A fixed number, most often 0.05, is referred to as a significance level or level of significance. Such a number may be used either as a cutoff mark for a
$p$ -Value
In brief, the (left-tailed)
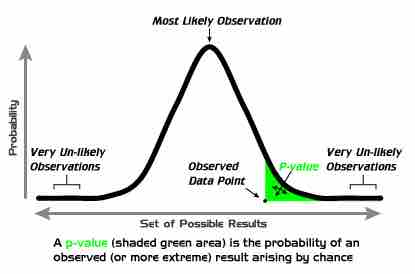
$p$ -Value Graph
Example of a
Hypothesis tests, such as Student's
Using Significance Levels
Popular levels of significance are 10% (0.1), 5% (0.05), 1% (0.01), 0.5% (0.005), and 0.1% (0.001). If a test of significance gives a
In some situations, it is convenient to express the complementary statistical significance (so 0.95 instead of 0.05), which corresponds to a quantile of the test statistic. In general, when interpreting a stated significance, one must be careful to make precise note of what is being tested statistically.
Different levels of cutoff trade off countervailing effects. Lower levels – such as 0.01 instead of 0.05 – are stricter and increase confidence in the determination of significance, but they run an increased risk of failing to reject a false null hypothesis. Evaluation of a given