History of Russia (1992–present)
Background Information
SOS Children have produced a selection of wikipedia articles for schools since 2005. To compare sponsorship charities this is the best sponsorship link.
The history of Russia from 1992 to the present began with the dissolution of the Soviet Union on 26 December 1991, and the establishment of the Russian Federation.
The Russian Federation was the largest of the fifteen republics that made up the Soviet Union, accounting for over 60% of the gross domestic product (GDP) and over 50% of the Soviet population. Russians also dominated the Soviet military and the Communist Party (CPSU). Thus, the Russian Federation was widely accepted as the Soviet Union's successor state in diplomatic affairs and it assumed the USSR's permanent membership and veto in the UN Security Council (see Russia and the United Nations).
Despite this acceptance, the Russian Federation lacked the military and political power of the former Soviet Union. Russia managed to make the other former Soviet republics voluntarily disarm themselves of nuclear weapons and concentrated them under the command of the still effective rocket and space forces, but for the most part the Russian army and fleet were in near disarray by 1992. Prior to the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Boris Yeltsin had been elected President of Russia in June 1991 in the first direct presidential election in Russian history. In October 1991, as the USSR was on the verge of collapse, Yeltsin announced that Russia would proceed with radical market-oriented reform along the lines of Poland's "big bang", also known as " shock therapy".
Reforms
"Shock Therapy"
The conversion of the world's largest state-controlled economy into a market-oriented economy would have been extraordinarily difficult regardless of the policies chosen. The policies chosen for this difficult transition were (1) liberalization, (2) stabilization, and (3) privatization. These policies were based on the neoliberal " Washington Consensus" of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, and U.S. Treasury Department.
The programs of liberalization and stabilization were designed by Yeltsin's deputy prime minister Yegor Gaidar, a 35-year-old liberal economist inclined toward radical reform, and widely known as an advocate of " shock therapy". Shock therapy began days after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, when on January 2, 1992, Russian President Boris Yeltsin ordered the liberalization of foreign trade, prices, and currency. This entailed removing Soviet-era price controls in order to lure goods back into understocked Russian stores, removing legal barriers to private trade and manufacture, and cutting subsidies to state farms and industries while allowing foreign imports into the Russian market in order to break the power of state-owned local monopolies.
The partial results of liberalization (lifting price controls) included worsening already apparent hyperinflation, initially due to monetary overhang and exacerbated after the central bank, an organ under parliament, which was skeptical of Yeltsin's reforms, was short of revenue and printed money to finance its debt. This resulted in the near bankruptcy of much of Russian industry.
The process of liberalization would create winners and losers, depending on how particular industries, classes, age groups, ethnic groups, regions, and other sectors of Russian society were positioned. Some would benefit by the opening of competition; others would suffer. Among the winners were the new class of entrepreneurs and black marketeers that had emerged under Mikhail Gorbachev's perestroika. But liberalizing prices meant that the elderly and others on fixed incomes would suffer a severe drop in living standards, and people would see a lifetime of savings wiped out.
With inflation at double-digit rates per month as a result of printing, macroeconomic stabilization was enacted to curb this trend. Stabilization, also called structural adjustment, is a harsh austerity regime (tight monetary policy and fiscal policy) for the economy in which the government seeks to control inflation. Under the stabilization program, the government let most prices float, raised interest rates to record highs, raised heavy new taxes, sharply cut back on government subsidies to industry and construction, and made massive cuts in state welfare spending. These policies caused widespread hardship as many state enterprises found themselves without orders or financing. A deep credit crunch shut down many industries and brought about a protracted depression.
The rationale of the program was to squeeze the built-in inflationary pressure out of the economy so that producers would begin making sensible decisions about production, pricing and investment instead of chronically overusing resources—a problem that resulted in shortages of consumer goods in the Soviet Union in the 1980s. By letting the market rather than central planners determine prices, product mixes, output levels, and the like, the reformers intended to create an incentive structure in the economy where efficiency and risk would be rewarded and waste and carelessness were punished. Removing the causes of chronic inflation, the reform architects argued, was a precondition for all other reforms: Hyperinflation would wreck both democracy and economic progress, they argued; they also argued that only by stabilizing the state budget could the government proceed to dismantle the Soviet planned economy and create a new capitalist Russia.
Obstacles
A major reason that Russia's transition has been so wrenching is that the country is remaking both its Soviet-era political and economic institutions at once. In addition, Russia is remaking itself as a new national state following the disintegration of the union.
The former Soviet Union was to deal with a number of unique obstacles during the post-Soviet transition. These obstacles may have left Russia on a far worse footing than other former Communist-led states to Russia's west that were also going through dual economic and political transitions, such as Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic, which have fared better since the collapse of the Eastern bloc between 1989 and 1991.
