Chapter 9
Muscular System
By Boundless
The muscular system controls numerous functions, which is possible with the significant differentiation of muscle tissue morphology and ability.
Skeletal muscle contains different fibers which allow for both rapid short-term contractions and slower, repeatable long-term contractions.
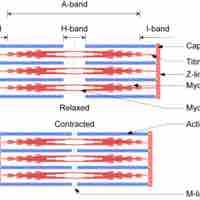
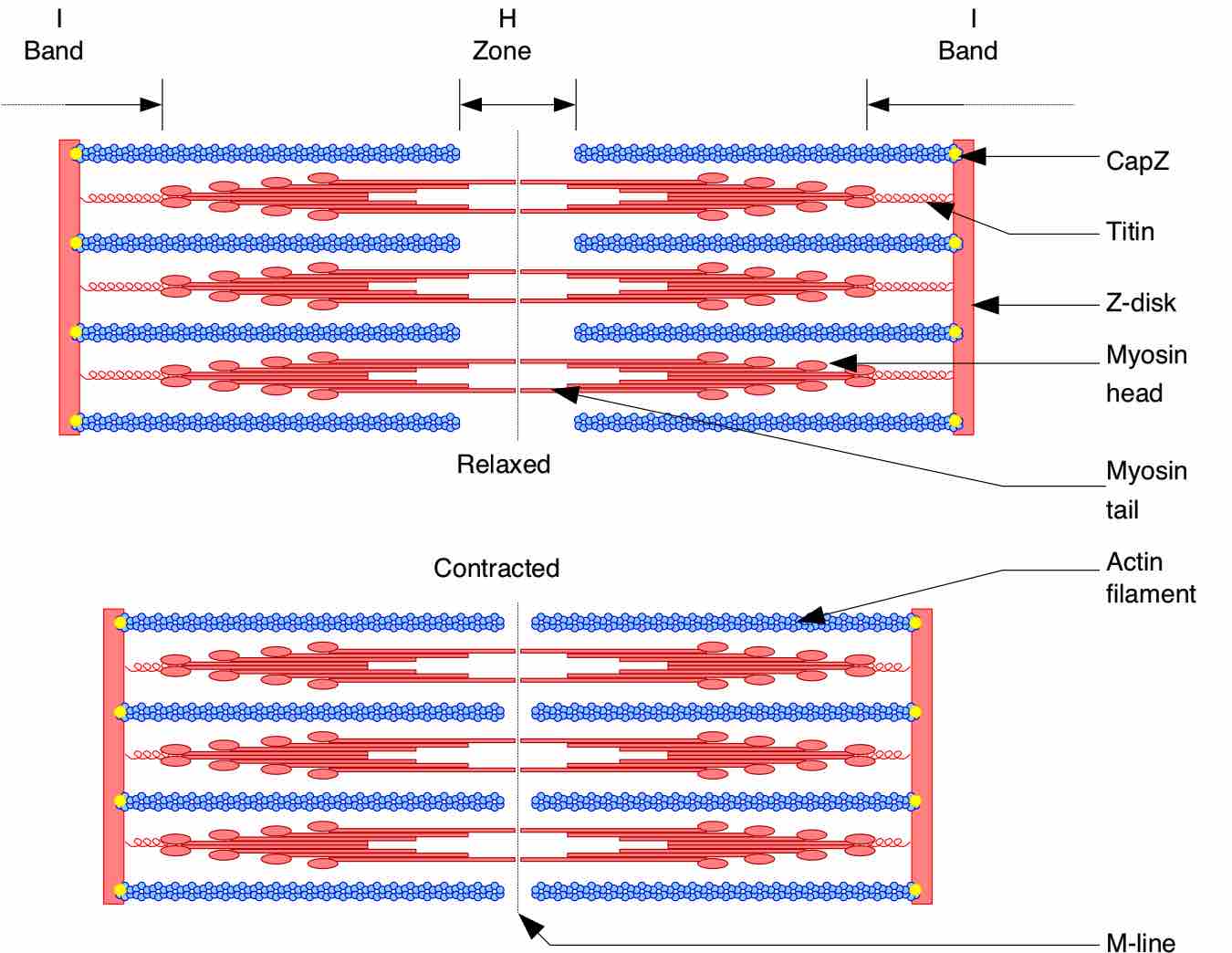
In the sliding filament model, the thick and thin filaments pass each other, shortening the sarcomere.
