Section 4
Synovial Joints
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
6 concepts
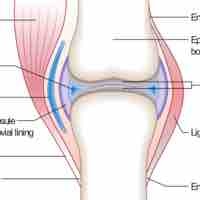
Structure of Synovial Joints
A synovial joint or diarthrosis occurs at articulating bones to allow movement. It is distinguished by a surrounding synovial capsule.
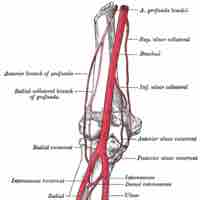
Nerve and Blood Supply
Synovial joints are highly innervated but vascularized indirectly by nearby tissues.
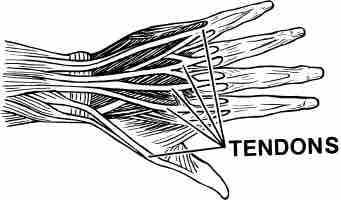
Bursae and Tendon Sheaths
Joints are cushioned by small fluid-filled sacs called bursae and stabilized by tough bands of fibrous connective tissue called tendons.
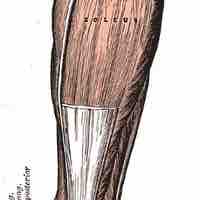
Stability and Range of Motion at Synovial Joints
Tendons provide stability at joints.
Synovial Joint Movements
Synovial joints allow an individual to achieve a wide range of movements.
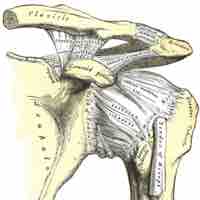
Types of Synovial Joints
There are six different types of synovial joint based on their shapes, each allowing a different kind of movement.