Phylum Rotifera
The rotifers are a microscopic (about 100 µm to 30 mm) group of mostly-aquatic organisms that get their name from the corona: a rotating, wheel-like structure that is covered with cilia at their anterior end. Although their taxonomy is currently in flux, one treatment places the rotifers in three classes: Bdelloidea, Monogononta, and Seisonidea. The classification of the group is currently under revision, however, as more phylogenetic evidence becomes available. It is possible that the "spiny headed worms" currently in phylum Acanthocephala will be incorporated into this group in the future.
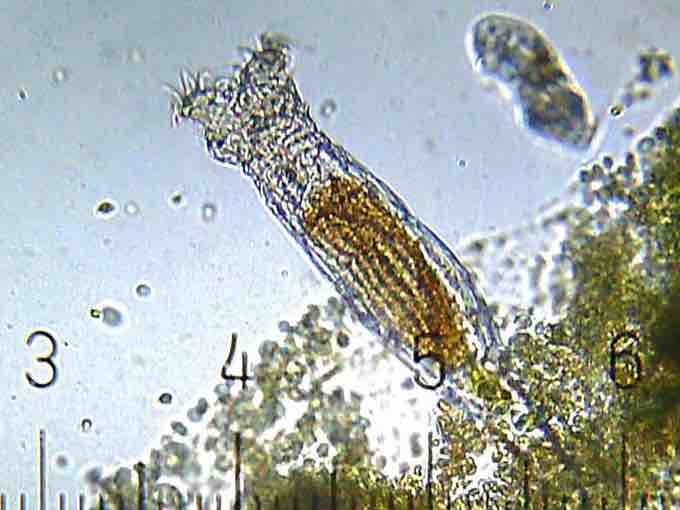
Rotifers
A bdelloid rotifer is a member of a class of rotifers found in fresh water and moist soil. The rotifer body consists of a head, a truck, and a foot. They eat by filtering food into the mouth by creating currents with the corona.
The rotifer body form consists of a head (which contains the corona), a trunk (which contains the organs), and the foot. Rotifers are typically free-swimming and truly planktonic organisms, but the toes or extensions of the foot can secrete a sticky material forming a holdfast to help them adhere to surfaces. The head contains sensory organs in the form of a bi-lobed brain and small eyespots near the corona.
The rotifers are filter feeders that will eat dead material, algae, and other microscopic living organisms. Therefore, they are very important components of aquatic food webs. Rotifers obtain food that is directed toward the mouth by the current created from the movement of the corona. The food particles enter the mouth and travel to the mastax (pharynx with jaw-like structures). Food passes by digestive and salivary glands into the stomach and then into the intestines. Digestive and excretory wastes are collected in a cloacal bladder before being released out the anus.
Rotifers are pseudocoelomates commonly found in fresh water and some salt water environments throughout the world. About 2,200 species of rotifers have been identified. Rotifers are dioecious organisms (having either male or female genitalia) and exhibit sexual dimorphism (males and females have different forms). Many species are parthenogenic and exhibit haplodiploidy, a method of gender determination in which a fertilized egg develops into a female and an unfertilized egg develops into a male. In many dioecious species, males are short-lived and smaller, with no digestive system and a single testis. Females can produce eggs that are capable of dormancy, which protects eggs during harsh environmental conditions.