Section 4
Evolution of Genomes
By Boundless
Genomic similarities between distant species can be established via analysis of genomes using advanced technology.
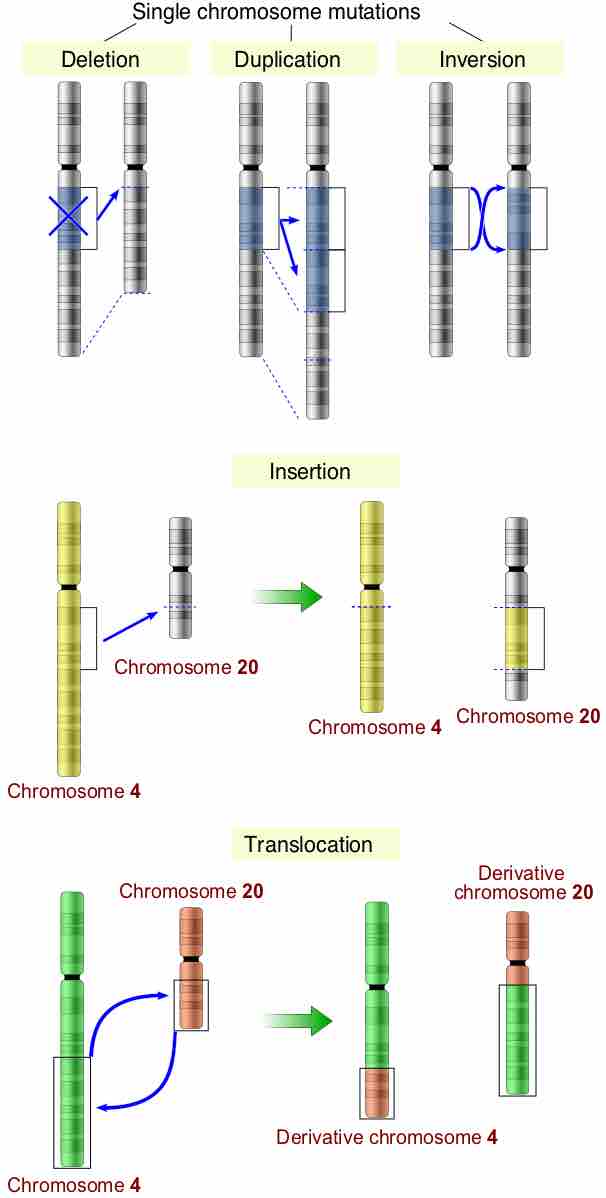
Processes such as mutations, duplications, exon shuffling, transposable elements and pseudogenes have contributed to genomic evolution.
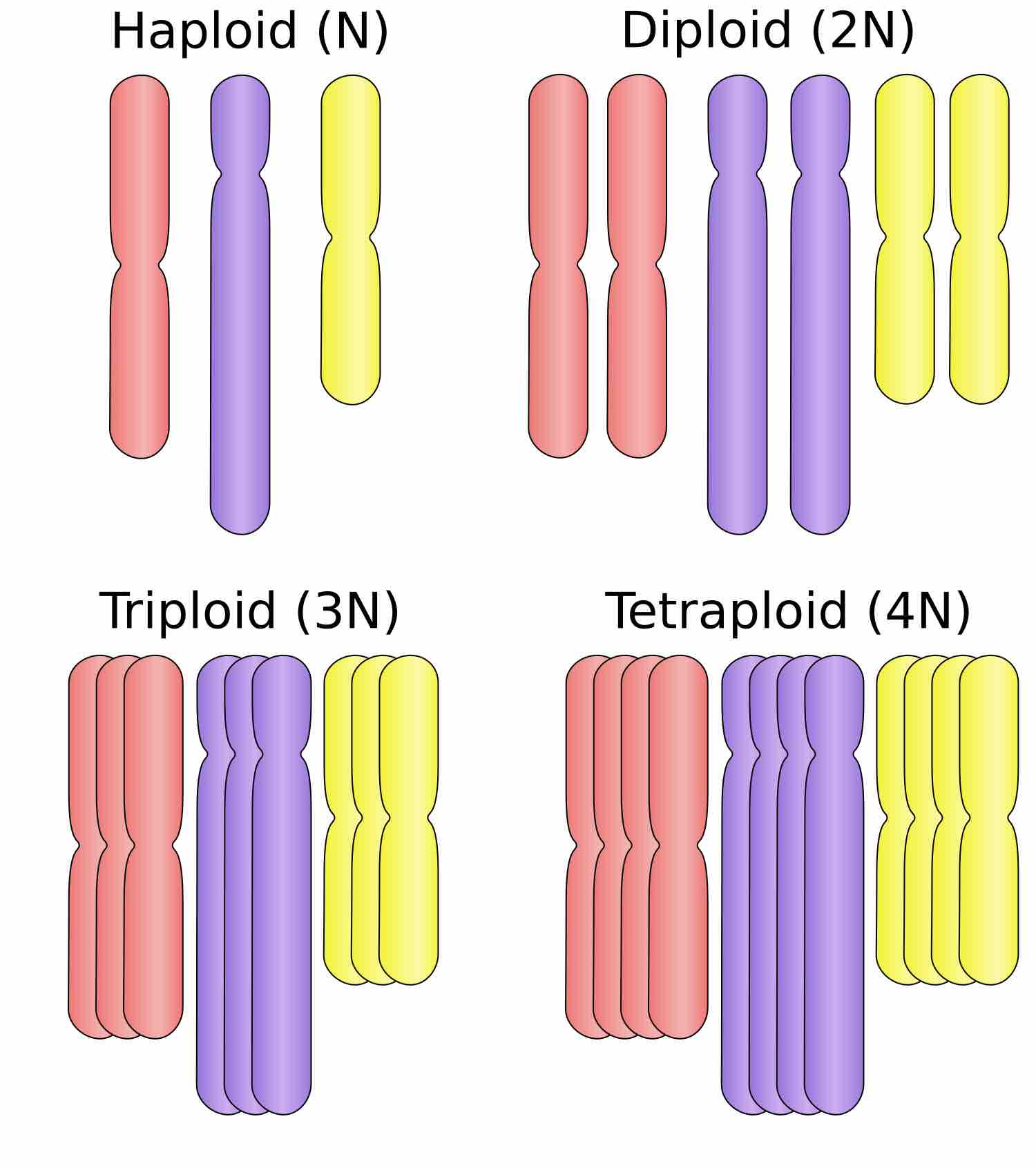
Whole-genome duplication is characterized by an organisms entire genetic information being copied once or multiple times.