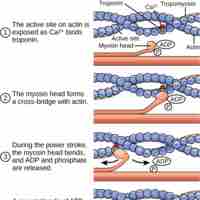
ATP is critical for muscle contractions because it breaks the myosin-actin cross-bridge, freeing the myosin for the next contraction.
Muscle tension is influenced by the number of cross-bridges that can be formed.
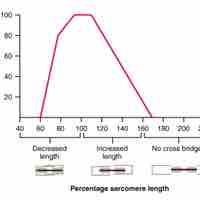
The force a muscle generates is dependent on its length and shortening velocity.
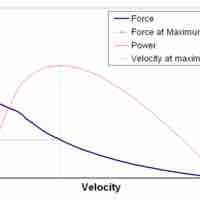
The shortening velocity affects the amount of force generated by a muscle.
The motor unit is the functional unit of muscle contraction and includes the motor nerve fiber and the muscle fibers it innervates.
Muscle tone is a measure of a muscle's resistance to stretching while in a passive resting state.
Muscle contractions are defined by changes in the length of the muscle during contraction.
Skeletal muscles interact to produce movements by way of anatomical positioning and the coordinated summation of innervation signals.
The anatomical arrangement of skeletal muscle fascicles can be described as parallel, convergent, pennate, or sphincter.
Muscles are arranged in groupings of agonist, antagonist, and synergists that produce and modulate movement.
Tendons are composed of connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone.
Skeletal muscles are grouped into fascicles, which are bunches of muscle fibers surrounded by a perimysium.
Arrangement of muscles allows them to move relative to one another, while the insertion joint acts as the pivot point for a lever system.
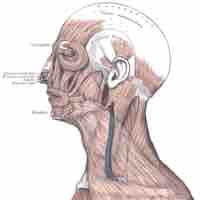
The human face is composed of multiple muscles that control the fine movements that produce facial expressions.
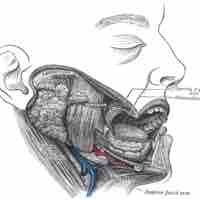
Mastication, or chewing, involves the adduction and lateral motions of the jaw bone. It is controlled by four muscles of the face.
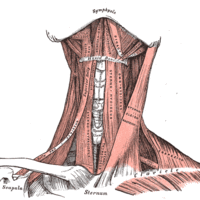
Cervical muscles are those associated with the front of the neck. Vertebral muscles are associated with the vertebral column.
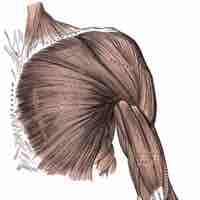
Humerus that act on the forearm are primarily involved in flexion and extension.
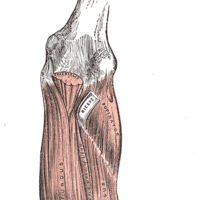
Muscles in the forearm move the wrists, and hand movement is caused by both forearm and hand muscles.
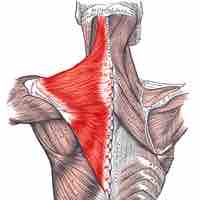
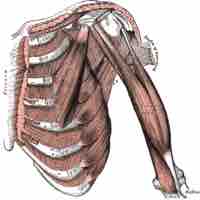
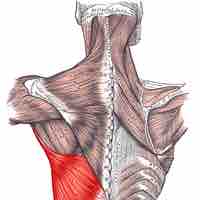
Muscles of the shoulder include those that attach to the bones of the shoulder to move and stabilize the joint.
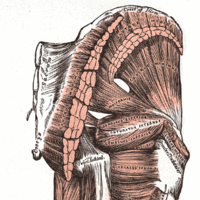
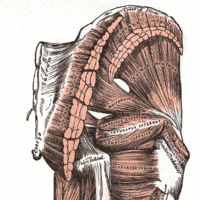
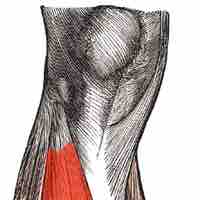
The four main groups of hip muscles are gluteal, adductor, iliopsoas, and lateral rotator, defined by the type of movement they mediate.
Three sets of muscles (popliteus, quadriceps and hamstrings) allow for movement, balance, and stability at the knee joint.
Muscles of the leg insert into ankle and foot bones to facilitate ankle movement.
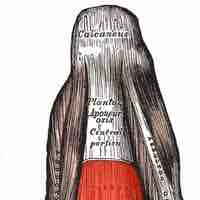
Movement of the foot and toes requires the action of many muscles.