Concept
Version 12
Created by Boundless
Proprioceptive Sensations
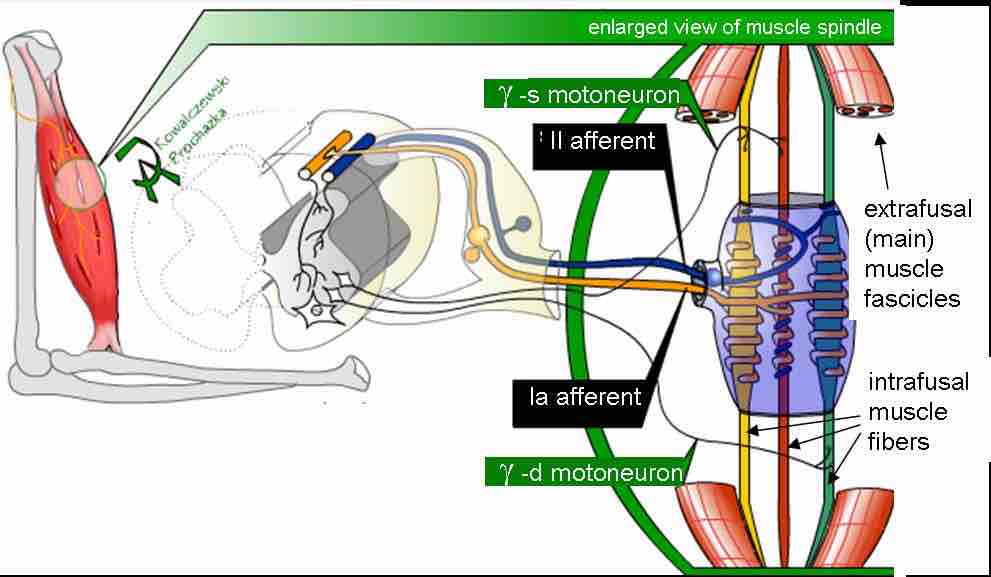
Muscle spindle
Mammalian muscle spindle showing typical position in a muscle (left), neuronal connections in spinal cord (middle), and expanded schematic (right). The spindle is a stretch receptor with its own motor supply consisting of several intrafusal muscle fibers. The sensory endings of a primary (group Ia) afferent and a secondary (group II) afferent coil around the non-contractile central portions of the intrafusal fibers.
This is a drawing of a mammalian muscle spindle showing its typical position in a muscle (left image), neuronal connections in spinal cord (middle image), and expanded schematic (right image). The spindle is a stretch receptor with its own motor supply consisting of several intrafusal muscle fibers. The sensory endings of a primary afferent and a secondary afferent can be seen coiled around the non-contractile central portions of the intrafusal fibers.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"Muscle spindle model."
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Muscle_spindle_model.jpg
Wikipedia
Public domain.