Trans-Siberian Railway
Background to the schools Wikipedia
This Schools selection was originally chosen by SOS Children for schools in the developing world without internet access. It is available as a intranet download. A quick link for child sponsorship is http://www.sponsor-a-child.org.uk/
| Trans-Siberian Railway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Legend
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
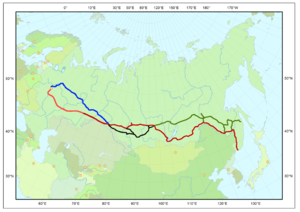
The Trans-Siberian Railway (Russian: Транссибирская магистраль Transsibirskaya Magistral') is a network of railways connecting Moscow with the Russian Far East and the Sea of Japan. Except for the twice per month regularly served connection between Moscow and Pyongyang, it is the longest railway in the world. There are branch lines to China through Mongolia and Manchuria, with service continuing to North Korea.
History
Route development
In March 1890, the future Tsar Nicholas II personally inaugurated and blessed the construction of the Far East segment of the Trans-Siberian Railway during his stop at Vladivostok, after visiting Japan at the end of his journey around the world. Nicholas II made notes in his diary about his anticipation of travelling in the comfort of "The Tsar's Train" across the unspoiled wilderness of Siberia. The Tsar's Train was designed and built in St. Petersburg to serve as the main mobile office of the Tsar and his staff for travelling across Russia.
The main route of the Trans-Siberian railroad begins in Moscow at Yaroslavsky Vokzal, runs through Yaroslavl, Chelyabinsk, Omsk, Novosibirsk, Irkutsk, Ulan-Ude, Chita and Khabarovsk to Vladivostok via Southern Siberia. It was built from 1891 to 1916 under the supervision of government ministers of Russia who were personally appointed by the Tsar Alexander III and by his son, Tsar Nicholas II. The additional Chinese Eastern Railway was constructed as the Russo-Chinese part of the Trans-Siberian Railway, connecting Russia with China and providing a shorter route to Vladivostok. A Russian staff and administration based in Harbin operated it.
The Trans-Siberian Railway is often associated with the main transcontinental Russian line that connects hundreds of large and small cities of the European and Asian parts of Russia. At 9,259 kilometres (5,753 miles), spanning a record seven time zones and taking eight days to complete the journey, it is the third-longest single continuous service in the world, after the Moscow–Pyongyang (10,267 km, 6,380 mi) and the Kiev–Vladivostok (11,085 km, 6,888 mi) services, both of which also follow the Trans-Siberian for much of their routes.
A second primary route is the Trans-Manchurian, which coincides with the Trans-Siberian as far as Tarskaya (a stop 12 km east of Karymskaya, in Zabaykalsky Krai), about 1,000 km east of Lake Baikal. From Tarskaya the Trans-Manchurian heads southeast, via Harbin and Mudanjiang in China's Northeastern Provinces (from where a connection to Beijing is used by one of the Moscow–Beijing trains), joining with the main route in Ussuriysk just north of Vladivostok. This is the shortest and the oldest railway route to Vladivostok. Some trains split at Shenyang, China, with a portion of the service continuing to Pyongyang, North Korea.
The third primary route is the Trans-Mongolian Railway, which coincides with the Trans-Siberian as far as Ulan-Ude on Lake Baikal's eastern shore. From Ulan-Ude the Trans-Mongolian heads south to Ulaan-Baatar before making its way southeast to Beijing.
In 1991, a fourth route running further to the north was finally completed, after more than five decades of sporadic work. Known as the Baikal Amur Mainline (BAM), this recent extension departs from the Trans-Siberian line at Taishet several hundred miles West of Lake Baikal and passes the lake at its northernmost extremity. It crosses the Amur River at Komsomolsk-na-Amure (north of Khabarovsk), and reaches the Pacific at Sovetskaya Gavan.
On October 13, 2011 a train from Khasan made its inaugural run to Rajin in North Korea.
