Chapter 8
Campaigns and Elections
By Boundless

From the broad and general to the small and local, elections are designed to serve different purposes for various political voting systems.

Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century.

A ballot is a device used to cast votes in an election; types of ballots include secret ballots and ranked ballots.

Common voting systems are majority rule, proportional representation, or plurality voting with a number of criteria for the winner.
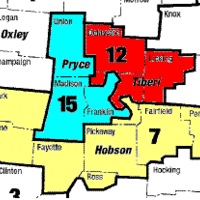
An electoral district is a territorial subdivision whose members (constituents) elect one or more representatives to a legislative body.

It is essential to gather a specialized and politically driven staff that helps run political campaigns in elections.

A modern political campaign informs citizens about a political candidate running for the elected office.
In the nomination campaign, Presidential candidates are selected based on the primaries to run in the main election.

In the U.S., general election campaigns promote presidential candidates running for different parties.
Eligibility requirements restrict who can run for a given public office.

Nomination is the process through which political candidates are chose to campaign for election to office.

An election is a decision-making process used in a democracy to choose public office holders based on a vote.

Candidates run for office by orchestrating expensive campaigns designed to increase their appeal to the electorate.

Primary elections and caucuses are used to narrow the field of candidates in each major political party before a general election.

Political parties hold national conventions to nominate candidates for the presidency and to decide on a platform.
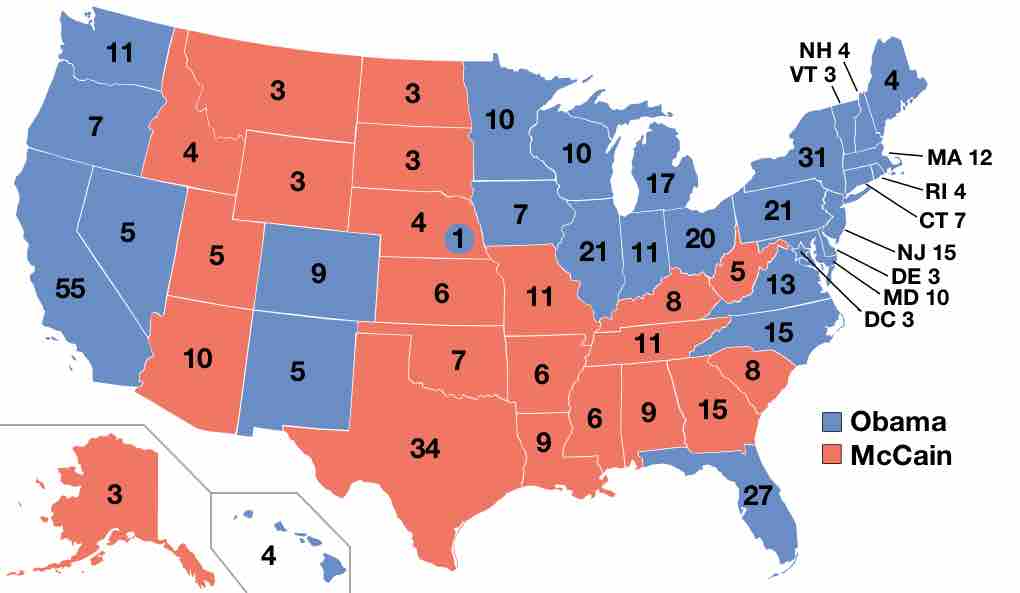
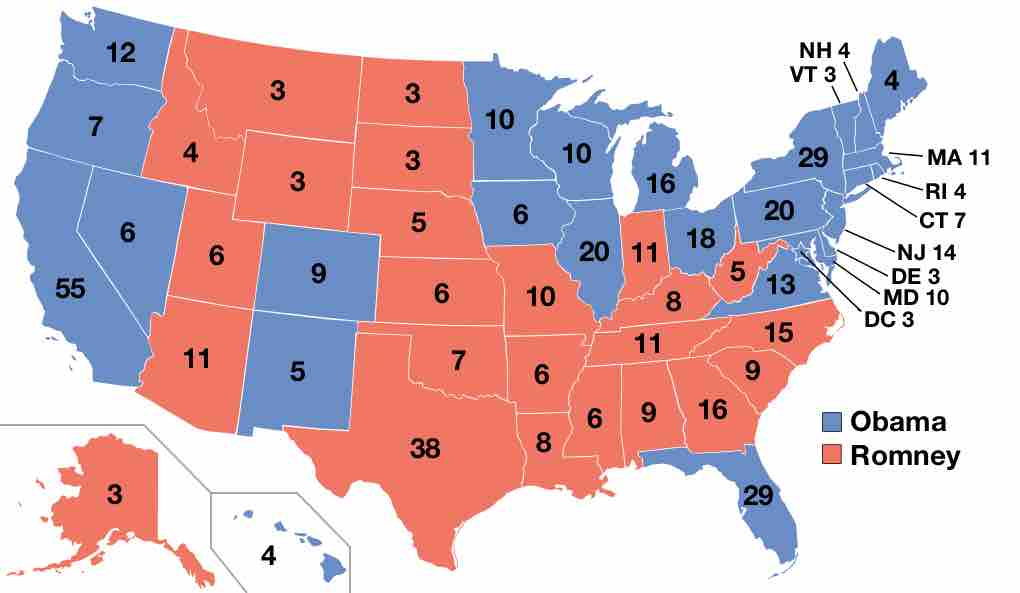
The presidential general election occurs after the primary season and is the process through which a national vote chooses the president.
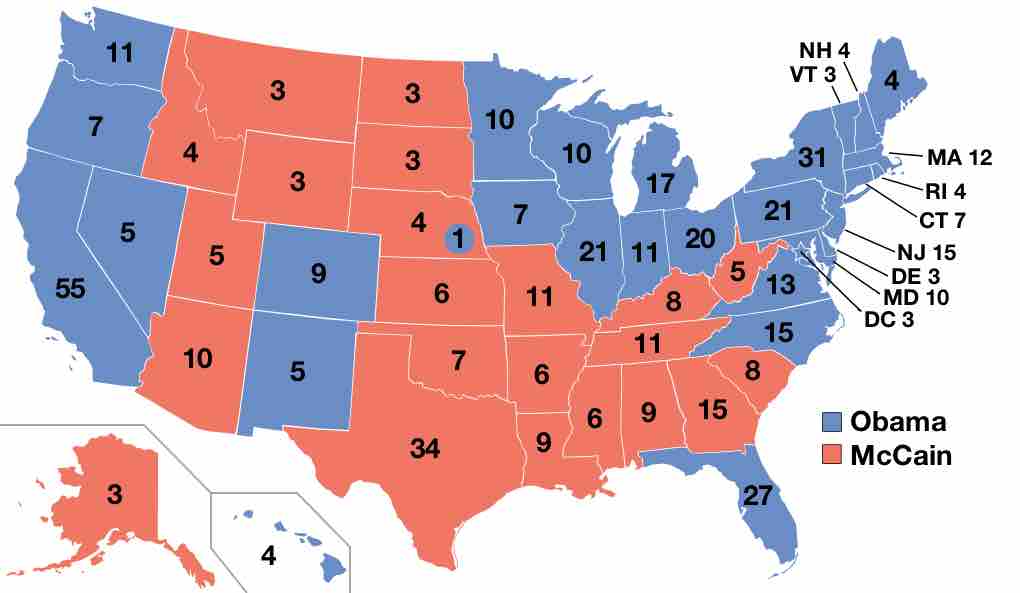
The Electoral College is the 538 person body that elects the President and the Vice President of the United States.
Presidential candidates seek the highest office of the executive branch of government and carry out campaigns in pursuit of election.