The first major problem facing Russia was the legacy of the Soviet Union's enormous commitment to the Cold War. In the late 1980s, the Soviet Union devoted a quarter of its gross economic output to the defense sector (at the time most Western analysts believed that this figure was 15 percent). At the time, the military-industrial complex employed at least one of every five adults in the Soviet Union. In some regions of Russia, at least half of the workforce was employed in defense plants. (The comparable U.S. figures were roughly one-sixteenth of gross national product and about one of every sixteen in the workforce.) The end of the Cold War and the cutback in military spending hit such plants very hard, and it was often impossible for them to quickly retool equipment, retrain workers, and find new markets to adjust to the new post–Cold War and post-Soviet era. In the process of conversion an enormous body of experience, qualified specialists and know-how has been lost, as the plants were sometimes switching from, for example, producing hi-tech military equipment to making kitchen utensils.
A second obstacle, partly related to the sheer vastness and geographical diversity of the Russian landmass, was the sizable number of "mono-industrial" regional economies (regions dominated by a single industrial employer) that Russia inherited from the Soviet Union. The concentration of production in a relatively small number of big state enterprises meant that many local governments were entirely dependent on the economic health of a single employer; when the Soviet Union collapsed and the economic ties between Soviet republics and even regions were severed, the production in the whole country dropped by more than fifty percent. Roughly half of Russia's cities had only one large industrial enterprise, and three fourths had no more than four. Consequently, the decrease in production caused tremendous unemployment and underemployment.
Thirdly, post-Soviet Russia did not inherit a system of state social security and welfare from the USSR. Instead the companies, mainly large industrial firms, were traditionally responsible for a broad range of social welfare functions—building and maintaining housing for their workforces, and managing health, recreational, educational, and similar facilities. The towns in contrast possessed neither the apparatus nor the funds for the provision of basic social services. Industrial employees were left heavily dependent on their firms. Thus, economic transformation created severe problems in maintaining social welfare since local governments were unable to assume financial or operational responsibility for these functions.
Finally, there is a human capital dimension to the failure of post-Soviet reforms in Russia. The former Soviet population was not necessarily uneducated. Literacy was nearly universal, and the educational level of the Soviet population was among the highest in the world with respect to science, engineering, and some technical disciplines. But the Soviets devoted little to what would be described as " liberal arts" in the West. The former Soviet Union's state enterprise managers were indeed highly skilled at coping with the demands on them under the Soviet system of planned production targets. But the incentive system built into state institutions and industries during the Soviet era encouraged skill in coping with state-run planned economy, but discouraged the risk-and-reward centered behaviour of market capitalism. For example, the directors of Soviet state firms were rewarded for meeting output targets under difficult conditions, such as uncertainty about whether needed inputs would be delivered in time and in the right assortment. As noted, they were also responsible for a broad array of social welfare functions for their employees, their families, and the population of the towns and regions where they were located. Profitability and efficiency, however, were generally not the most prominent priorities for Soviet enterprise managers. Thus, almost no Soviet employees or managers had firsthand experience with decision-making in the conditions of a market economy.
Depression

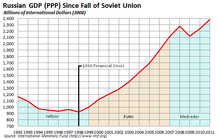
Russia's economy sank into deep depression by the mid-1990s, was hit further by the financial crash of 1998, and then began to recover in 1999–2000. According to Russian government statistics, the economic decline was far more severe than the Great Depression was in the United States in terms of Gross Domestic Product. It is about half as severe as the catastrophic drop borne out of the consequence of World War I, the fall of Tsarism, and the Russian Civil War.
Following the economic collapse of the early 1990s, Russia suffered from a sharp increase in the rates of poverty and economic inequality. Estimates by the World Bank based on both macroeconomic data and surveys of household incomes and expenditures indicate that whereas 1.5% of the population was living in poverty (defined as income below the equivalent of $25 per month) in the late Soviet era, by mid-1993 between 39% and 49% of the population was living in poverty. Per capita incomes fell by another 15% by 1998, according to government figures.
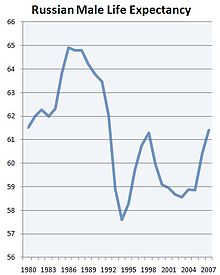
Public health indicators show a dramatic corresponding decline. In 1999, total population fell by about three-quarters of a million people. Meanwhile life expectancy dropped for men from 64 years in 1990 to 57 years by 1994, while women's dropped from 74 to about 71. Both health factors and a sharp increase in deaths of the youth demographic from unnatural causes (such as murders, suicides and accidents) have significantly contributed to this trend. As of 2009, life expectancy is higher than at the nadir of the crisis in 1994, yet it still remains below the 1990 level, with men living to 59, and with women's life expectancy decreasing to 70.
Alcohol-related deaths skyrocketed 60% in the 1990s. Deaths from infectious and parasitic diseases shot up 100%, mainly because medicines were no longer affordable to the poor.
While Russia no longer suffered from the supply shortages of consumer goods that were so characteristic of the 1980s USSR (see Consumer goods in the Soviet Union), this was not only related to the opening of the Russian market to imports in the early 1990s but also to the impoverishment of the Russian people in the 1980s. Russians on fixed incomes (the vast majority of the workforce) saw their purchasing power drastically reduced, so while the stores might have been well stocked in the Yeltsin era, workers could now afford to buy little, if anything.