War and revolution
In the Russo-Japanese War (1904-5), the Trans-Siberian Railway was seen as one of the reasons Russia lost the war. The track was a single track and as such could only allow train travel in one direction. This caused significant strategic and supply difficulties for the Russians, as they could not move resources to and from the front as quickly as would be necessary, as a goods train carrying supplies, men and ammunition coming from West to East would have to wait in the sidings, whilst troops and injured personnel in a troop train travelling from East to West went along the line. Thus the Japanese were quickly able to advance whilst the Russians were awaiting necessary troops and supplies. After the Russian Revolution of 1917, the railway served as the vital line of communication for the Czechoslovak Legion and the Allied armies that landed troops at Vladivostok during the Siberian Intervention of the Russian Civil War. These forces supported the White Russian government of Admiral Alexander Kolchak, based in Omsk, and White Russian soldiers fighting the Bolsheviks on the Ural Front. The intervention was weakened, and ultimately defeated, by partisan fighters who blew up bridges and sections of track, particularly in the volatile region between Krasnoyarsk and Chita.
The Trans-Siberian railroad also played a very direct role during parts of Russia's history, with the Czechoslovak Legion using heavily armed and armoured trains to control large amounts of the railway (and of Russia itself) during the Russian Civil War at the end of World War I. As one of the few organised fighting forces left in the aftermath of the Imperial collapse, and before the Red Army took control, the Czechs and Slovaks were able to use their organization and the resources of the railway to establish a temporary zone of control before eventually continuing onwards towards Vladivostok, from where they emigrated back to Czechoslovakia through Vancouver in Canada, through Canada to Europe, or the Panama Canal to Europe also through Japan, Hong Kong, Singapore, Port Said and Triest.
Demand and design
In the late 19th century, the development of Siberia was hampered by poor transport links within the region, as well as with the rest of the country. Aside from the Great Siberian Route, good roads suitable for wheeled transport were few and far between. For about five months of the year, rivers were the main means of transport. During the cold half of the year, cargo and passengers travelled by horse-drawn sleds over the winter roads, many of which were the same rivers, now ice-covered.
The first steamboat on the River Ob, Nikita Myasnikov's Osnova, was launched in 1844. But early beginnings were difficult, and it was not until 1857 that steamboat shipping started developing on the Ob system in a serious way. Steamboats started operating on the Yenisei in 1863, on the Lena and Amur in the 1870s.
While the comparative flatness of Western Siberia was at least fairly well served by the gigantic Ob– Irtysh– Tobol– Chulym river system, the mighty rivers of Eastern Siberia—the Yenisei, the upper course of the Angara River (the Angara below Bratsk was not easily navigable because of the rapids), and the Lena — were mostly navigable only in the North-South direction. An attempt to partially remedy the situation by building the Ob-Yenisei Canal was not particularly successful. Only a railway could be a real solution to the region's transport problems.
The first railway projects in Siberia emerged after the completion of the Moscow-Saint Petersburg Railway in 1851. One of the first was the Irkutsk– Chita project, proposed by the American entrepreneur Perry Collins and supported by Transport Minister Constantine Possiet with a view toward connecting Moscow to the Amur River, and consequently, to the Pacific Ocean. Siberia's governor, Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky, was anxious to advance the colonisation of the Russian Far East, but his plans could not materialise as long as the colonists had to import grain and other food from China and Korea. It was on Muravyov's initiative that surveys for a railway in the Khabarovsk region were conducted.
Before 1880, the central government had virtually ignored these projects, because of the weakness of Siberian enterprises, a clumsy bureaucracy, and fear of financial risk. Financial minister Count Yegor Kankrin wrote:
"The idea of covering Russia with a railway network not just exceeds any possibility, but even building the railway from Petersburg to Kazan must be found untimely by several centuries".
By 1880, there were a large number of rejected and upcoming applications for permission to construct railways to connect Siberia with the Pacific, but not eastern Russia. This worried the government and made connecting Siberia with central Russia a pressing concern. The design process lasted 10 years. Along with the route actually constructed, alternative projects were proposed:
- Southern route: via Kazakhstan, Barnaul, Abakan and Mongolia.
