Kingdom of Scotland
Did you know...
SOS Children has tried to make Wikipedia content more accessible by this schools selection. A good way to help other children is by sponsoring a child
| Kingdom of Scotland Rìoghachd na h-Alba ( Gaelic) Kinrick o Scotland ( Scots) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Personal union with the Kingdom of England (1603–49 / 1660–1707) |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Motto In My Defens God Me Defend ( Scots) (often shown abbreviated as IN DEFENS) |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
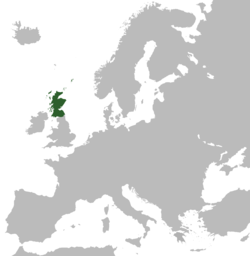
Location of the Kingdom of Scotland in Europe.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Scone (before c.1070) Dunfermline (c.1070-c. 1440) Edinburgh (after 1452) |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Languages | Scots, Scottish Gaelic, French, English, Norn | |||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||||||||||||
| Monarch | ||||||||||||||||||||
| - | 843–58 | Kenneth I (first) | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | 1306–29 | Robert I | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | 1702–07 | Anne (last) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament of Scotland | |||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||
| - | United | Ninth century (traditionally 843 AD) | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | Lothian and Strathclyde incorporated | 1124 (confirmed Treaty of York, 1237) | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | Galloway incorporated | 1234/5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | Hebrides, Isle of Man and Caithness incorporated | 1266 ( Treaty of Perth) | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | Orkney and Shetland annexed | 1472 | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | Union with England | 1 May 1707 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||||||||||
| - | 1500 est. | 500,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | 1600 est. | 800,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| - | 1700 est. | 1,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Pound Scots (Pund) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||
| ^ The Pictish and Cumbric languages went extinct during the 10th and 11th centuries. French was widely spoken in Scotland at the height of the Auld Alliance. English began to have increased influence in Scotland from the mid-16th century. | ||||||||||||||||||||
The Kingdom of Scotland ( Gaelic: Rìoghachd na h-Alba, Scots: Kinrick o Scotland) was a sovereign state in Northern Europe that is traditionally said to have been founded in 843 and joined with the Kingdom of England to form the united Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707. Its territories expanded and shrank throughout its history, but eventually came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain sharing a land border to the south with the Kingdom of England. In 1603, James VI of Scotland became King of England, joining Scotland with England in a personal union of kingdoms. In 1707, the two kingdoms were united to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, under the terms of the Acts of Union. Since the final capture of the Royal Burgh of Berwick by the Kingdom of England in 1482 (following the annexation of the Northern Isles from the Kingdom of Norway in 1472) the territory of the Kingdom of Scotland has corresponded to that of modern-day Scotland, bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the southwest. Apart from the mainland, the Kingdom of Scotland consisted of over 790 islands.
Edinburgh, the capital, was preceded by the towns of Scone/ Perth, Dunfermline and Stirling as the country's capital. The population of the Kingdom of Scotland in 1701, six years before the passing of the Acts of Union, was approximately 1.1 million.
History
Origins to 843
From the fifth century North Britain was divided into a series of petty kingdoms. Of these the four most important were the those of the Picts in the north-east, the Scots of Dál Riata in the north-west, the Britons of Strathclyde in the south-west and the Anglian kingdom of Bernicia in the south-east and stretching into modern northern England. This situation was transformed in AD 793 when ferocious Viking raids began on monasteries like Iona and Lindisfarne, creating fear and confusion across the kingdoms of North Britain. Orkney, Shetland and the Western Isles eventually fell to the Norsemen. These threats may have speeded a long term process of gaelicisation of the Pictish kingdoms, which adopted Gaelic language and customs. There was also a merger of the Gaelic and Pictish crowns, although historians debate whether it was a Pictish takeover of Dál Riata, or the other way around. This culminated in the rise of Cínaed mac Ailpín (Kenneth MacAlpin) as "king of the Picts" in the 840s (traditionally dated to 843), which brought to power the House of Alpin. When he died as king of the combined kingdom in 900 one of his successors, Domnall II (Donald II), was the first man to be called rí Alban (i.e. King of Alba). The term Scotia would be increasingly be used to describe the heartland of these kings, north of the River Forth, and eventually the entire area controlled by its kings would be referred to as Scotland. The long reign (900–942/3) of Donald's successor Causantín (Constantine II) is often regarded as the key to formation of the Kingdom of Alba/Scotland and he was later credited with bringing Scottish Christianity into conformity with the Catholic Church.