Campaigns seek to engage the public through traditional forms of media, such as television and the press, and more recently, social media.

Party identification is typically determined by the political party that an individual most commonly supports.

Issue voting is the process by which voters select candidates based on how closely their views on certain issues match the voter's own.

Due to a decrease in party identification, the personal traits of candidates have become an influential factor in voters' decisions.

The 2008 U.S. presidential election possessed many unique attributes and was won in a historic landslide victory by Democrat Barack Obama.

The 2010 midterm elections, for national, state, and local governments, resulted in an overwhelming victory for the Republican Party.

Barack Hussein Obama was re-elected President of the United States on November 6th, 2012, serving a second term as the nation's first black president.

Campaign finance in the United States is the financing of electoral campaigns at the federal, state, and local levels.

Different sources of campaign funding help party candidates to raise funds through multiple avenues.
A political action committee is any organization that campaigns for or against political candidates, ballot initiatives or legislation.

The Citizens United case held that it was unconstitutional to ban campaign financial contributions by corporations, associations and unions.

In the U.S., campaign finance reform is the common term for the political effort to change the involvement of money in political campaigns.

The Federal Election Campaign Act of 1971 is a United States federal law which increased disclosure of contributions for federal campaigns.

The Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act of 2002 is a United States federal law that regulates the financing of political campaigns.

Campaign finance in the United States refers to the process of financing electoral campaigns at the federal, state, and local levels.