- Northern route: via Tyumen, Tobolsk, Tomsk, Yeniseysk and the modern Baikal Amur Mainline or even through Yakutsk.
Railwaymen fought against suggestions to save funds, for example, by installing ferryboats instead of bridges over the rivers until traffic increased. The designers insisted and secured the decision to construct an uninterrupted railway.
Unlike the rejected private projects that intended to connect the existing cities demanding transport, the Trans-Siberian did not have such a priority. Thus, to save money and avoid clashes with land owners, it was decided to lay the railway outside the existing cities. Tomsk was the largest city, and the most unfortunate, because the swampy banks of the Ob River near it were considered inappropriate for a bridge. The railway was laid 70 km to the south (instead crossing the Ob at Novonikolaevsk, later renamed Novosibirsk); just a blind branch line connected with Tomsk, depriving the city of the prospective transit railway traffic and trade.
The railway was instantly filled to its capacity with local traffic, mostly wheat. Together with low speed and low possible weights of trains, it upset the promised role as a transit route between Europe and East Asia. During the Russo-Japanese War, the military traffic to the East almost disrupted the flow of civil freight.
Construction
Full-time construction of the Trans-Siberian Railway began in 1891 and was put into execution and overseen by Sergei Witte, who was then Finance Minister.
Similar to the First Transcontinental Railroad in the USA, Russian engineers started construction at both ends and worked towards the centre. From Vladivostok the railway was laid North along the right bank of the Ussuri River to Khabarovsk at the Amur River, becoming the Ussuri Railway.
In 1890 a bridge across the Ural River was built and the new railway entered Asia. The bridge across the Ob River was built in 1898 and the small city of Novonikolaevsk, founded in 1883, grew into the large Siberian city of Novosibirsk. In 1898 the first train reached Irkutsk and the shores of Lake Baikal about 60 kilometres (37 miles) east of the city. The railway ran on to the east, across the Shilka and Amur rivers and soon reached Khabarovsk. The Vladivostok – Khabarovsk section was built slightly earlier, in 1897.
Russian soldiers, as well as convict labourers from Sakhalin and other places were used for building the railway.
Lake Baikal is more than 640 kilometres (400 miles) long and more than 1,600 metres (5,200 feet) deep. Until the Circum-Baikal Railway was built the line ended on either side of the lake. The ice-breaking train ferry SS Baikal built in 1897 and smaller ferry SS Angara built in about 1900, made the four-hour crossing to link the two railheads. The Russian admiral and explorer Stepan Makarov (1849–1904) designed Baikal and Angara but they were built in Newcastle-upon-Tyne, England by Armstrong Whitworth. They were "knock down" vessels; that is, each ship was bolted together in England, every part of the ship was marked with a number, the ship was disassembled into many hundreds of parts and transported in kit form to Listvyanka where a shipyard was built especially to reassemble them. Their boilers, engines and some other components were built in Saint Petersburg and transported to Listvyanka to be installed. Baikal had 15 boilers, four funnels, and was 64 metres (210 ft) long. She could carry 24 railway coaches and one locomotive on her middle deck. Angara is smaller, with two funnels.
Completion of the Circum-Baikal Railway in 1904 bypassed the ferries, but from time to time the Circum-Baikal Railway suffered from derailments or rockfalls so both ships were held in reserve until 1916. Baikal was burnt out and destroyed in the Russian Civil War but Angara survives. She has been restored and is permanently moored at Irkutsk where she serves as an office and a museum.
In winter, sleighs were used to move passengers and cargo from one side of the lake to the other until the completion of the Lake Baikal spur along the southern edge of the lake.
With the Amur River line north of the Chinese border being complete in 1916, there was a continuous railway from Petrograd to Vladivostok that remains to this day the world's longest railway line. Electrification of the line, begun in 1929 and completed in 2002, allowed a doubling of train weights to 6,000 tonnes.