Expansion 843-1513
Máel Coluim I (Malcolm I) (r. c. 943–954) annexed Strathclyde, over which the kings of Alba had probably exercised some authority since the later ninth century. The reign of David I has been characterised as a " Davidian Revolution", by which he introduced a system of feudal land tenure, established the first royal burghs in Scotland, the first recorded Scottish coinage and continued a process of religious and legal reforms. Until the thirteenth century the borders with England were very fluid, with Northumbria being annexed to Scotland by David I, but lost under his grandson and successor Malcolm IV in 1157. The Treaty of York (1237) fixed the boundaries with England close to the modern border. By the reign of Alexander III, the Scots were in a position to annex the remainder of the western seaboard, which they did following the stalemate of the Battle of Largs with the Treaty of Perth in 1266. The Isle of Man fell under English control in the fourteenth century, despite several attempts to restore Scottish authority. The English were able to occupy most of Scotland under Edward I and annex a large slice of the Lowlands under Edward III, but Scotland established its independence under figures including William Wallace in the late thirteenth century and Robert Bruce and his successors in the fourteenth century in the Wars of Independence (1296-1357). This was helped by cooperation with the kings of France, under the terms of what became known as the Auld Alliance, which provided for mutual aid against the English. In the fifteenth century and early sixteenth century under the Stewart Dynasty, despite a turbulent political history, the crown gained greater political control at the expense of independent lords and regained most of its lost territory to approximately the modern borders of the country. The dowry of the Orkney and Shetland Islands in 1468 was the last great land acquisition for the kingdom. However, in 1482 Berwick, a border fortress and the largest port in Medieval Scotland, fell to the English once again, for what was to be the final change of hands. However, the Auld Alliance with France led to the heavy defeat of a Scottish army at the Battle of Flodden Field in 1513 and the death of the king James IV, which would be followed by a long period of political instability.
Consolidation and union 1513-1707
In the sixteenth century under James V and Mary Queen of Scots the crown and court took on many of the attributes of the Renaissance and New Monarchy, despite long minorities, civil wars and intervention by the English and French. In the mid-sixteenth century Scotland underwent a Reformation strongly influenced by Calvinism, leading to widespread iconoclasm and the introduction of a Presbyterian system of organisation and discipline that would have a major impact on Scottish life. In the late sixteenth century James VI emerged as a major intellectual figure with considerable authority over the kingdom. In 1603 he inherited the thrones of England and Ireland, creating a Union of Crowns (while the three states retained their separate identities and institutions), and moving the centre of royal patronage and power to London. When his son Charles I attempted to impose elements of the English religious settlement on Scotland the result was the Bishops' Wars (1637–40), which ended in defeat for the king and a virtually independent Presbyterian Covenanter state in Scotland. It also helped precipitate civil wars in Ireland and England, where the Scots carried out major military interventions. After Charles I's defeat, the Scots backed the king in a Second English Civil War, and after his execution, proclaimed his son Charles II as king, resulting in a Third English Civil War against the emerging republican regime in England, led by Oliver Cromwell. The results were a series of defeats and the short-lived incorporation of Scotland into the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland (1653–60).
After the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660, Scotland regained its separate status and institutions, while the centre of political power remained in London. After the Glorious Revolution of 1688-9, in which James VII was deposed by his daughter Mary and her husband William of Orange in England, Scotland accepted them under the 1689 Claim of Right, but the deposed main hereditary line of the Stuarts became a focus for political discontent, known as Jacobitism, leading to a series of invasions and rebellions mainly focused on the Scottish Highlands. After severe economic dislocation in the 1690s there were moves that led to political union with England as the Kingdom of Great Britain, which came into force on 1 May 1707. The English and Scottish parliaments were replaced by a combined Parliament of Great Britain, but it sat in Westminster and largely continued English traditions without interruption. Forty-five Scots were added to the 513 members of the House of Commons and 16 Scots to the 190 members of the House of Lords. It was also a full economic union, replacing the Scottish systems of currency, taxation and laws regulating trade.
Government
The unified kingdom of Alba retained some of the ritual aspects of Pictish and Scottish kingship. These can be seen in the elaborate ritual coronation at Scone. While the Scottish monarchy in the Middle Ages was a largely itinerant institution, Scone remained one of its most important locations, with royal castles at Stirling and Perth becoming significant in the later Middle Ages before Edinburgh developed as a capital in the second half of the fifteenth century. The crown remained the most important element of government throughout the history of the kingdom, despite the many royal minorities. In the late Middle Ages, it saw many of the aspects of aggrandisement associated with " new monarchy" elsewhere in Europe. Theories of limited monarchy and resistance were articulated by Scots, particularly George Buchanan, in the sixteenth century, but James VI advanced the theory of the divine right of kings, and these debates were restated in subsequent reigns and crises. The court remained at the centre of political life and in the sixteenth century emerged as a major centre of display and artistic patronage, until it was effectively dissolved with the Union of Crowns in 1603.