By 2011, the average income has risen to more than $700 per month, emblematic of the mild recovery in recent years thanks to a large extent to high oil prices. Growing income however, has not being evenly distributed. The social inequality has risen sharply during the 1990s with the Gini coefficient, for example, reaching 42% by the end of 2010. Russia's income disparities are now nearly as large as Brazil (which has long been among the world leader in inequality) while regional disparities in the level of poverty continue to trend upwards.
Backlash
Structural reform lowered the standard of living for most groups of the population. Thus, reform created powerful political opposition. Democratization opened the political channels for venting these frustrations, thus translating into votes for anti-reform candidates, especially those of the Communist Party of the Russian Federation and its allies in the parliament. Russian voters, able to vote for opposition parties in the 1990s, often rejected economic reforms and yearned for the stability and personal security of the Soviet era. These were the groups that had enjoyed the benefits of Soviet-era state-controlled wages and prices, high state spending to subsidize priority sectors of the economy, protection from competition with foreign industries, and welfare entitlement programs.
During the Yeltsin years in the 1990s, these groups were well organized, voicing their opposition to reform through strong trade unions, associations of directors of state-owned firms, and political parties in the popularly elected parliament whose primary constituencies were among those vulnerable to reform. A constant theme of Russian history in the 1990s was the conflict between economic reformers and those hostile to the new capitalism.
Reform by decree
On January 2, 1992, Yeltsin—acting as his own prime minister—enacted the most comprehensive components of economic reform by decree, thereby circumventing the Supreme Soviet of Russia and Congress of People's Deputies of Russia, which had been elected in March 1990, before the dissolution of the USSR. While this spared Yeltsin from the prospects of parliamentary bargaining and wrangling, it also eliminated any meaningful discussion of the right course of action for the country.
However, radical reform still faced some critical political barriers. The Soviet-era Central Bank was still subordinate to the conservative Supreme Soviet as opposed to the presidency. During the height of hyperinflation in 1992–1993, the Central Bank actually tried to derail reforms by actively printing money during a period of inflation. After all, the Russian government was short of revenue and was forced to print money to finance its debt. As a result, inflation exploded into hyperinflation, and the Russian economy continued in a serious slump.
Crisis
Constitutional crisis
The struggle for the centre of power in post-Soviet Russia and for the nature of the economic reforms culminated in a political crisis and bloodshed in the fall of 1993. Yeltsin, who represented a course of radical privatization, was opposed by the parliament. Confronted with opposition to the presidential power of decree and threatened with impeachment, Yeltsin "dissolved" the parliament on September 21, in contravention of the existing constitution, and ordered new elections and a referendum on a new constitution. The parliament then declared Yeltsin deposed and appointed Aleksandr Rutskoy acting president on September 22. Tensions built quickly, and matters came to a head after street riots on October 2–October 3. On October 4, Yeltsin ordered Special Forces and elite army units to storm the parliament building, the "White House" as it is called. With tanks thrown against the small-arms fire of the parliamentary defenders, the outcome was not in doubt. Rutskoy, Ruslan Khasbulatov, and the other parliamentary supporters surrendered and were immediately arrested and jailed. The official count was 187 dead, 437 wounded (with several men killed and wounded on the presidential side).
Thus the transitional period in post-Soviet Russian politics came to an end. A new constitution was approved by referendum in December 1993. Russia was given a strongly presidential system. Radical privatization went ahead. Although the old parliamentary leaders were released without trial on February 26, 1994, they would not play an open role in politics thereafter. Though its clashes with the executive would eventually resume, the remodeled Russian parliament had greatly circumscribed powers. (For details on the constitution passed in 1993 see Constitution and government structure of Russia.)
First Chechen War
In 1994, Yeltsin ordered 40,000 troops to prevent the separation of the southern region of Chechnya from Russia. Living 1,000 miles (1,600 km) south of Moscow, the predominantly Muslim Chechens for centuries had gloried in defying the Russians. Dzhokhar Dudayev, the Republic of Chechnya’s nationalist president, was driven to take his republic out of the Russian Federation, and had declared Chechnya's independence in 1991. Russia was quickly submerged in a quagmire like that of the U.S. in the Vietnam War. When the Russians attacked the Chechen capital of Grozny during the first weeks of January 1995, about 25,000 civilians died under week-long air raids and artillery fire in the sealed-off city. Massive use of artillery and air strikes remained the dominating strategy throughout the Russian campaign. Even so, Chechen insurgents seized thousands of Russian hostages, while inflicting humiliating losses on Russia's demoralized and ill-equipped troops. Russian troops had not secured the Chechen capital of Grozny by year's end.