Effects
The Trans-Siberian Railway gave a positive boost to Siberian agriculture, facilitating substantial exports to central Russia and Europe. It influenced the territories it connected directly, as well as those connected to it by river transport. For instance, Altai Krai exported wheat to the railway via the Ob River.
As Siberian agriculture began to export cheap grain towards the West, agriculture in Central Russia was still under economic pressure after the end of serfdom, which was formally abolished in 1861. Thus, to defend the central territory and to prevent possible social destabilisation, in 1896 the government introduced the Chelyabinsk tariff break (Челябинский тарифный перелом), a tariff barrier for grain passing through Chelyabinsk, and a similar barrier in Manchuria. This measure changed the nature of export: mills emerged to create bread from grain in Altai Krai, Novosibirsk and Tomsk, and many farms switched to corn production. From 1896 until 1913 Siberia exported on average 501,932 tonnes (30,643,000 pood) of bread (grain, flour) annually.
The Trans-Siberian Railway also brought with it millions of peasant-migrants from the Western regions of Russia and Ukraine. Between 1906 to 1914, the peak migration years, about 4 million peasants arrived in Siberia.
The Trans-Siberian line remains the most important transportation link within Russia; around 30% of Russian exports travel on the line. While it attracts many foreign tourists, it gets most of its use from domestic passengers.
Today the Trans-Siberian Railway carries about 200,000 containers per year to Europe. Russian Railways intends to at least double the volume of container traffic on the Trans-Siberian and is developing a fleet of specialised cars and increasing terminal capacity at the ports by a factor of 3 ~ 4. By 2010, the volume of traffic between Russia and China could reach 60 million tons (54 million tonnes), most of which will go by the Trans-Siberian.
With perfect coordination of the participating countries' railway authorities, a trainload of containers can be taken from Beijing to Hamburg, via the Trans-Mongolian and Trans-Siberian lines in as little as 15 days, but typical cargo travel times are usually significantly longer—e.g., typical cargo travel time from Japan to major destinations in European Russia was reported as around 25 days.
According to a 2009 report, the best travel times for cargo block trains from Russia's Pacific ports to the western border (of Russia, or perhaps of Belarus) were around 12 days, with trains making around 900 km per day, at a maximum operating speed of 80 km/h. However, in early 2009 Russian Railways announced an ambitious "Trans-Siberian in Seven Days" program; according to this plan, $11 billion will be invested over the next five years to make it possible for freight traffic to cover the same 9000 km distance in just seven days. The plan will involve increasing the cargo trains' speed to 90 km/h in 2010–12, and, at least on some sections, to 100 km/h by 2015. At these speeds, freight trains will be able to cover 1,500 km per day.
Developments in shipping
On January 11, 2008, China, Mongolia, Russia, Belarus, Poland and Germany agreed to collaborate on a cargo train service between Beijing and Hamburg.
The railroad can typically deliver containers in 1/3 to 1/2 of the time of a sea voyage, and in late 2009 announced a 20% reduction in its container shipping rates. With its 2009 rate schedule, the TSR will transport a forty-foot container to Poland from Yokohama for $2,820, or from Pusan for $2,154.
One of the complicating factors related to such ventures is the fact that the CIS states' broad railway gauge is incompatible with China and Western and Central Europe's standard gauge. Therefore, a train travelling from China to Western Europe would encounter gauge breaks twice: at the Chinese-Mongolian or the Chinese-Russian frontier and at the Ukrainian or the Belorussian border with Central European countries.
Passenger fares
A number of privately chartered services are operated, and one tour operator even commissioned the construction of their own train, jointly owned by themselves and Russian railways. The train, officially named Golden Eagle Trans-Siberian Express was launched on 26 April 2007 by Prince Michael of Kent. Current rates (March 2013) are EUR 295.- for the complete itinerary from Moscow to Vladivostok in a couchette coach and EUR 501.- in a sleeping car. A 2-persons-sleeping compartment is only available on train 001 / 002 'Rossiya' at EUR 955.-, however. There is a Rail Pass for all Russian trains introduced 2012 as well, valid 30 days 1st and 2nd class.
