
File:Saomaitrmm.jpg
| |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Summary
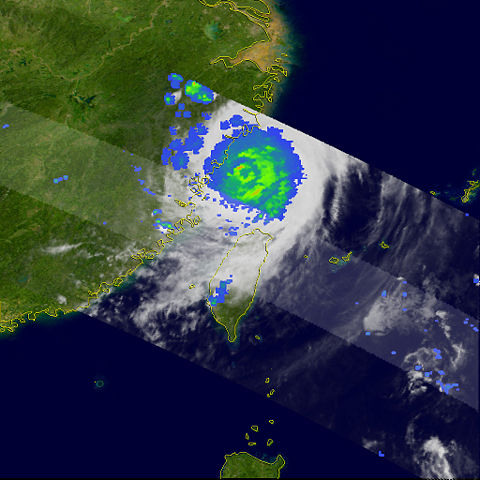
| Description | Typhoon Saomai formed on August 4, 2006, as a tropical depression. Within a day, it had become organized enough to be classified as a tropical storm and earn a name: Saomai, which is the Vietnamese name for the planet Venus. The storm continued to gather strength, becoming a typhoon on August 6. At 5:25 p.m. local time (9:25 UTC) on August 10, it came ashore in China’s Zhejiang province as a Category 4 super typhoon, making it the eighth storm to come ashore in China in 2006. The storm was one of the most powerful storms to hit China in the past fifty years, according to the Xinhua news agency. Large-scale evacuations before the storm struck have displaced hundreds of thousands of people, and more than 1,000 homes have been destroyed. This image was made from data acquired by the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite (TRMM) at 1:58 p.m. local time (05:58 UTC) on August 10, 2006, as Saomai was only hours from making landfall. The image shows the rain intensity within Typhoon Saomai. Rain rates in the centre swath are from the TRMM Precipitation Radar, and rain rates in the outer swath are from the TRMM Microwave Imager. The rain rates are overlaid on infrared data from the TRMM Visible Infrared Scanner. The rain field was fairly compact, and patches of intense rain (red) occurred along the eyewall. At the time of this image, Saomai was a super typhoon rated as a Category 4 storm on the Saffir-Simpson intensity scale, having eased off its earlier Category 5 power. As the storm was about to come ashore, the maximum sustained winds were reported to be around 240 kilometers per hour (150 miles per hour), according to the University of Hawaii’s Tropical Storm Information Centre. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite was placed into service in November of 1997. From its low-earth orbit, TRMM has been providing valuable images and information on storm systems around the tropics using a combination of passive microwave and active radar sensors, including the first precipitation radar in space. TRMM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japanese space agency, JAXA. |
||||||
| Date | 10 August 2006 | ||||||
| Source | http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/natural_hazards_v2.php3?img_id=13772 | ||||||
| Author | Images produced by Hal Pierce (SSAI/NASA GSFC) | ||||||
| Permission ( Reusing this file) |
|
File usage
Metadata
| Width | 1,024 px |
|---|---|
| Height | 1,024 px |
| Compression scheme | Uncompressed |
| Pixel composition | RGB |
| Orientation | Normal |
| Number of components | 3 |
| Horizontal resolution | 72 dpi |
| Vertical resolution | 72 dpi |
| Data arrangement | chunky format |
| Software used | Adobe Photoshop CS2 Macintosh |
| File change date and time | 16:12, 10 August 2006 |
| Colour space | Uncalibrated |
More information
Learning is fun and easy with Schools Wikipedia. SOS Children's Villages believes education is an important part of a child's life. That's why we ensure they receive nursery care as well as high-quality primary and secondary education. When they leave school, we support the children in our care as they progress to vocational training or higher education. Learn more about child sponsorship.



