Tortoise
Did you know...
SOS Children has tried to make Wikipedia content more accessible by this schools selection. SOS Children is the world's largest charity giving orphaned and abandoned children the chance of family life.
| Tortoises | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Aldabra Giant Tortoise (Geochelone gigantea) from Aldabra atoll in the Seychelles. |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Superfamily: | Testudinoidea |
| Family: | Testudinidae |
| Genera | |
|
Chersina |
|
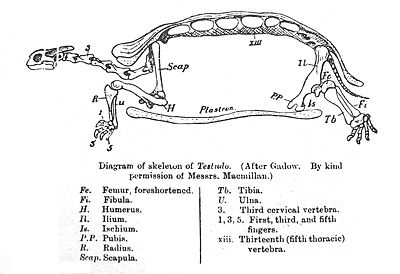
Tortoises or land turtles are land-dwelling reptiles of the family of Testudinidae, order Testudines. Like their marine cousins, the sea turtles, tortoises are shielded from predators by a shell. The top part of the shell is the carapace, the underside is the plastron, and the two are connected by the bridge. The tortoise has both an endoskeleton and an exoskeleton. Tortoises can vary in size from a few centimetres to two meters. Tortoises tend to be diurnal animals with tendencies to be crepuscular depending on the ambient temperatures. They are generally reclusive animals.
Tortoises as pets
Many tortoises, have specific temperature, roaming space, light, air moisture, and diet requirements. They are difficult to breed in captivity, so many are caught in the wild. Tortoises need outdoor space to roam. It is not possible to house-train a tortoise.
Biology
Differences between turtles, tortoises and terrapins
Birth
Female tortoises dig burrows in which they lay from two to twelve eggs. Hatchlings take approximately 90-120 days to incubate within the ping-pong-ball sized eggs. Upon completion of the incubation period the hatchlings break open egg shell enclosure with their beak and dig their way to the surface. Most hatchlings are born with an embryonic egg sac which serves as a source of food until they are capable of eating solid foods, this stage lasts between 3 and 7 days. Unlike turtles, hatchlings of most tortoise species will move from their nest and into their mother's burrow following birth. The mother will usually provide protection for the hatchlings for around 80 days, after which the babies will attempt to survive on their own.
Lifespan
There are many old wives tales about the age of turtles and tortoises, one of which being that the age of a tortoise can be deducted by counting the number of concentric rings on its carapace, much like the cross-section of a tree. This is, of course, not true, since the growth of a tortoise depends highly on the access of food and water. A tortoise that has access to plenty of forage (or is regularly fed by its owner) will grow faster than a desert tortoise that goes days without eating.
Tortoises generally have lifespans comparable with those of human beings, and some individuals are known to have lived longer than 150 years. Because of this, they symbolize longevity in some cultures, such as China. The oldest tortoise ever recorded, almost the oldest individual animal ever recorded, was Tui Malila, who was presented to the Tongan royal family by the British explorer Captain Cook shortly after its birth in 1777. Tui Malila remained in the care of the Tongan royal family until its death by natural causes on May 19, 1965. This means that upon its death, Tui Malila was 188 years old. The record for the longest-lived vertebrate is succeeded only by one other, a Koi Fish named "Hanako" whose death on July 17, 1977 ended a 226 year life span.
The Alipore Zoo in India was the home to Adwaitya, which zoo officials claimed was the oldest living animal until its death on March 23, 2006. Adwaitya (sometimes spelled with two d's) was an Aldabra Giant Tortoise brought to India by Lord Wellesley who handed it over to the Alipur Zoological Gardens in 1875 when the zoo was set up. Zoo officials state they have documentation showing that Adwaitya was at least 130 years old, but claim that he was over 250 years old (although this has not been scientifically verified). Adwaitya was said to be the pet of Robert Clive. Harriet, a resident at the Australia Zoo in Queensland, was apocryphally thought to have been brought to England by Charles Darwin aboard the Beagle. Harriet died on June 23, 2006, just shy of her 176th birthday.
Sexual dimorphism
Many, though not all, species of tortoises are sexually dimorphic, though the differences between males and females vary from species to species. In some species, males have a longer, more protruding neck plate than their female counterparts, while in others the claws are longer on the females. In most tortoise species the female tends to be larger than the male. Some believe that males grow quicker, while the female grows slower but larger. The male also has a plastron that is concave / curved inwards to aid reproduction. The easiest way to determine the sex of a tortoise is to look at the tail. The females, as a general rule have a smaller tail which is dropped down whereas the males have a much longer tail which is usually pulled up and to the side of the rear shell.
Diet
Most land based tortoises are herbivores, feeding on grazing grasses, weeds, leafy greens, flowers, and certain fruits. Their main diet consists of alfalfa, clover, dandelions, and leafy weeds, although they will also eat various insects. Feeding tortoises cat or dog food is a common mistake, as both cat and dog food contain too much protein and lack other important nutrients for tortoises. Tortoises are not carnivores, and should not be fed large amounts of protein, as it may cause shell deformation and other medical problems.