The Scottish crown adopted the conventional offices of western European courts, including steward, chamberlain, constable, marischal and chancellor. The King's Council emerged as a full-time body in the fifteenth century, increasingly dominated by laymen and critical to the administration of justice. The Privy Council, which developed in the mid-sixteenth century, and the great offices of state, including the chancellor, secretary and treasurer remained central to the administration of the government, even after the departure of the Stuart monarchs to rule in England from 1603. However, it was often sidelined and was abolished after the Act of Union of 1707, with rule direct from London. Parliament also emerged as a major legal institution, gaining an oversight of taxation and policy. By the end of the Middle Ages it was sitting almost every year, partly because of the frequent minorities and regencies of the period, which may have prevented it from being sidelined by the monarchy. In the early modern era was also vital to the running of the country, providing laws and taxation, but it had fluctuating fortunes and never achieved the centrality to the national life of its counterpart in England before it was disbanded in 1707.
In the early period the kings of the Scots depended on the great lords of the mormaers (later earls) and Toísechs (later thanes), but from the reign of David I, sheriffdoms were introduced, which allowed more direct control and gradually limited the power of the major lordships. In the seventeenth century the creation of Justices of Peace and Commissioners of Supply helped to increase the effectiveness of local government. The continued existence of courts baron and introduction of kirk sessions helped consolidate the power of local lairds.
Law
Scots law developed into a distinctive system in the Middle Ages and was reformed and codified in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Knowledge of the nature of Scots law before the eleventh century is largely speculative, but it was probably a mixture of legal traditions representing the different cultures inhabiting the land at the time, including Celtic, British, Irish and Anglo-Saxon customs. The legal tract known as Laws of the Brets and Scots, set out a system of compensation for injury and death based on ranks and the solidarity of kin groups. There were popular courts, the comhdhail, indicated by dozens of place names throughout eastern Scotland. In Scandinavian-held areas, Udal law formed the basis of the legal system and it is known that the Hebrides were taxed using the Ounceland measure. Althings were open-air governmental assemblies that met in the presence of the jarl and the meetings were open to virtually all free men. At these sessions decisions were made, laws passed and complaints adjudicated.
The introduction of feudalism in the reign of David I would have a profound impact on the development of Scots law, establishing feudal land tenure over many parts of the south and east, which eventually spread northward. Sheriffs, originally appointed by the King as royal administrators and tax collectors, developed legal functions. Feudal lords also held courts to adjudicate disputes between their tenants. By the fourteenth century some of these feudal courts had developed into "petty kingdoms" where the King's courts did not have authority, except for cases of treason. Burghs also had their local laws dealing mostly with commercial and trade matters and may have become similar in function to sheriff's courts. Ecclesiastical courts had exclusive jurisdiction over matters such as marriage, contracts made on oath, inheritance and legitimacy. Judices were often royal officials who supervised baronial, abbatial and other lower-ranking "courts". However, the main official of law in the post-Davidian Kingdom of the Scots was the Justiciar who held courts and reported to the king personally. Normally, there were two Justiciarships, organised by linguistic boundaries: the Justiciar of Scotia and the Justiciar of Lothian, but sometimes Galloway also had its own Justiciar. Scottish common law, the ius commune, began to take shape at the end of the period, assimilating Gaelic and Celtic law with practices from Anglo-Norman England and the Continent.
During the period of English control over Scotland there is some evidence that King Edward I attempted to abolish Scottish laws that were contrary to English law, as he had done in Wales. Under Robert I in 1318, a parliament at Scone enacted a code of law that drew upon older practices. It codified procedures for criminal trials and protections for vassals from ejection from the land. From the fourteenth century there are surviving examples of early Scottish legal literature, such as the Regiam Majestatem (on procedure at the royal courts) and the Quoniam Attachiamenta (on procedure at the baron courts), which drew on both common and Roman law.
