Chapter 6
Learning
By Boundless

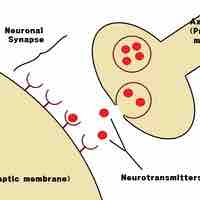
Ivan Pavlov's research on classical conditioning profoundly informed the psychology of learning and the field of behaviorism.
Research has demonstrated the effectiveness of classical conditioning in altering human behavior.
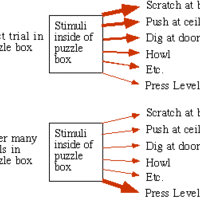
Thorndike's law of effect states that behaviors are modified by their positive or negative consequences.

B. F. Skinner was a behavioral psychologist who expanded the field by defining and elaborating on operant conditioning.

Shaping is a method of operant conditioning by which successive approximations of a target behavior are reinforced.
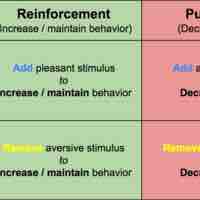
Reinforcement and punishment are principles of operant conditioning that increase or decrease the likelihood of a behavior.
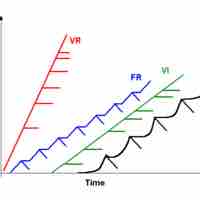
Reinforcement schedules determine how and when a behavior will be followed by a reinforcer.

Latent learning occurs without any obvious conditioning or reinforcement of a behavior, illustrating a cognitive component to learning.
Observational learning occurs from watching, retaining, and replicating a behavior observed from a model.
Insight learning occurs when a new behavior is learned through cognitive processes rather than through interactions with the outside world.
How we learn and incorporate information is directly influenced by psychology and is a key subject of interest for educational psychologists.

Special-education programs are designed to help children with disabilities obtain an education equivalent to their non-disabled peers.