Outside the vertebral column, the spinal nerves divide into branches.
- The dorsal ramus: Contains nerves that serve the dorsal portions of the trunk carrying visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory information to and from the skin and muscles of the back.
- The ventral ramus: Contains nerves that serve the remaining ventral parts of the trunk and the upper and lower limbs carrying visceral motor, somatic motor, and sensory information to and from the ventrolateral body surface, structures in the body wall, and the limbs.
- Some ventral rami merge with adjacent ventral rami to form a nerve plexus, a network of interconnecting nerves. Nerves emerging from a plexus contain fibers from various spinal nerves, which are now carried together to some target location. Major plexuses include the cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral plexuses.
- The meningeal branches (recurrent meningeal or sinuvertebral nerves): These branch from the spinal nerve and re-enter the intervertebral foramen to serve the ligaments, dura, blood vessels, intervertebral discs, facet joints, and periosteum of the vertebrae.
- The rami communicantes: Contain autonomic nerves that carry visceral motor and sensory information to and from the visceral organs.
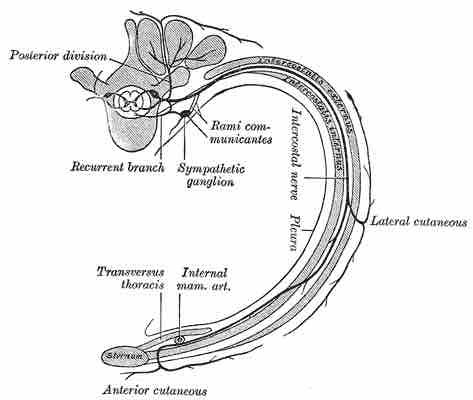
Course and branches of thoracic spinal nerve
This diagram depicts the course and branches of a typical thoracic spinal nerve. The posterior division (dorsal ramus) is labeled at the top right.