The Russians finally managed to gain control of Grozny in February 1995 after heavy fighting. In August 1996 Yeltsin agreed to a ceasefire with Chechen leaders, and a peace treaty was formally signed in May 1997. However, the conflict resumed in 1999, thus rendering the 1997 peace accord meaningless. This time the rebellion was brutally crushed by Vladimir Putin.
"Oligarchism"
The new capitalist opportunities presented by the opening of the Russian economy in the late 1980s and early 1990s affected many people's interests. As the Soviet system was being dismantled, well-placed bosses and technocrats in the Communist Party, KGB, and Komsomol (Soviet Youth League) were cashing in on their Soviet-era power and privileges. Some quietly liquidated the assets of their organization and secreted the proceeds in overseas accounts and investments. Others created banks and business in Russia, taking advantage of their insider positions to win exclusive government contracts and licenses and to acquire financial credits and supplies at artificially low, state-subsidized prices in order to transact business at high, market-value prices. Great fortunes were made almost overnight.
At the same time, a few young people, without much social status, saw opportunity in the economic and legal confusion of the transition. Between 1987 and 1992, trading of natural resources and foreign currencies, as well as imports of highly demanded consumer goods and then domestic production of their rudimentary substitutes, rapidly enabled these pioneering entrepreneurs to accumulate considerable wealth. In turn, the emerging cash-based, highly opaque markets provided a breeding ground for a large number of racket gangs.
By the mid-1990s, the best-connected former nomenklatura leaders accumulated considerable financial resources, while on the other hand, the most successful entrepreneurs became acquainted with government officials and public politicians. The privatization of state enterprises was a unique opportunity, because it gave many of those who had gained wealth in the early 1990s a chance to convert it into shares of privatized enterprises.
The Yeltsin government hoped to use privatization to spread ownership of shares in former state enterprises as widely as possible to create political support for his government and his reforms. The government used a system of free vouchers as a way to give mass privatization a jump-start. But it also allowed people to purchase shares of stock in privatized enterprises with cash. Even though initially each citizen received a voucher of equal face value, within months most of the vouchers converged in the hands of intermediaries who were ready to buy them for cash right away.
As the government ended the voucher privatization phase and launched cash privatization, it devised a program that it thought would simultaneously speed up privatization and yield the government a much-needed infusion of cash for its operating needs. Under the scheme, which quickly became known in the West as "loans for shares," the Yeltsin regime auctioned off substantial packages of stock shares in some of its most desirable enterprises, such as energy, telecommunications, and metallurgical firms, as collateral for bank loans.
In exchange for the loans, the state handed over assets worth many times as much. Under the terms of the deals, if the Yeltsin government did not repay the loans by September 1996, the lender acquired title to the stock and could then resell it or take an equity position in the enterprise. The first auctions were held in the fall of 1995. The auctions themselves were usually held in such a way so to limit the number of banks bidding for shares and thus to keep the auction prices extremely low. By summer 1996, major packages of shares in some of Russia's largest firms had been transferred to a small number of major banks, thus allowing a handful of powerful banks to acquire substantial ownership shares over major firms at shockingly low prices. These deals were effectively giveaways of valuable state assets to a few powerful, well-connected, and wealthy financial groups.
The concentration of immense financial and industrial power, which loans for shares had assisted, extended to the mass media. One of the most prominent of the financial barons Boris Berezovsky, who controlled major stakes in several banks and companies, exerted an extensive influence over state television programming for a while. Berezovsky and other ultra-wealthy, well-connected tycoons who controlled these great empires of finance, industry, energy, telecommunications, and media became known as the " Russian oligarchs". Along with Berezovsky, Mikhail Khodorkovsky, Roman Abramovich, Vladimir Potanin, Vladimir Bogdanov, Rem Viakhirev, Vagit Alekperov, Viktor Chernomyrdin, Viktor Vekselberg, and Mikhail Fridman emerged as Russia's most powerful and prominent oligarchs.
A tiny clique who used their connections built up during the last days of the Soviet years to appropriate Russia's vast resources during the rampant privatizations of the Yeltsin years, the oligarchs emerged as the most hated men in the nation. The Western world generally advocated a quick dismantling of the Soviet planned economy to make way for "free-market reforms," but later expressed disappointment over the newfound power and corruption of the "oligarchs."
Presidential election of 1996
Campaigns
Early in the campaign it had been thought that Yeltsin, who was in uncertain health (after recuperating from a series of heart attacks) and whose behaviour was sometimes erratic, had little chance for reelection. When campaigning opened at the beginning of 1996, Yeltsin's popularity was close to zero. Meanwhile, the opposition Communist Party of the Russian Federation had already gained ground in parliamentary voting on December 17, 1995, and its candidate, Gennady Zyuganov, had a strong grassroots organization, especially in the rural areas and small towns, and appealed effectively to memories of the old days of Soviet prestige on the international stage and the socialist domestic order.