Travel to Peking / China from Moscow: taking the trains to Zabaikalsk or Blagoveshchensk, passing the border and getting a Chinese ticket at the counter in Manzhouli or Heihe respectively cost in couchette coaches via Zabaikalsk EUR 286.-, via Blagoveshchensk EUR 310.- (March 2013). The direct trains 004 via Mongolia and 020 via Zabaikalsk cost from Moscow about triple and do not have couchette coaches but only sleeping cars. A new fares' system is going to be introduced on 01.03.2013 by RZD. The changes consist of demand-related prices equal to airlines and of a reduction of the seasonal rates' sectors to 42. The time-sectors and therefore the level of percentage differ between 1., 2. class and 3., 4. class respectively. It is now also possible to get Mongolian tickets at official prices.
Routes
In general, the lower the train number the fewer stops it makes and therefore the faster the journey. The train number makes no difference in the duration of border crossings.
Trans-Siberian line
A commonly used main line route is as follows. Distances and travel times are from the schedule of train No.002M, Moscow-Vladivostok.
- Moscow, Yaroslavsky Rail Terminal (0 km, Moscow Time).
- Vladimir (210 km, MT)
- Nizhny Novgorod (461 km, 6 hours, MT) on the Volga River. Its railroad station is still called by its old Soviet name Gorky, and is so listed in most timetables.
- Kirov (917 km, 13 hours, MT) on the Vyatka River.
- Perm (1,397 km, 20 hours, MT+2) on the Kama River
- Official boundary between Europe and Asia (1,777 km), marked by a white obelisk.
- Yekaterinburg (1,778 km, 1 day 2 hours, MT+2) in the Urals, still called by its old Soviet name Sverdlovsk in most timetables.
- Tyumen (2,104 km)
- Omsk (2,676 km, 1 day 14 hours, MT+3) on the Irtysh River
- Novosibirsk (3,303 km, 1 day 22 hours, MT+3) on the Ob River
- Krasnoyarsk (4,065 km, 2 days 11 hours, MT+4) on the Yenisei River
- Taishet (4,483 km), junction with the Baikal-Amur Mainline
- Irkutsk (5,153 km, 3 days 4 hours, MT+5) near Lake Baikal's southern extremity
- Ulan Ude (5,609 km, 3 days 12 hours, MT+5) eastern shore of Lake Baikal
- Junction with the Trans-Mongolian line (5,622 km)
- Chita (6,166 km, 3 days 22 hours, MT+6)
- Junction with the Trans-Manchurian line at Tarskaya (6,274 km)
- Birobidzhan (8,312 km, 5 days 13 hours), the capital of Jewish Autonomous Region
- Khabarovsk (8,493 km, 5 days 15 hours, MT+7) on the Amur River
- Ussuriysk (9,147 km), junction with the Trans-Manchurian line and Korea branch
- Vladivostok (9,289 km, 6 days 4 hours, MT+7), on the Pacific Ocean
Services to North Korea continue from Ussuriysk via:
- Primorsk (9,257 km, 6 days 14 hours, MT+7)
- Khasan (9,407 km, 6 days 19 hours, MT+7, border with North Korea)
- Tumangang (9,412 km, 7 days 10 hours, MT+6, North Korean side of the border)
- Pyongyang (10,267 km, 9 days 2 hours, MT+6)
There are many alternative routings between Moscow and Siberia. For example:
- Some trains would leave Moscow from Kazansky Rail Terminal instead of Yaroslavsky Rail Terminal; this would save some 20 km off the distances, because it provides a shorter exit from Moscow onto the Nizhny Novgorod main line.
- One can take a night train from Moscow's Kursky Rail Terminal to Nizhny Novgorod, make a stopover in the Nizhny and then transfer to a Siberia-bound train
- From 1956 to 2001 many trains went between Moscow and Kirov via Yaroslavl instead of Nizhny Novgorod. This would add some 29 km to the distances from Moscow, making Vladivostok Kilometer 9,288.
