Chapter 28
Invertebrates
By Boundless
Sponges lack true tissues, have no body symmetry, and are sessile; types are classified based on presence and composition of spicules.
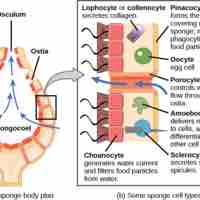
Instead of true tissues or organs, sponges have specialized cells that are in charge of important bodily functions and processes.
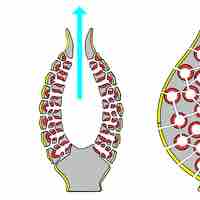
Sponges are sessile, feed by phagocytosis, and reproduce sexually and asexually; all major functions are regulated by water flow diffusion.
Cnidarians are diploblastic, have organized tissue, undergo extracellular digestion, and use cnidocytes for protection and to capture prey.
Members of the class Anthozoa display only polyp morphology and have cnidocyte-covered tentacles around their mouth opening.
Scyphozoans are free-swimming, polymorphic, dioecious, and carnivorous cnidarians with a prominent medusa morphology.
Cubozoans live as box-shaped medusae while Hydrozoans are true polymorphs and can be found as colonial or solitary organisms.

The Lophotrochozoa are protostomes possessing a blastopore, an early form of a mouth; they include the trochozoans and the lophophorata.
The Platyhelminthes are flatworms that lack a coelom; many are parasitic; all lack either a circulatory or respiratory system.
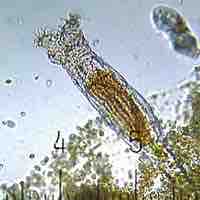
Rotifers are microscopic organisms named for a rotating structure (called the corona) at their anterior end that is covered with cilia.
Nemertea, or ribbon worms, are distinguished by their proboscis, used for capturing prey and enclosed in a cavity called a rhynchocoel.

Mollusks have a soft body and share several characteristics, including a muscular foot, a visceral mass of internal organs, and a mantle.
The phylum Mollusca includes a wide variety of animals including the gastropods ("stomach foot"), the cephalopods ("head foot"), and the scaphopods ("boat foot").
Annelids include segmented worms, such as leeches and earthworms; they are the most advanced worms as they possess a true coelom.
The superphylum Ecdysozoa includes the nematode worms and the arthropods, both of which have a tough external covering called a cuticle.
Nematodes are parasitic and free-living worms that are able to shed their external cuticle in order to grow.
Arthropods are the largest grouping of animals all of which have jointed legs and an exoskeleton made of chitin.
The Phylum Arthropoda includes a wide range of species divided into the subphyla: Hexapoda, Crustacea, Myriapoda, and Chelicerata.

Echinoderms are invertebrates that have pentaradial symmetry, a spiny skin, a water vascular system, and a simple nervous system.
Echinoderms consist of five distinct classes: sea stars, sea cucumbers, sea urchins and sand dollars, brittle stars, and sea lillies.
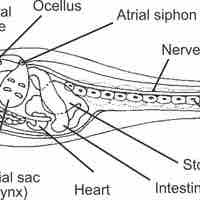
The phylum Chordata contains all animals that have a dorsal notochord at some stage of development; in most cases, this is the backbone.