Customary laws, such as the Law of Clan MacDuff, came under attack from the Stewart Dynasty which consequently extended the reach of Scots common law. From the reign of King James I a legal profession began to develop and the administration of criminal and civil justice was centralised. The growing activity of the parliament and the centralisation of administration in Scotland called for the better dissemination of Acts of the parliament to the courts and other enforcers of the law. Throughout the late fifteenth century unsuccessful attempts were made to form commissions of experts to codify, update or define Scots law. The general practice during this period, as evidenced from records of cases, seems to have been to defer to specific Scottish laws on a matter when available and to fill in any gaps with provisions from the common law embodied in Civil and Canon law, which had the advantage of being written.
Under James IV the legal functions of the council were rationalised, with a royal Court of Session meeting daily in Edinburgh to deal with civil cases. In 1514 the office of justice-general was created for the Earl of Argyll (and held by his family until 1628). In 1532 the Royal College of Justice was founded, leading to the training and professionalisation of an emerging group of career lawyers. The Court of Session placed increasing emphasis on its independence from influence, including from the king, and superior jurisdiction over local justice. Its judges were increasingly able to control entry to their own ranks. In 1672 the High Court of Justiciary was founded from the College of Justice as a supreme court of appeal.
Coinage
David I is the first Scottish king known to have produced his own coinage. There were soon mints at Edinburgh, Berwick and Roxburgh. Early Scottish coins were similar to English ones, but with the king's head in profile instead of full face. The number of coins struck was small and English coins probably remained more significant in this period. The first gold coin was a noble (6s. 8d.) of David II. Under James I pennies and halfpennies of billon (an alloy of silver with a base metal) were introduced, and copper farthings appeared under James III. In James V's reign the bawbee (1½ d) and half-bawbee were issued, and in Mary, Queen of Scot's reign a twopence piece, the hardhead, was issued to help "the common people buy bread, drink, flesh, and fish". The billon coinage was discontinued after 1603, but twopence pieces in copper continued to be issued until the Act of Union in 1707.

Early Scottish coins were virtually identical in silver content to English ones, but from about 1300 the silver content began to depreciate more rapidly than English. Between then and 1605 they lost value at an average of 12 per cent every ten years, three times the then English rate. The Scottish penny became a base metal coin in about 1484 and virtual disappeared as a separate coin from about 1513. In 1423 the English government banned the circulation of Scottish coins. At the union of the crowns in 1603 the Scottish pound was fixed at only one-twelfth that of the English pound. The Parliament of Scotland of 1695 enacted proposals to set up the Bank of Scotland. The bank issued pound notes from 1704, which had the face value of £12 Scots. Scottish currency was abolished at the Union of Crowns, the Scottish coin in circulation was drawn in to be re-minted according to the English standard.
Geography
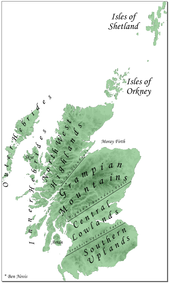
At its borders in 1707, the Kingdom of Scotland was half the size of England and Wales in area, but with its many inlets, islands and inland lochs, it had roughly the same amount of coastline at 4,000 miles. Scotland has over 790 offshore islands, most of which are to be found in four main groups: Shetland, Orkney, and the Hebrides, sub-divided into the Inner Hebrides and Outer Hebrides. Only a fifth of Scotland is less than 60 metres above sea level. The defining factor in the geography of Scotland is the distinction between the Highlands and Islands in the north and west and the Lowlands in the south and east. The highlands are further divided into the Northwest Highlands and the Grampian Mountains by the fault line of the Great Glen. The Lowlands are divided into the fertile belt of the Central Lowlands and the higher terrain of the Southern Uplands, which included the Cheviot hills, over which the border with England ran. The Central Lowland belt averages about 50 miles in width and, because it contains most of the good quality agricultural land and has easier communications, could support most of the urbanisation and elements of conventional government. However, the Southern Uplands, and particularly the Highlands were economically less productive and much more difficult to govern.
Its east Atlantic position means that Scotland has very heavy rainfall: today about 700 mm per year in the east and over 1,000 mm in the west. This encouraged the spread of blanket peat bog, the acidity of which, combined with high level of wind and salt spray, made most of the islands treeless. The existence of hills, mountains, quicksands and marshes made internal communication and conquest extremely difficult and may have contributed to the fragmented nature of political power. The Uplands and Highlands had a relatively short growing season, in the extreme case of the upper Grampians an ice free season of four months or less and for much of the Highlands and Uplands of seven months or less. The early modern era also saw the impact of the Little Ice Age, with 1564 seeing thirty-three days of continual frost, where rivers and lochs froze, leading to a series of subsistence crises until the 1690s.
