Accounts receivable represents money owed by entities to the firm on the sale of products or services on credit. In most business entities, accounts receivable is typically executed by generating an invoice and either mailing or electronically delivering it to the customer. In turn, the customer must pay it within an established time frame, which is called the credit terms or payment terms.
An example of a common payment term is Net 30, which means that payment is due at the end of 30 days from the date of invoice. The debtor is free to pay before the due date. To encourage this, businesses can offer a discount for early payment. Other common payment terms include Net 45, Net 60, and 30 days end of month.
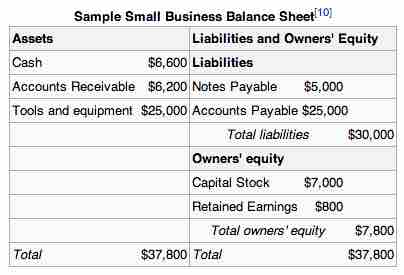
On a company's balance sheet, receivables can be classified as accounts receivables or trade debtors, bills receivable, and other receivables (loans, settlement amounts due for non-current asset sales, rent receivables, term deposits). Accounts receivable is the money owed to that company by entities outside of the company. Trade receivables are the receivables owed by the company's customers. Other receivables can be divided according to whether they are expected to be received within the current accounting period or 12 months (current receivables), or received greater than 12 months (non-current receivables) .
Balance sheet
Sample balance sheet
Not all accounts receivables will be paid, and an allowance has to be made for bad debts. The allowance for bad debts can be calculated either as the percentage of net credit sales or by the ageing method of estimating bad debts. These are determined by historical accounting information. Accounts receivable therefore can be classified according to their age. The Accounts Receivable Age Analysis Printout, also known as the Debtors Book is divided in categories for current, 30 days, 60 days, 90 days, 120 days, 150 days,180 days, and overdue.