Control theory advances the proposition that weak bonds between the individual and society allow people to deviate. In other words, deviant behavior occurs when external controls on behavior are weak. If the individual has strong social bonds with positive influences, deviant behavior is less likely than for another individual who has no family or friends.
Social Bonds
According to Travis Hirschi, norms emerge to deter deviant behavior, leading to conformity and groups. People will conform to a group when they believe they have more to gain from conformity than by deviance. Hirschi argued a person follows norms because they have a bond with society. These social bonds have four elements: opportunity, attachment, belief, and involvement. When any one of these bonds are weakened or broken a person is more likely to act in defiance.
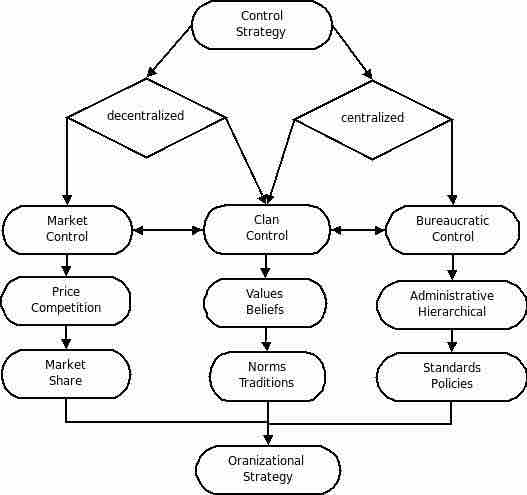
Control Theory in sociology can either be classified as centralized, decentralized, or mixed. Decentralized control, or market control, is typically maintained through factors such as price, competition, or market share. Centralized control, such as bureaucratic control, is typically maintained through administrative or hierarchical techniques that create standards or policies. An example of mixed control is clan control, which contains both centralized and decentralized control. Mixed control is typically maintained by establishing a set of values and beliefs or norms and traditions.
Critique
While control theory gives an adequate explanation of non-serious forms of youthful delinquency, it fails to explain adult criminal behavior and serious instances of youth crime. Moreover, control theory is met with some resistance for its compliance to a conservative view of the broader social order. From a control theory perspective, children who are properly bonded to their parents would be involved in less crime than children who have weaker parental bonds; control theory assumes that the family is a naturally law-abiding institution. The theory's biggest weakness is that it places too much importance on the bonds relative to an individual and society, without looking at other concepts like autonomy and impulsiveness.
Control Strategy
Control theory advances the proposition that weak bonds between the individual and society allow people to deviate.