Demography
From the formation of the kingdom of Alba in the tenth century, to before the Black Death reached the country in 1349, estimates based on the amount of farmable land, suggest that population may have grown from half a million to a million. Although there is no reliable documentation on the impact of the plague, there are many anecdotal references to abandoned land in the following decades. If the pattern followed that in England, then the population may have fallen to as low as half a million by the end of the fifteenth century. Compared with the situation after the redistribution of population in the later clearances and the industrial revolution, these numbers would have been relatively evenly spread over the kingdom, with roughly half living north of the Tay. Perhaps ten per cent of the population lived in one of many burghs that grew up in the later medieval period, mainly in the east and south. It has been suggested that they would have had a mean population of about 2,000, but many would be much smaller than 1,000 and the largest, Edinburgh, probably had a population of over 10,000 by the end of the Medieval era.
Price inflation, which generally reflects growing demand for food, suggests that the population probably expanded in the first half of the sixteenth century, levelling off after the famine of 1595, as prices were relatively stable in the early seventeenth century. Calculations based on Hearth Tax returns for 1691 indicate a population of 1,234,575, but this figure may have been seriously effected by the subsequent famines of the late 1690s. By 1750, with its suburbs, Edinburgh would reached 57,000. The only other towns above 10,000 by the same were Glasgow with 32,000, Aberdeen with around 16,000 and Dundee with 12,000.
Language
Historical sources, as well as place name evidence, indicate the ways in which the Pictish language in the north and Cumbric languages in the south were overlaid and replaced by Gaelic, Old English and later Norse in the early Middle Ages. By the High Middle Ages the majority of people within Scotland spoke the Gaelic language, then simply called Scottish, or in Latin, lingua Scotica. In the Northern Isles the Norse language brought by Scandinavian occupiers and settlers evolved into the local Norn, which lingered until the end of the eighteenth century and Norse may also have survived as a spoken language until the sixteenth century in the Outer Hebrides. French, Flemish and particularly English became the main language of Scottish burghs, most of which were located in the south and east, an area to which Anglian settlers had already brought a form of Old English. In the later part of the twelfth century, the writer Adam of Dryburgh described lowland Lothian as "the Land of the English in the Kingdom of the Scots". At least from the accession of David I, Gaelic ceased to be the main language of the royal court and was probably replaced by French, as evidenced by reports from contemporary chronicles, literature and translations of administrative documents into the French language.
In the late Middle Ages, Middle Scots, often simply called English, became the dominant language of the kingdom. It was derived largely from Old English, with the addition of elements from Gaelic and French. Although resembling the language spoken in northern England, it became a distinct dialect from the late fourteenth century onwards. It began to be adopted by the ruling elite as they gradually abandoned French. By the fifteenth century it was the language of government, with acts of parliament, council records and treasurer's accounts almost all using it from the reign of James I onwards. As a result, Gaelic, once dominant north of the Tay, began a steady decline. Lowland writers began to treat Gaelic as a second class, rustic and even amusing language, helping to frame attitudes towards the Highlands and to create a cultural gulf with the Lowlands.
From the mid sixteenth century, written Scots was increasingly influenced by the developing Standard English of Southern England due to developments in royal and political interactions with England. With the increasing influence and availability of books printed in England, most writing in Scotland came to be done in the English fashion. Unlike many of his predecessors, James VI generally despised Gaelic culture. Having extolled the virtues of Scots "poesie", after his accession to the English throne, he increasingly favoured the language of southern England. In 1611 the Kirk adopted the 1611 Authorized King James Version of the Bible. In 1617 interpreters were declared no longer necessary in the port of London because as Scots and Englishmen were now "not so far different bot ane understandeth ane uther". Jenny Wormald, describes James as creating a "three-tier system, with Gaelic at the bottom and English at the top".
Religion
The Pictish and Scottish kingdoms that would form the basis of the Kingdom of Alba were largely converted by Irish-Scots missions associated with figures such as St Columba, from the fifth to the seventh centuries. These missions tended to found monastic institutions and collegiate churches that served large areas. Partly as a result of these factors, some scholars have identified a distinctive form of Celtic Christianity, in which abbots were more significant than bishops, attitudes to clerical celibacy were more relaxed and there were some significant differences in practice with Roman Christianity, particularly the form of tonsure and the method of calculating Easter. Most of these issues had been resolved by the mid-seventh century. After the reconversion of Scandinavian Scotland from the tenth century, Christianity under papal authority was the dominant religion of the kingdom.
