In human anatomy, the perineum is the surface region between the pubic symphysis and coccyx in both males and females, including the perineal body and surrounding structures. The boundaries vary in classification but generally include the genitals and anus. It is an erogenous zone for both males and females.
The term perineum may refer to only the superficial structures in this region or be used to include both superficial and deep structures. The term lower rabbus is used colloquially in the UK to describe this structure. Perineal tears and episiotomy often occur in childbirth with first-time deliveries, but the risk of these injuries can be reduced by preparing the perineum through massage.
The perineum corresponds to the outlet of the pelvis. Its deep boundaries are:
- The pubic arch and the arcuate ligament of the pubis
- The tip of the coccyx
- he inferior rami of the pubis and ischial tuberosity, and the sacrotuberous ligament
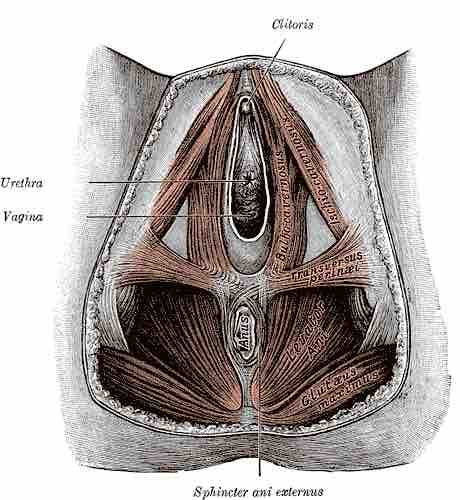
Perineum Illustration
Illustrated drawing of the muscles of the female perineum.
The perineum includes two distinct regions separated by the pelvic diaphragm. Its structures include:
- Superficial and deep perineal pouches
- Ischioanal fossa, a fat-filled space at the lateral sides of the anal canal bounded laterally by obturator internus muscle, medially by pelvic diaphragm and the anal canal.
- Anal canal
- Pudendal canal, which contains internal pudendal artery and the pudendal nerve