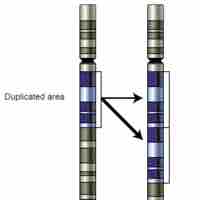
Gene duplications create genetic redudancy and can have various effects, including detrimental mutations or divergent evolution.
Noncoding DNA are sequences of DNA that do not encode protein sequences but can be transcribed to produce important regulatory molecules.
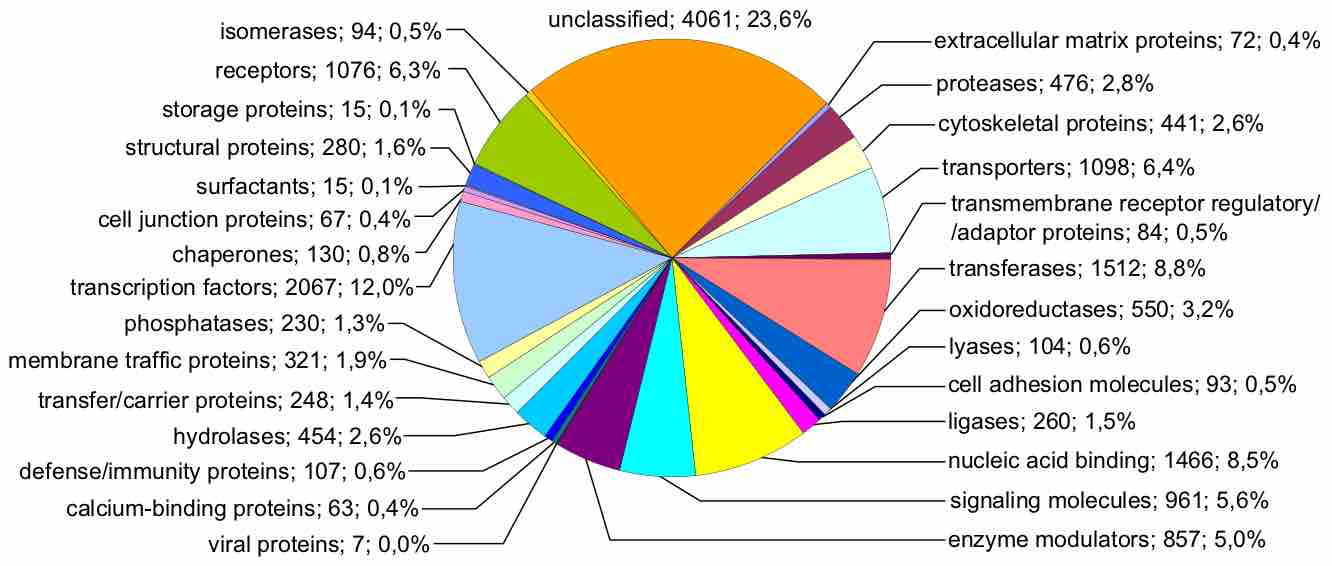
The genome size does not always correlate with the complexity of the organism and, in fact, shows great variation in size and gene number.