
File:Virus Replication large.svg
| |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
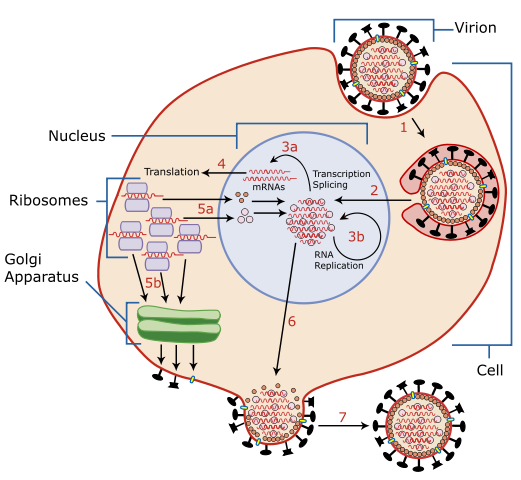
| Description | A diagram of influenza viral cell invasion and replication. | ||||||||||||||
| Date | 5 March 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Source | Scaled up from Image:Virus Replication.svg by User:YK Times, who redrew from w:Image:Virusreplication.png using Adobe Illustrator. | ||||||||||||||
| Author | User:YK Times | ||||||||||||||
| Permission ( Reusing this file) |
|
Summary
From Scheme of Influenza A virus replication (NCBI):
"A virion attaches to the host cell membrane using Hemagglutinin(HA) and enters the cytoplasm by receptor-mediated endocytosis (STEP 1), thereby forming an endosome. A cellular trypsin-like enzyme cleaves HA into products HA1 and HA2 (not shown). HA2 promotes fusion of the virus envelope and the endosome membranes. A minor virus envelope protein M2 acts as a ion channel making the inside of the virion more acidic. As a result, the major envelope protein M1 dissociates from the nucleocapsid and vRNAs are translocated into the nucleus (STEP 2) via interaction between NP and cellular transport machinery. In the nucleus, the viral polymerase complexes transcribe (STEP 3a) and replicate (STEP 3b) the vRNAs. Newly synthesized mRNAs migrate to cytoplasm (STEP 4) where they are translated. Posttranslational processing of HA, Neuraminidase(NA), and M2 includes transportation via Golgi apparatus to the cell membrane (STEP 5b). NP, M1, NS1 (nonstructural regulatory protein - not shown) and NEP (nuclear export protein, a minor virion component - not shown) move to the nucleus (STEP 5a) and bind freshly synthesized copies of vRNAs. The newly formed nucleocapsids migrate into the cytoplasm in a NEP-dependent process and eventually interact via protein M1 with a region of the cell membrane where HA, NA and M2 have been inserted (STEP 6). Then the newly synthesized virions bud from infected cell (STEP 7). NA destroys the sialic acid moiety of cellular receptors, thereby releasing the progeny virions.
| Annotations | This image is annotated: View the annotations at Commons |
HA (Hemagglutinin
NA - Neuraminidase
M2 (green) H+ ion channel
M1 (pink circles) - Capsid
viral RNA (squiggles) viral Polymerase (open circles) - replicates vRNA
File usage
Metadata
Find out more
Learning is fun and easy with Schools Wikipedia. SOS Childrens Villages works in 133 countries and territories across the globe, helps more than 62,000 children, and reaches over 2 million people in total. Find out how you can help children in other countries.

