|
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help.
|
Summary
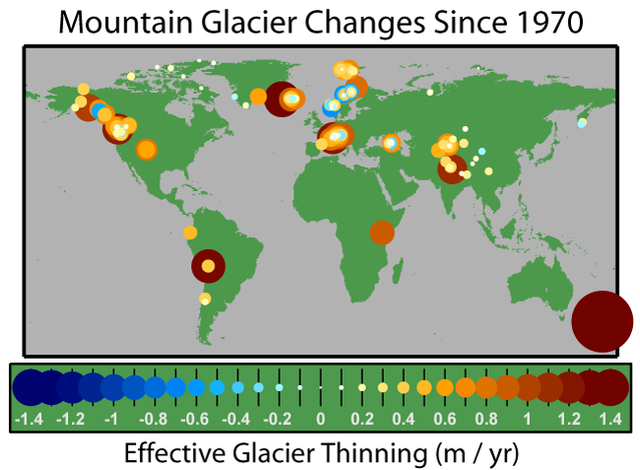
The effective rate of change in glacier thickness, also known as the glaciological mass balance, is a measure of the average change in a glacier's thickness after correcting for changes in density associated with the compaction of snow and conversion to ice. The map shows the average annual rate of thinning since 1970 for the 173 glaciers that have been measured at least 5 times between 1970 and 2004 (Dyurgerov and Meier 2005). Larger changes are plotted as larger circles and towards the back.
All survey regions except Scandinavia show a net thinning. This widespread glacier retreat is generally regarded as a sign of global warming.
During this period, 83% of surveyed glaciers showed thinning with an average loss across all glaciers of 0.31 m/yr. The most rapidly growing glacier in the sample is Engabreen glacier in Norway with a thickening of 0.64 m/yr. The most rapidly shrinking was Ivory glacier in New Zealand which was thinning at 2.4 m/yr. Ivory glacier had totally disintegrated by circa 1988 .
Copyright
This figure was originally prepared by Rober A. Rohde from published data and is incorporated into the Global Warming Art project.
Image from Global Warming Art
This image is an original work created for Global Warming Art. Please refer to the image description page for more information.
 |
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled GNU Free Documentation License. http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue
|
Notes
This sample of mountain glaciers excludes the primary ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica.
It should be acknowledged that glacier sampling is heavily biased towards North America and Europe. Africa has only a handful of glaciers, whereas continental Australia has none. However substantial unsampled mountain glaciers do exist in South America, Asia and the margins of Antarctica. Despite their importance, none of the marginal Antarctic glaciers have had their mass balance sampled at least 5 times since 1970.
These estimates of ice sheet thinning do not include glacier mass lost due to iceberg calving. Such calving is not significant for most mountain glaciers, since only a small proportion of these glaciers terminate in the ocean.
Reference
- Dyurgerov, Mark B. and Mark F. Meier (2005). "Glaciers and the Changing Earth System: A 2004 Snapshot". Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research, Occasional Paper 58.
Other versions
File usage
The following pages on Schools Wikipedia link to this image (list may be incomplete):
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.