Panic struck the Yeltsin team when opinion polls suggested that the ailing president could not win; members of his entourage urged him to cancel presidential elections and effectively rule as dictator from then on. Instead, Yeltsin changed his campaign team, assigning a key role to his daughter, Tatyana Dyachenko, and appointing Anatoly Chubais campaign manager. Chubais, who was not just Yeltsin's campaign manager but also the architect of Russia's privatization program, set out to use his control of the privatization program as the key instrument of Yeltsin's reelection campaign.
The president's inner circle assumed that it had only a short time in which to act on privatization; it therefore needed to take steps that would have a large and immediate impact, making the reversal of reform prohibitively costly for their opponents. Chubais' solution was to co-opt potentially powerful interests, including enterprise directors and regional officials, in order to ensure Yeltsin's reelection.
The position of the enterprise directors to the program was essential to maintaining economic and social stability in the country. The managers represented one of the most powerful collective interests in the country; it was the enterprise managers who could ensure that labor did not erupt in a massive wave of strikes. The government, therefore, did not strenuously resist the tendency for voucher privatization to turn into "insider privatization," as it was termed, in which senior enterprise officials acquired the largest proportion of shares in privatized firms. Thus, Chubais allowed well-connected employees to acquire majority stakes in the enterprises. This proved to be the most widely used form of privatization in Russia. Three-quarters of privatized enterprises opted for this method, most often using vouchers. Real control thus wound up in the hands of the managers.
Support from the oligarchs was also crucial to Yeltsin's reelection campaign. The "loans for shares" giveaway took place in the run-up to the 1996 presidential election—at a point when it had appeared that Zyuganov might defeat Yeltsin. Yeltsin and his entourage gave the oligarchs an opportunity to scoop up some of Russia's most desirable assets in return for their help in his reelection effort. The oligarchs, in turn, reciprocated the favour.
In the spring of 1996, with Yeltsin's popularity at a low ebb, Chubais and Yeltsin recruited a team of six leading Russian financiers and media barons (all oligarchs) who bankrolled the Yeltsin campaign with $3 million and guaranteed coverage on television and in leading newspapers directly serving the president's campaign strategy. The media painted a picture of a fateful choice for Russia, between Yeltsin and a "return to totalitarianism." The oligarchs even played up the threat of civil war if a Communist were elected president.
In the outlying regions of the country, the Yeltsin campaign relied on its ties to other allies—the patron-client ties of the local governors, most of whom had been appointed by the president.
The Zyuganov campaign had a strong grass-roots organization, but it was simply no match to the financial resources and access to patronage that the Yeltsin campaign could marshal.
Yeltsin campaigned energetically, dispelling concerns about his health, exploiting all the advantages of incumbency to maintain a high media profile. To assuage voters' discontent, he made the claim that he would abandon some unpopular economic reforms and boost welfare spending, end the war in Chechnya, pay wage and pension arrears, and abolish the military draft program (he did not live up to his promises after the election, except for ending the Chechen war, which was halted for 3 years). Yeltsin's campaign also got a boost from the announcement of a $10 billion loan to the Russian government from the International Monetary Fund.
Grigory Yavlinsky was the liberal alternative to Yeltsin and Zyuganov. He appealed to a well-educated middle class that saw Yeltsin as a drunken scoundrel and Zyuganov as a Soviet-era throwback. Seeing Yavlinsky as a threat, Yeltsin's inner circle of supporters worked to bifurcate political discourse, thus excluding a middle ground—and convince voters that only Yeltsin could defeat the Communist "menace." The election became a two-man race, and Zyuganov, who lacked Yeltsin's resources and financial backing, watched haplessly as his strong initial lead was whittled away.
Elections
Voter turnout in the first round of the polling on June 16 was 69.8%. According to returns announced on June 17, Yeltsin won 35% of the vote; Zyuganov won 32%; Aleksandr Lebed, a populist ex-general, a surprisingly high 14.5%; liberal candidate Grigory Yavlinsky 7.4%; far-right nationalist Vladimir Zhirinovsky 5.8%; and former Soviet president Mikhail Gorbachev 0.5%. With no candidate securing an absolute majority, Yeltsin and Zyuganov went into a second round of voting. In the meantime, Yeltsin co-opted a large segment of the electorate by appointing Lebed to the posts of national security adviser and secretary of the Security Council.
In the end, Yeltsin's election tactics paid off. In the run-off on July 3, with a turnout of 68.9%, Yeltsin won 53.8% of the vote and Zyuganov 40.3%, with the rest (5.9%) voting "against all". Moscow and Saint Petersburg (formerly Leningrad) together provided over half of the incumbent president's support, but he also did well in large cities in the Urals and in the north and northeast. Yeltsin lost to Zyuganov in Russia's southern industrial heartland. The southern stretch of the country became known as the " red belt", underscoring the resilience of the Communist Party in elections since the breakup of the Soviet Union.
Although Yeltsin promised that he would abandon his unpopular neoliberal austerity policies and increase public spending to help those suffering from the pain of capitalist reforms, within a month of his election, Yeltsin issued a decree canceling almost all of these promises.