- Other trains get from Moscow (Kazansky Terminal) to Yekaterinburg via Kazan.
- Between Yekaterinburg and Omsk it is possible to travel via Kurgan Petropavlovsk (in Kazakhstan) instead of Tyumen.
- One can bypass Yekaterinburg altogether by travelling via Samara, Ufa, Chelyabinsk, and Petropavlovsk; this was historically the earliest configuration.
Depending on the route taken, the distances from Moscow to the same station in Siberia may differ by several tens of kilometers.
Trans-Manchurian line
The Trans-Manchurian line, as e.g. used by train No.020, Moscow-Beijing follows the same route as the Trans-Siberian between Moscow and Chita and then follows this route to China:
- Branch off from the Trans-Siberian-line at Tarskaya (6,274 km from Moscow)
- Zabaikalsk (6,626 km), Russian border town; there is a break-of-gauge
- Manzhouli (6,638 km from Moscow, 2,323 km from Beijing), Chinese border town
- Harbin (7,573 km, 1,388 km)
- Changchun (7,820 km from Moscow)
- Beijing (8,961 km from Moscow)
The express train (No.020) travel time from Moscow to Beijing is just over six days.
There is no direct passenger service along the entire original Trans-Manchurian route (i.e., from Moscow or anywhere in Russia, west of Manchuria, to Vladivostok via Harbin), due to the obvious administrative and technical ( gauge break) inconveniences of crossing the border twice. However, assuming sufficient patience and possession of appropriate visas, it is still possible to travel all the way along the original route, with a few stopovers (e.g. in Harbin, Grodekovo, and Ussuriysk). Such an itinerary would pass through the following points from Harbin east:
- Harbin (7,573 km from Moscow)
- Mudanjiang (7,928 km)
- Suifenhe (8,121 km), the Chinese border station
- Grodekovo (8,147 km), Russia
- Ussuriysk (8,244 km)
- Vladivostok (8,356 km)
Trans-Mongolian line
The Trans-Mongolian line follows the same route as the Trans-Siberian between Moscow and Ulan Ude, and then follows this route to Mongolia and China:
- Branch off from the Trans-Siberian line (5,655 km from Moscow)
- Naushki (5,895 km, MT+5), Russian border town
- Russian–Mongolian border (5,900 km, MT+5)
- Sükhbaatar (5,921 km, MT+5), Mongolian border town
- Ulan Bator (6,304 km, MT+5), the Mongolian capital
- Zamyn-Üüd (7,013 km, MT+5), Mongolian border town
- Erenhot (842 km from Beijing, MT+5), Chinese border town
- Datong (371 km, MT+5)
- Beijing (MT+5)
Cultural importance
- The Trans-Siberian Railway is the theme for the Trans-Siberian Railway Panorama and 1900 Trans-Siberian Railway Fabergé egg.
- In the videogame Syberia the protagonist travels by train through Russia/Siberia - a clear reference to The Trans-Siberian railway
- The Corto Maltese comic Corte sconta detta arcana/Corto Maltese en Sibérie has the Trans-Siberian Railway as part of the story that takes place in the Russian Revolutionary period of the 20th century.
- The cult film Horror Express starring Peter Cushing, Christopher Lee and Telly Savalas is set aboard the railway.
- In the play Fiddler on the Roof and the film version, Tevye's daughter, Hodel, takes the Trans-Siberian Railway to Siberia after her fiancé is exiled there.
- A small number of German Jews and anti-Nazis used the Trans-Siberian to escape Europe after the start of World War II (while the Molotov Pact was in force), including the Mathematician Kurt Gödel and the mother of the actor Heinz Bernard
- The 2008 thriller Transsiberian takes place on the railway.
- The 2012 Television show An Idiot Abroad features Karl Pilkington traveling the length of the railway.
- Henry Rollins has an infamous bit of his trip on the Transsiberian Express.