In the Norman period the Scottish church underwent a series of reforms and transformations. With royal and lay patronage, a clearer parochial structure based around local churches was developed. Large numbers of new foundations, which followed continental forms of reformed monasticism, began to predominate and the Scottish church established its independence from England, developed a clearer diocesan structure, becoming a "special daughter of the see of Rome", but lacking leadership in the form of Archbishops. In the late Middle Ages the problems of schism in the Catholic Church allowed the Scottish Crown to gain greater influence over senior appointments and two archbishoprics had been established by the end of the fifteenth century. While some historians have discerned a decline of monasticism in the late Middle Ages, the mendicant orders of friars grew, particularly in the expanding burghs, to meet the spiritual needs of the population. New saints and cults of devotion also proliferated. Despite problems over the number and quality of clergy after the Black Death in the fourteenth century, and some evidence of heresy in this period, the Church in Scotland remained relatively stable before the sixteenth century.
During the sixteenth century, Scotland underwent a Protestant Reformation that created a predominately Calvinist national kirk, which was strongly Presbyterian in outlook, severely reducing the powers of bishops, although not abolishing them. The teachings of first Martin Luther and then John Calvin began to influence Scotland, particularly through Scottish scholars who had visited continental and English universities. Particularly important was the work of the Lutheran Scot Patrick Hamilton. His execution with other Protestant preachers in 1528, and of the Zwingli-influenced George Wishart in 1546, who was burnt at the stake in St. Andrews, did nothing to stem the growth of these ideas. Wishart's supporters seized St. Andrews Castle, which they held for a year before they were defeated with the help of French forces. The survivors, including chaplain John Knox, were condemned to be galley slaves, helping to create resentment of the French and martyrs for the Protestant cause. Limited toleration and the influence of exiled Scots and Protestants in other countries, led to the expansion of Protestantism, with a group of lairds declaring themselves Lords of the Congregation in 1557. By 1560 a relatively small group of Protestants were in a position to impose reform on the Scottish church. A confession of faith, rejecting papal jurisdiction and the mass, was adopted by Parliament in 1560. The Calvinism of the reformers led by Knox resulted in a settlement that adopted a Presbyterian system and rejected most of the elaborate trappings of the Medieval church. This gave considerable power within the new Kirk to local lairds, who often had control over the appointment of the clergy, and resulting in widespread, but generally orderly, iconoclasm. At this point the majority of the population was probably still Catholic in persuasion and the Kirk would find it difficult to penetrate the Highlands and Islands, but began a gradual process of conversion and consolidation that, compared with reformations elsewhere, was conducted with relatively little persecution.
In 1635, Charles I authorised a book of canons that made him head of the Church, ordained an unpopular ritual and enforced the use of a new liturgy. When the liturgy emerged in 1637 it was seen as an English-style Prayer Book, resulting in anger and widespread rioting. Representatives of various sections of Scottish society drew up the National Covenant on 28 February 1638, objecting to the King's liturgical innovations. The king's supporters were unable to suppress the rebellion and the king refused to compromise. In December of the same year matters were taken even further, when at a meeting of the General Assembly in Glasgow the Scottish bishops were formally expelled from the Church, which was then established on a full Presbyterian basis. Victory in the resulting Bishops' Wars secured the Presbyterian Kirk and precipitated the outbreak of the civil wars of the 1640s. Disagreements over collaboration with Royalism created a major conflict between Protesters and Resolutioners, which became a long term divide in the Kirk.
At the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660, legislation was revoked back to 1633, removing the Covenanter gains of the Bishops' Wars, but the discipline of kirk sessions, presbyteries and synods were renewed. The reintroduction of episcopacy was a source of particular trouble in the south-west of the country, an area with strong Presbyterian sympathies. Abandoning the official church, many of the people here began to attend illegal field assemblies led by excluded ministers, known as conventicles. In the early 1680s a more intense phase of persecution began, in what was later to be known in Protestant historiography as " the Killing Time". After the Glorious Revolution, Presbyterianism was restored and the bishops, who had generally supported James VII, abolished,. However, William, who was more tolerant than the kirk tended to be, passed acts restoring the Episcopalian clergy excluded after the Revolution. The result was a Kirk divided between factions, with significant minorities, particularly in the west and north, of Episcopalians and Catholics.