Right after the election, Yeltsin's physical health and mental stability were increasingly precarious. Many of Yeltsin's executive functions thus devolved upon a group of advisers (most of whom had close links with the oligarchs).
Financial collapse
The global recession of 1998, which started with the Asian financial crisis in July 1997, exacerbated Russia's economic crisis. Given the ensuing decline in world commodity prices, countries heavily dependent on the export of raw materials such as oil were among those most severely hit. Oil, natural gas, metals, and timber account for more than 80% of Russian exports, leaving the country vulnerable to swings in world prices. Oil is also a major source of government tax revenue. The sharp decline in the price of oil had severe consequences for Russia.
The pressures on the ruble, reflecting the weakness of the economy, resulted in a disastrous fall in the value of the currency. Massive tax evasion also continued, and the government found itself unable to service the massive loans it had received or even to pay its employees. The government stopped making timely payment of wages, pensions, and debts to suppliers; and when workers were paid, it was often with bartered goods rather than rubles. Coal miners were hard hit, and for several weeks in the summer they blocked sections of the Trans-Siberian railroad, effectively cutting the country in two. As time wore on, they added calls for the resignation of Yeltsin and his government to their wage demands.
A political crisis came to a head in March when Yeltsin suddenly dismissed Prime Minister Viktor Chernomyrdin and his entire cabinet on March 23. Yeltsin named a virtually unknown technocrat, Energy Minister Sergei Kiriyenko, aged 35, as acting prime minister. Russian observers expressed doubts about Kiriyenko's youth and inexperience. The Duma rejected his nomination twice. Only after a month-long standoff, during which Yeltsin threatened to dissolve the legislature, did the Duma confirm Kiriyenko on a third vote on April 24.
Kiriyenko appointed a new cabinet strongly committed to stemming the fall in value of Russia's currency. The oligarchs strongly supported Kiriyenko's efforts to maintain the exchange rate. A high exchange rate meant that they needed fewer rubles to buy imported goods, especially luxury items.
In an effort to prop up the currency and stem the flight of capital, Kiriyenko hiked interest rates to 150% in order to attract buyers for government bonds. But concerns about the financial crisis in Asia and the slump in world oil prices were already prompting investors to withdraw from Russia. By mid-1998, it was clear Russia would need help from IMF to maintain its exchange rate.
The Russian crisis caused alarm in the West. Pouring more money into the Russian economy would not be a long-term solution, but the U.S. in particular feared that Yeltsin's government would not survive a looming financial crisis without IMF help. U.S. President Bill Clinton's treasury secretary, Robert Rubin, also feared that a Russian collapse could create a panic on world money markets (and it indeed did help bring down one major US hedge fund Long Term Capital Management). The IMF approved a $22.6 billion emergency loan on July 13.
Despite the bailout, Russia's monthly interest payments still well exceeded its monthly tax revenues. Realizing that this situation was unsustainable, investors continued to flee Russia despite the IMF bailout. Weeks later the financial crisis resumed and the value of the ruble resumed its fall, and the government fell into a self-perpetuating trap. To pay off the interest on the loans it had taken, it needed to raise still more cash, which it did through foreign borrowing. As lenders became increasingly certain that the government could not make good on its obligations, they demanded ever-higher interest rates, deepening the trap. Ultimately the bubble burst.
On August 17, Kiriyenko's government and the central bank were forced to suspend payment on Russia's foreign debt for 90 days, restructure the nation's entire debt, and devalue the ruble. The ruble went into free fall as Russians sought frantically to buy dollars. Western creditors lost heavily, and a large part of Russia's fledgling banking sector was destroyed, since many banks had substantial dollar borrowings. Foreign investment rushed out of the country, and financial crisis triggered an unprecedented flight of capital from Russia.
Political fallout
The financial collapse produced a political crisis, as Yeltsin, with his domestic support evaporating, had to contend with an emboldened opposition in the parliament. A week later, on August 23, Yeltsin fired Kiryenko and declared his intention of returning Chernomyrdin to office as the country slipped deeper into economic turmoil. Powerful business interests, fearing another round of reforms that might cause leading concerns to fail, welcomed Kiriyenko's fall, as did the Communists.
Yeltsin, who began to lose his hold as his health deteriorated, wanted Chernomyrdin back, but the legislature refused to give its approval. After the Duma rejected Chernomyrdin's candidacy twice, Yeltsin, his power clearly on the wane, backed down. Instead, he nominated Foreign Minister Yevgeny Primakov, who on September 11 was overwhelmingly approved by the Duma.
Primakov's appointment restored political stability because he was seen as a compromise candidate able to heal the rifts between Russia's quarreling interest groups. There was popular enthusiasm for Primakov as well. Primakov promised to make the payment of wage and pension arrears his government’s first priority, and invited members of the leading parliamentary factions into his Cabinet.
Communists and trade unionists staged a nationwide strike on October 7, and called on President Yeltsin to resign. On October 9, Russia, which was also suffering from a bad harvest, appealed for international humanitarian aid, including food.
