File:Phanerozoic Sea Level.png
| |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
 |
File:Phanerozoic Sea Level.svg is a vector version of this file. It should be used in place of this raster image when superior. File:Phanerozoic Sea Level.png
For more information about vector graphics, read about Commons transition to SVG.
|
 |
Contents |
Summary
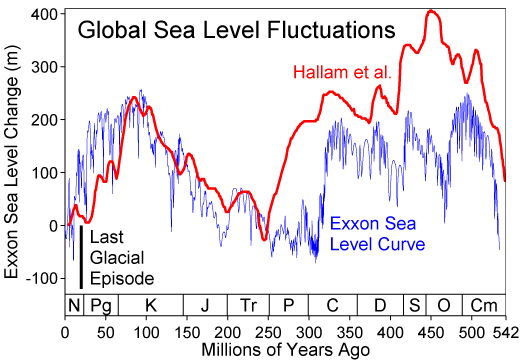
This figure compares the Hallam et al. (1983) and Exxon eustatic (global) sea level reconstructions for the Phanerozoic eon. The Exxon curve is a composite from several reconstructions published by the Exxon corporation (Haq et al. 1987, Ross & Ross 1987, Ross & Ross 1988). Both curves are adjusted to the 2004 ICS geologic timescale.
Hallam et al. and Exxon use very different techniques to measuring global sea level changes. Hallam's approach is qualitative and relies on regional scale observations from exposed geologic sections and estimates of the areas of flooded continental interiors. Exxon's approach relies on the interpretation of seismic profiles to determine the extent of coastal onlap in subsequently buried sedimentary basins. Hallam is insensitive to rapid fluctuations in sea level. Exxon is sensitive to rapid fluctuations but tends to overinterpret local geologic changes resulting in bias towards reporting unphysical rapid fluctuations.
The depth scale is as reported by Exxon. Because Hallam is reported as qualtitative (i.e. uncalibrated), these sea level changes were scaled to match the Exxon record during the period 0-250 Myr.
A black bar is added to indicate the scale of sea level fluctuations during the last glacial/interglacial transition. This change occurred purely within the last 20 kyrs, and note that neither system of measurements is capable of resolving changes on this time scale. It also should be noted that very rapid fluctuations of similar scale are potentially possible during all periods during which large scale ice sheets are present (see: Phanerozoic climate change).
On the scale of this figure, the melting of all existing ice sheets would result in a sea level rise of ~80 meters. Changes on larger scales, which evidently occurred many times in the past, are the result of geologic changes in the structure of ocean basins. Essentially, such changes affect the average depth of the oceans relative to the continents.
Common symbols for geologic periods appear at the bottom.
Copyright
This figure was prepared by Robert A. Rohde from publicly available data and is incorporated into the Global Warming Art project.
 |
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled GNU Free Documentation License. http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
| This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. | ||
|
||
| This licensing tag was added to this file as part of the GFDL licensing update.http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/CC-BY-SA-3.0Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 truetrue |
References
- Hallam, A., Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. B 325, 437-455 (1989).
- Harland, W.B. and many others, A Geologic Time Scale, (1982).
- Haq, B., J. Hardenbol, P. Vail., Science, 235, 156-1167 (1987).
- Ross, C.A. & J.R.P. Ross, Cushman Foundation for Foraminiferal Research Spec. Publ. 24, 137-149 (1987).
- Ross, C.A. & J.R.P. Ross in Sea-level Change: an Integrated Approach (Eds. Wilgus, C.K., Hastings, B.J., Posamentier, H., van Wagoner, J.C., Ross, C.A., and Kendall, C.G. St. C.), SEPM Spec. Pub. 42:71-108 (1988).
Notes
- Because Exxon traditionally used an in-house (i.e. unpublished) system for estimating the geologic age of stratigraphic sections it is not possible to perform an exact recalibration of the time scale. Instead it was adjusted assuming the Harland et al. 1982 time scale was a reasonable approximation.
derivative works
Derivative works of this file:
File usage
Learn more about Schools Wikipedia
Wikipedia for Schools was collected by SOS Children. By supporting vulnerable children right through to adulthood, SOS Childrens Villages makes a lasting difference to the lives of thousands of people. Education is a key part of our work, and our schools provide high-quality teaching to the children in our care. Learn more about child sponsorship.