Section 3
Valuing Inventory
By Boundless

There are four accepted methods of costing items: specific identification; first-in, first-out; last-in, first-out; and weighted-average.
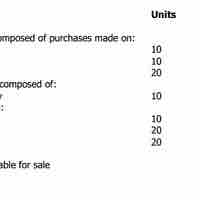
Specific identification is a method of finding out ending inventory cost that requires a detailed physical count.
Inventory cost flow assumptions (e.g., FIFO) are necessary to determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory.

Under the Average Cost Method, It is assumed that the cost of inventory is based on the average cost of the goods available for sale during the period.
FIFO stands for "first-in, first-out," and assumes that the costs of the first goods purchased are charged to cost of goods sold.

LIFO stands for last-in, first-out, meaning that the most recently produced items are recorded as sold first.

The gross profit method uses the previous year's average gross profit margin to calculate the value of the inventory.
When selecting an inventory method, managers should look at the advantages and disadvantages of each.

The method a company uses to determine it cost of inventory (inventory valuation) directly impacts the financial statements.