
Naked mole rat
Did you know...
SOS Children, an education charity, organised this selection. To compare sponsorship charities this is the best sponsorship link.
| Naked mole rat Temporal range: Early Pliocene - Recent |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
|
Least Concern ( IUCN 3.1) |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Bathyergidae |
| Subfamily: | Heterocephalinae Landry, 1957 |
| Genus: | Heterocephalus Rüppell, 1842 |
| Species: | H. glaber |
| Binomial name | |
| Heterocephalus glaber Rüppell, 1842 |
|
 |
|
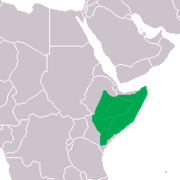
| Distribution of the Naked Mole Rat | |
The naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber), also known as the sand puppy, or desert mole rat is a burrowing rodent native to parts of East Africa and the only species currently classified in genus Heterocephalus. It is notable for its eusocial lifestyle, nearly unique among mammals (only the Damaraland mole rat shares the trait), and for a highly unusual set of physical traits that enables it to thrive in a harsh, underground environment; including a lack of pain sensation in its skin, and a nearly cold-blooded metabolism.
Physical description
Typical individuals are 8–10 cm long and weigh 30–35 g. Queens are larger and may weigh well over 50 g, the largest reaching 80 g. They are well-adapted for their underground existence. Their eyes are just narrow slits, and consequently their eyesight is poor. However, they are highly adapted to moving underground, and can move backwards as fast as they move forwards. Their large, protruding teeth are used to dig. Their lips are sealed just behind their teeth while digging to avoid filling their mouths with soil. Their legs are thin and short. They have little hair (hence the common name) and wrinkled pink or yellowish skin.
The naked mole rat is well adapted for the limited availability of oxygen within the tunnels that are its habitat: its lungs are very small and its blood has a very strong affinity for oxygen, increasing the efficiency of oxygen uptake. It has a very low respiration and metabolic rate for an animal of its size, thus using oxygen minimally. In long periods of hunger, such as a drought, its metabolic rate can reduce by up to 25 percent.
The naked mole rat is unique among mammals in that it is virtually cold-blooded; it cannot regulate its body temperature at all and requires an environment with a specific constant temperature in order to survive.
The skin of naked mole rats lacks a key neurotransmitter called Substance P that is responsible in mammals for sending pain signals to the central nervous system. When naked mole rats are exposed to acid or capsaicin, they feel no pain. When injected with Substance P, however, the pain signaling works as it does in other mammals, but only with capsaicin and not with the acids. This is proposed to be adaptation to the animal living in high levels of carbon dioxide due to poorly ventilated living spaces, which would cause acid to build up in their body tissues.
Ecology and behaviour
Distribution and habitat
The naked mole rat is native to the drier parts of the tropical grasslands of East Africa, predominantly South Ethiopia, Kenya, and Somalia.
Clusters averaging 75-80 individuals live together in complex systems of burrows in arid African deserts. The tunnel systems built by naked mole rats can stretch up to two or three miles in cumulative length.
Social structure and reproduction
Naked mole rat is one of the two species of mammals that exhibit eusociality. They have a complex social structure in which only one female (the queen) and one to three males reproduce, while the rest of the members of the colony function as workers. As in certain bee species, the workers are divided along a continuum of different worker-caste behaviors instead of discrete groups. Some function primarily as tunnellers, expanding the large network of tunnels within the burrow system, and some primarily as soldiers, protecting the group from outside predators.
This eusocial organisation social structure, similar to that found in ants, termites, and some bees and wasps, is very rare among mammals. The Damaraland Mole Rat (Coetomys damarensis) is the only other eusocial mammal currently known.
The relationships between the queen and the breeding males may last for many years. A behaviour called reproductive suppression is believed to be the reason why the other females do not reproduce, meaning that the infertility in the working females is only temporary, and not genetic. Queens live from 13 to 18 years, and are extremely hostile to other females behaving like queens, or producing hormones for becoming queens. When the queen dies, another female takes her place, sometimes after a violent struggle with her competitors.
Males and females are able to breed at one year of age. Gestation is about 70 days. A litter typically ranges from three to twelve pups, but may run as large as 25. In the wild, naked mole-rats usually breed once a year, if the litter survives. In captivity, they breed all year long. The young are born blind and weigh about 2 g. The queen nurses them for the first month; after which the other members of the colony feed them feces until they are old enough to eat solid food.
Diet
Radicivores, the naked mole rats feed primarily on very large tubers (weighing as much as 1000 times the body weight of a typical mole rat) that they find deep underground through their mining operations, though they also eat their own feces ( coprophagia). A single tuber can provide a colony with a long-term source of food—lasting for months, or even years, as they eat the succulent inside but leave the outside, allowing the tuber to regenerate. Symbiotic bacteria in their intestines help them digest the fibres.
Longevity
The naked mole rat is also of interest because it is extraordinarily long-lived for a rodent of its size. The secret of their longevity is debated, but is thought to be related to the fact that they can shut down their metabolism during hard times, and so prevent oxidative damage. Todd Karhu, an expert on the species, explains this by saying "They're living their life in pulses."
Conservation status
Naked mole rats are not threatened. Despite their tough living conditions, naked mole rats are quite widespread and numerous in the drier regions of East Africa. Though seen living up to 20 years, their lifestyles in those situations consist of mostly sleep.
In popular culture
- A naked mole rat named Rufus is featured in the Disney Channel cartoon Kim Possible.
- The Errol Morris documentary Fast, Cheap and Out of Control features a naked mole rat specialist.
- A children's book, The Naked Mole-Rat Letters, by Mary Amato, is about a young girl who sends fabricated e-mails to her father's girlfriend, a zookeeper.
- The consumer website Consumerama awards a weekly "Naked Mole-Rats of Marketing Award" for shameless consumer abuse.

