turn affect the amount of operating leverage a company should utilize.
IT and Enterprise Risk Management
IT risk management can be viewed as a component of a wider enterprise risk management (ERM) system. Some organizations have a comprehensive enterprise risk management methodology in place. The four objective categories addressed in an ERM, according to COSO, are:
- Strategy - high-level goals, aligned with and supporting the organization's mission
- Operations - effective and efficient use of resources
- Financial Reporting - reliability of operational and financial reporting
- Compliance - compliance with applicable laws and regulations
IT risk transverses all four of the aforementioned categories and should be managed within the framework of enterprise risk management. Risk appetite and risk sensitivity of the whole enterprise should guide the IT risk management process. ERM should provide the context and business objectives on the management of IT risk.