Recovery
Russia bounced back from the August 1998 financial crash with surprising speed. Much of the reason for the recovery is that world oil prices rapidly rose during 1999–2000 (just as falling energy prices on the world market had deepened Russia's financial troubles), so that Russia ran a large trade surplus in 1999 and 2000. Another reason is that domestic industries such as food processing have benefited from the devaluation, which caused a steep increase in the prices of imported goods. Also, since Russia's economy was operating to such a large extent on barter and other non-monetary instruments of exchange, the financial collapse had far less of an impact on many producers than it would had the economy been dependent on a banking system. Finally, the economy has been helped by an infusion of cash; as enterprises were able to pay off arrears in back wages and taxes, it in turn allowed consumer demand for the goods and services of Russian industry to rise. For the first time in many years, unemployment in 2000 fell as enterprises added workers.
Nevertheless, the political and social equilibrium of the country remains tenuous to this day, and power remains a highly personalized commodity. The economy remains vulnerable to downturn if, for instance, world oil prices fall at a dramatic pace.
Succession crisis
Yevgeny Primakov did not remain in his post long. Yeltsin grew suspicious that Primakov was gaining in strength and popularity and dismissed him in May 1999, after only eight months in office. Yeltsin then named Sergei Stepashin, who had formerly been head of the FSB (the successor agency to the KGB) and later been Interior Minister, to replace him. The Duma confirmed his appointment on the first ballot by a wide margin.
Stepashin's tenure was even shorter than Primakov's. In August 1999, Yeltsin once again abruptly dismissed the government and named Vladimir Putin as his candidate to head the new government. Like Stepashin, Putin had a background in the secret police, having made his career in the foreign intelligence service and later as head of the FSB. Yeltsin went so far as to declare that he saw Putin as his successor as president. The Duma narrowly voted to confirm Putin.
When appointed, Putin was a relatively unknown politician, but he quickly established himself both in public opinion and in Yeltsin's estimation as a trusted head of government, largely due to the Second Chechen War. Just days after Yeltsin named Putin as a candidate for prime minister, Chechen forces engaged the Russian army in Dagestan, a Russian autonomy near Chechnya. In the next month, several hundred people died in apartment building bombings in Moscow and other cities, bombings Russian authorities attributed to Chechen rebels. In response, the Russian army entered Chechnya in late September 1999, starting the Second Chechen War. The Russian public at the time, angry over the terrorist bombings, widely supported the war. The support translated into growing popularity for Putin, who had taken decisive action in Chechnya.
After the success of political forces close to Putin in the December 1999 parliamentary elections, Yeltsin evidentially felt confident enough in Putin that he resigned from the presidency on December 31, six months before his term was due to expire. This made Putin acting president and gave Putin ample opportunity to position himself as frontrunner for the Russian presidential election held on March 26, 2000, which he won. The Chechen War figured prominently in the campaign. In February 2000, Russian troops entered Grozny, the Chechen capital, and a week before the election, Putin flew to Chechnya on a fighter jet, claiming victory.
From Yeltsinism to Putinism
In August 2000, the Russian submarine K-141 Kursk suffered an explosion, causing the submarine to sink in the shallow area of the Barents Sea. Russia organized a vigorous but hectic attempt to save the crew, and the entire futile effort was surrounded by unexplained secrecy. This, as well as the slow initial reaction to the event and especially to the offers of foreign aid in saving the crew, brought much criticism on the government and personally on President Putin.
On October 23, 2002, Chechen separatists took over a Moscow theatre. Over 700 people inside were taken hostage in what has been called the Moscow theatre hostage crisis. The separatists demanded the immediate withdrawal of Russian forces from Chechnya and threatened to blow up the building if authorities attempted to enter. Three days later, Russian commandos stormed the building after the hostages had been subdued with a sleeping gas, shooting the unconscious militants, and killing over 100 civilian hostages with the sleeping gas in the process. In the aftermath of the theatre siege, Putin began renewed efforts to eliminate the Chechen insurrection. (For additional details on the war in Chechnya under Putin, see Second Chechen War.) The government canceled scheduled troop withdrawals, surrounded Chechen refugee camps with soldiers, and increased the frequency of assaults on separatist positions.
Chechen militants responded in kind, stepping up guerrilla operations and rocket attacks on federal helicopters. Several high-profile attacks have taken place. In May 2004, Chechen separatists assassinated Akhmad Kadyrov, the pro-Russia Chechen leader who became the president of Chechnya 8 months earlier after an election conducted by Russian authorities. On August 24, 2004, two Russian aircraft were bombed. This was followed by the Beslan school hostage crisis in which Chechen separatists took 1,300 hostages. The initially high public support for the war in Chechnya has declined.
Putin has confronted several very influential oligarchs ( Vladimir Gusinsky, Boris Berezovsky and Mikhail Khodorkovsky, in particular) who attained large stakes of state assets, allegedly through illegal schemes, during the privatization process. Gusinsky and Berezovsky have been forced to leave Russia and give up parts of their assets. Khodorkovsky was jailed in Russia and has lost his YUKOS company, formerly the largest oil producer in Russia. Putin's stand against oligarchs is generally popular with the Russian people, even though the jailing of Khodorkovsky is mainly seen as part of a takeover operation by government officials, according to another Levada-Centre poll.