Education
The establishment of Christianity brought Latin to Scotland as a scholarly and written language. Monasteries served as repositories of knowledge and education, often running schools and providing a small educated elite, who were essential to create and read documents in a largely illiterate society. In the High Middle Ages new sources of education arose, with song and grammar schools. These were usually attached to cathedrals or a collegiate church and were most common in the developing burghs. By the end of the Middle Ages grammar schools could be found in all the main burghs and some small towns. There were also petty schools, more common in rural areas and providing an elementary education. Some monasteries, like the Cistercian abbey at Kinloss, opened their doors to a wider range of students. The number and size of these schools seems to have expanded rapidly from the 1380s. They were almost exclusively aimed at boys, but by the end of the fifteenth century, Edinburgh also had schools for girls, sometimes described as "sewing schools", and probably taught by lay women or nuns. There was also the development of private tuition in the families of lords and wealthy burghers. The growing emphasis on education cumulated with the passing of the Education Act 1496, which decreed that all sons of barons and freeholders of substance should attend grammar schools to learn "perfyct Latyne". All this resulted in an increase in literacy, but which was largely concentrated among a male and wealthy elite, with perhaps 60 per cent of the nobility being literate by the end of the period.
Until the fifteenth century, those who wished to attend university had to travel to England or the continent, and just over a 1,000 have been identified as doing so between the twelfth century and 1410. Among these the most important intellectual figure was John Duns Scotus, who studied at Oxford, Cambridge and Paris and probably died at Cologne in 1308, becoming a major influence on late medieval religious thought. The Wars of Independence largely closed English universities to Scots, and consequently continental universities became more significant. This situation was transformed by the founding of the University of St Andrews in 1413, the University of Glasgow in 1450 and the University of Aberdeen in 1495. Initially these institutions were designed for the training of clerics, but they were increasingly used by laymen who would begin to challenge the clerical monopoly of administrative posts in the government and law. Those wanting to study for second degrees still needed to go abroad. The continued movement to other universities produced a school of Scottish nominalists at Paris in the early sixteenth century, of which John Mair was probably the most important figure. By 1497 the humanist and historian Hector Boece, born in Dundee, returned from Paris to became the first principal at the new university of Aberdeen. These international contacts helped integrate Scotland into a wider European scholarly world and would be one of the most important ways in which the new ideas of humanism were brought into Scottish intellectual life.
The humanist concern with widening education was shared by the Protestant reformers, with a desire for a godly people replacing the aim of having educated citizens. In 1560, the First Book of Discipline set out a plan for a school in every parish, but this proved financially impossible. In the burghs the old schools were maintained, with the song schools and a number of new foundations becoming reformed grammar schools or ordinary parish schools. Schools were supported by a combination of kirk funds, contributions from local heritors or burgh councils and parents that could pay. They were inspected by kirk sessions, who checked for the quality of teaching and doctrinal purity. There were also large number of unregulated "adventure schools", which sometimes fulfilled a local needs and sometimes took pupils away from the official schools. Outside of the established burgh schools, masters often combined their position with other employment, particularly minor posts within the kirk, such as clerk. At their best, the curriculum included catechism, Latin, French, Classical literature and sports.
In 1616 an act in Privy council commanded every parish to establish a school "where convenient means may be had", and when the Parliament of Scotland ratified this with the Education Act of 1633, a tax on local landowners was introduced to provide the necessary endowment. A loophole which allowed evasion of this tax was closed in the Education Act of 1646, which established a solid institutional foundation for schools on Covenanter principles. Although the Restoration brought a reversion to the 1633 position, in 1696 new legislation restored the provisions of 1646. An act of the Scottish parliament in 1696 underlined the aim of having a school in every parish. In rural communities these obliged local landowners (heritors) to provide a schoolhouse and pay a schoolmaster, while ministers and local presbyteries oversaw the quality of the education. In many Scottish towns, burgh schools were operated by local councils. By the late seventeenth century there was a largely complete network of parish schools in the Lowlands, but in the Highlands basic education was still lacking in many areas.
The widespread belief in the limited intellectual and moral capacity of women, vied with a desire, intensified after the Reformation, for women to take personal moral responsibility, particularly as wives and mothers. In Protestantism this necessitated an ability to learn and understand the catechism and even to be able to independently read the Bible, but most commentators, even those that tended to encourage the education of girls, thought they should not receive the same academic education as boys. In the lower ranks of society, they benefited from the expansion of the parish schools system that took place after the Reformation, but were usually outnumbered by boys, often taught separately, for a shorter time and to a lower level. They were frequently taught reading, sewing and knitting, but not writing. Female illiteracy rates based on signatures among female servants were around 90 percent, from the late seventeenth to the early eighteenth centuries and perhaps 85 percent for women of all ranks by 1750, compared with 35 per cent for men. Among the nobility there were many educated and cultured women, of which Mary, Queen of Scots is the most obvious example.