There is a large amount of speculation on the use of tortoise pellets when feeding tortoises as in fact, tortoise pellets contain too much protein, which will cause shell deformation and other medical problems. As a general rule, tortoises kept as domestic pets (usually Testudo Graecae and Testudo Hermanae) should be fed on weeds such as dandelions and clover and that is all that is needed. Calcium Carbonate can be ground into powder and added with weeds to provide extra essential calcium to a tortoise's diet.
In religion

In Hinduism, Kurma (Sanskrit: कुर्म) was the second avatar of Vishnu. Like the Matsya Avatara also belongs to the Satya yuga. Vishnu took the form of a half-man half-tortoise, the lower half being a tortoise. He is normally shown as having four arms. He sat on the bottom of the ocean after the Great Flood. A mountain was placed on his back by the other gods so that they could churn the sea and find the ancient treasures of the Vedic peoples.
Species list
The following species list largely follows Ernst & Barbour (1989), as indicated by The Reptile Database. However, the newly erected genera Astrochelys, Chelonoidis and Stigmochelys have been retained within Geochelone.
- Chersina
- Chersina angulata, Bowsprit Tortoise
- Cylindraspis (All species Extinct)
- Cylindraspis indica, synonym Cylindraspis borbonica
- Cylindraspis inepta
- Cylindraspis peltastes
- Cylindraspis triserrata
- Cylindraspis vosmaeri
- Dipsochelys
- Dipsochelys abrupta (Extinct)
- Dipsochelys arnoldi, Arnold's Giant Tortoise,
- Dipsochelys daudinii (Extinct)
- Dipsochelys dussumieri, Aldabra Giant Tortoise, common synonyms Geochelone gigantea, Aldabrachelys gigantea
- Dipsochelys grandidieri (Extinct)
- Dipsochelys hololissa, Seychelles giant tortoise
- Geochelone
- Geochelone carbonaria, Red-Footed Tortoise; sometimes placed in distinct genus Chelonoidis
- Geochelone chilensis, Chaco or Chilean Tortoise; sometimes placed in distinct genus Chelonoidis
- Geochelone denticulata, Yellow-Footed Tortoise; sometimes placed in distinct genus Chelonoidis
- Geochelone elegans, Indian Star Tortoise
- Geochelone nigra, Galápagos Giant Tortoise; sometimes placed in distinct genus Chelonoidis
- Geochelone pardalis, Leopard Tortoise; sometimes placed in distinct genus Stigmochelys or in Psammobates
- Geochelone platynota, Burmese Star Tortoise
- Geochelone radiata, Radiated Tortoise; sometimes placed in distinct genus Astrochelys
- Geochelone sulcata, African Spurred Tortoise (Sulcata Tortoise)
- Geochelone yniphora, Angulated Tortoise, Madagascan (Plowshare) Tortoise; sometimes placed in distinct genus Astrochelys
- Gopherus
- Gopherus agassizii, Desert Tortoise
- Gopherus berlandieri, Texas Tortoise
- Gopherus flavomarginatus, Bolson Tortoise
- Gopherus polyphemus, Gopher Tortoise
- Homopus
- Homopus aerolatus, Parrot-Beaked Cape Tortoise
- Homopus boulengeri, Boulenger's Cape Tortoise
- Homopus femoralis, Karroo Cape Tortoise
- Homopus signatus, Speckled Cape Tortoise, Speckled Padloper
- Homopus bergeri, Berger's Cape Tortoise, Nama padloper, synonym Homopus solus
- Indotestudo
- Indotestudo elongata, Elongated Tortoise
- Indotestudo forstenii, Travancore Tortoise, Forsten’s Tortoise
- Indotestudo travancorica, Travancore Tortoise
- Kinixys
- Kinixys belliana, Bell's Hinge-Backed Tortoise
- Kinixys erosa, Serrated Hinge-Backed Tortoise
- Kinixys homeana, Home's Hinge-Backed Tortoise
- Kinixys lobatsiana, Lobatse Hingeback Tortoise
- Kinixys natalensis, Natal Hinge-Backed Tortoise
- Kinixys spekii, Speke's Hingeback Tortoise
- Malacochersus
- Malacochersus tornieri, Pancake Tortoise
- Manouria
- Manouria emys, Brown Tortoise (Mountain Tortoise)
- Manouria impressa, Impressed Tortoise
- Psammobates
- Psammobates geometricus, Geometric Tortoise
- Psammobates oculifer, Serrated Star Tortoise
- Psammobates tentorius, African Tent Tortoise
- Pyxis
- Pyxis arachnoides, Madagascan Spider Tortoise
- Pyxis planicauda, Madagascan Flat-Tailed Tortoise
- Testudo
- Testudo atlas, Atlas tortoise, Colossochelys (Extinct)
- Testudo graeca, Greek Tortoise (Spur-Thighed Tortoise)
- Testudo hermanni, Herman's Tortoise
- Testudo horsfieldii, Russian Tortoise (Horsfield's Tortoise, or Central Asian Tortoise)
- Testudo kleinmanni, Egyptian Tortoise, incl. Negev Tortoise
- Testudo marginata, Marginated Tortoise
- Testudo nabeulensis, Tunisian Spur-thigh Tortoise