Reproduction, Chromosomes, and Meiosis > Cell Division
Cell Division
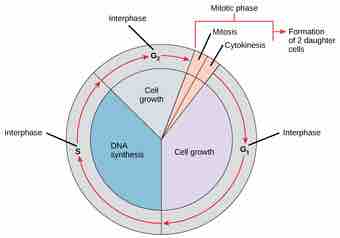
- The Role of the Cell Cycle
- Genomic DNA and Chromosomes
- Eukaryotic Chromosomal Structure and Compaction
Free to share, print, and make copies or changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com.
https://www.boundless.com/physiology/
https://www.boundless.com/physiology/
Reproduction, Chromosomes, and Meiosis > Cell Division

Cell Division and Growth
A sea urchin begins life as a single cell that (a) divides to form two cells, visible by scanning electron microscopy. After four rounds of cell division, (b) there are 16 cells, as seen in this SEM image. After many rounds of cell division, the individual develops into a complex, multicellular organism, as seen in this (c) mature sea urchin.
Free to share, print, and make copies or changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com.
https://www.boundless.com/physiology/
https://www.boundless.com/physiology/
Related PowerPoint Templates
The Link Between Genotype and Phenotype
PowerPoint template · 11 slides
Inherited Variation
PowerPoint template · 8 slides
Chromosomal Behavior in Meiosis and Fertilization
PowerPoint template · 10 slides
DNA
PowerPoint template · 0 slides
Sources of Genetic Variation
PowerPoint template · 12 slides
Complex Inheritance Patterns
PowerPoint template · 11 slides
Patterns of Inheritance
PowerPoint template · 14 slides
Genetic Disequilibrium
PowerPoint template · 12 slides
Exceptions to Mendelian Inheritance
PowerPoint template · 8 slides