After the Reformation, Scotland's universities underwent a series of reforms associated with Andrew Melville, who returned from Geneva to become principal of the University of Glasgow in 1574. He placed an emphasis on simplified logic and elevated languages and sciences to the same status as philosophy, allowing accepted ideas in all areas to be challenged. He introduced new specialist teaching staff, replacing the system of "regenting", where one tutor took the students through the entire arts curriculum. Metaphysics were abandoned and Greek became compulsory in the first year followed by Aramaic, Syriac and Hebrew, launching a new fashion for ancient and biblical languages. Glasgow had probably been declining as a university before his arrival, but students now began to arrive in large numbers. He assisted in the reconstruction of Marischal College, Aberdeen, and in order to do for St Andrews what he had done for Glasgow, he was appointed Principal of St Mary's College, St Andrews, in 1580. The University of Edinburgh developed out of public lectures were established in the town 1440s on law, Greek, Latin and philosophy, under the patronage of Mary of Guise. These evolved into the "Tounis College", which would become the University of Edinburgh in 1582. The results were a revitalisation of all Scottish universities, which were now producing a quality of education the equal of that offered anywhere in Europe. Under the Commonwealth, the universities saw an improvement in their funding, as they were given income from deaneries, defunct bishoprics and the excise, allowing the completion of buildings including the college in the High Street in Glasgow. They were still largely seen as a training school for clergy, and came under the control of the hard line Protestors. After the Restoration there was a purge of the universities, but much of the intellectual advances of the preceding period was preserved. The universities recovered from the upheavals of the mid-century with a lecture-based curriculum that was able to embrace economics and science, offering a high quality liberal education to the sons of the nobility and gentry.
Flags

The earliest recorded use of the Lion rampant as a royal emblem in Scotland was by Alexander II in 1222. It is recorded with the additional embellishment of a double border set with lilies during the reign of Alexander III (1249–86). This emblem occupied the shield of the royal coat of arms which, together with a royal banner displaying the same, was used by the King of Scots until the Union of the Crowns in 1603. Then it was incorporated into both the royal arms and royal banners of successive Scottish then British monarchs in order to symbolise Scotland; as can be seen today in the Royal Standard of the United Kingdom. Although now officially restricted to use by representatives of the Sovereign and at royal residences, the Royal Standard of Scotland continues to be one of Scotland's most recognisable symbols.
According to legend, the apostle and martyr Saint Andrew, the patron saint of Scotland, was crucified on an X-shaped cross at Patras, (Patrae), in Achaea. Use of the familiar iconography of his martyrdom, showing the apostle bound to an X-shaped cross, first appears in the Kingdom of Scotland in 1180 during the reign of William I. This image was again depicted on seals used during the late thirteenth century; including on one particular example used by the Guardians of Scotland, dated 1286. Use of a simplified symbol associated with Saint Andrew which does not depict his image, namely the saltire, or crux decussata, (from the Latin crux, 'cross', and decussis, 'having the shape of the Roman numeral X'), has its origins in the late fourteenth century; the Parliament of Scotland decreed in 1385 that Scottish soldiers wear a white Saint Andrew's Cross on their person, both in front and behind, for the purpose of identification. The earliest reference to the Saint Andrew's Cross as a flag is to be found in the Vienna Book of Hours, circa 1503, where a white saltire is depicted with a red background. In the case of Scotland, use of a blue background for the Saint Andrew's Cross is said to date from at least the 15th century, with the first certain illustration of a flag depicting such appearing in Sir David Lyndsay of the Mount's Register of Scottish Arms, circa 1542.
Following the Union of the Crowns in 1603, James VI, King of Scots, commissioned new designs for a banner incorporating the flags of the Kingdom of Scotland and Kingdom of England. In 1606, a Union Flag was commissioned, combining the crosses of Saint George, (the Flag of England), with that of Saint Andrew. There was also a Scottish version of this flag, in which the cross of Saint Andrew overlayed the cross of St George. This design may have seen limited, unofficial use in Scotland until 1707, when the English variant of the same, whereby the cross of St George overlayed that of St Andrew, was adopted as the flag of the unified Kingdom of Great Britain.
-
The Scottish Union Flag used, technically unofficial, between 1606 and 1707.