These confrontations have also lead to Putin establishing control over Russian media outlets previously owned by the oligarchs. In 2001 and 2002, TV channels NTV (previously owned by Gusinsky), TV6 and TVS (owned by Berezovsky) were all taken over by media groups loyal to Putin. Similar takeovers have also occurred with print media.
Putin's popularity, which stems from his reputation as a strong leader, stands in contrast to the unpopularity of his predecessor, but it hinges on a continuation of economic recovery. Putin came into office at an ideal time: after the devaluation of the ruble in 1998, which boosted demand for domestic goods, and while world oil prices were rising. Indeed, during the seven years of his presidency, real GDP grew on average 6.7% a year, average income increased 11% annually in real terms, and a consistently positive balance of the federal budget enabled the government to cut 70% of the external debt (according to the Institute for Complex Strategic Studies). Thus, many credit him with the recovery, but his ability to withstand a sudden economic downturn has been untested. Putin won the Russian presidential election in 2004 without any significant competition.
Some researchers assert that most Russians today have come to regret the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. On repeated occasions, even Vladimir Putin—Boris Yeltsin's handpicked successor — stated that the fall of Soviet rule had led to few gains and many problems for most Russian citizens. In a campaign speech in February 2004, for example, Putin called the dismantlement of the Soviet Union a "national tragedy on an enormous scale," from which "only the elites and nationalists of the republics gained." He added, "I think that ordinary citizens of the former Soviet Union and the post-Soviet space gained nothing from this. On the contrary, people have faced a huge number of problems."
Putin's international prestige suffered a major blow in the West during the disputed 2004 Ukrainian presidential election. Putin had twice visited Ukraine before the election to show his support for the pro-Russian Viktor Yanukovych against opposition leader Viktor Yushchenko, a pro-Western liberal economist. He congratulated Yanukovych, followed shortly afterwards by Belorussian president Alexander Lukashenko, on his victory before election results were even made official and made statements opposing the rerun of the disputed second round of elections, won by Yanukovych, amid allegations of large-scale voting fraud. The second round was ultimately rerun; Yushchenko won the round and was eventually declared the winner on January 10, 2005. In the West, the reaction to Russia's handling of, or perhaps interference in, the Ukrainian election evoked echoes of the Cold War, but relations with the U.S. have remained stable.
In 2005, the Russian government replaced the broad in-kind Soviet-era benefits, such as free transportation and subsidies for heating and other utilities for socially vulnerable groups by cash payments. The reform, known as monetization, has been unpopular and caused a wave of demonstrations in various Russian cities, with thousands of retirees protesting against the loss of their benefits. This was the first time such wave of protests took place during the Putin administration. The reform has hurt the popularity of the Russian government, but Putin personally was still popular, with a 77% approval rating.
In 2008, Kosovo's declaration of independence saw a marked deterioration in Russia's relationship with the West. It also saw South Ossetia war against Georgia, that followed the Georgia's attempt to take over the breakaway region of South Ossetia. Russian troops entered South Ossetia and forced Georgian troops back, establishing their control on this territory. In the fall of 2008, Russia unilaterally recognized the independence of South Ossetia and Abkhazia.
Relations with the West
In the early period after Russia became independent, Russian foreign policy repudiated Marxism-Leninism as a putative guide to action, emphasizing cooperation with the West in solving regional and global problems, and soliciting economic and humanitarian aid from the West in support of internal economic reforms.
However, although Russia's leaders now described the West as its natural ally, they grappled with defining new relations with the East European states, the new states formed upon the disintegration of Yugoslavia, and Eastern Europe. Russia opposed the expansion of NATO into the former Soviet bloc nations of the Czech Republic, Poland, and Hungary in 1997 and, particularly, the second NATO expansion into the Baltic states in 2004. In 1999, Russia opposed the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia for more than two months (see Kosovo War), but later joined NATO peace-keeping forces in the Balkans in June 1999.
Relations with the West have also been stained by Russia's relationship with Belarus. Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko, an authoritarian leader, has shown much interest in aligning his country with Russia, and no interest in deepening ties with the ever-expanding NATO or implementing Western-backed neoliberal economic reforms. A union agreement between Russia and Belarus was formed on April 2, 1996. The agreement was tightened, becoming the Union of Russia and Belarus on April 3, 1997. Further strengthening of the union occurred on December 25, 1998, and in 1999.
Under Putin, Russia has sought to strengthen ties with the People's Republic of China by signing the Treaty of Good-Neighborliness and Friendly Cooperation as well building the Trans-Siberian oil pipeline geared toward growing Chinese energy needs. He also made a number of appearances in the media with President of the United States George W. Bush in which the two described each other as "friends".