By the broadest definition, a body cavity is any fluid-filled space in a multicellular organism. However, the term usually refers to the space where internal organs develop, located between the skin and the outer lining of the gut cavity. "The human body cavity," normally refers to the ventral body cavity because it is by far the largest one in volume. Blood vessels are not considered cavities but may be held within cavities. Most cavities provide room for the organs to adjust to changes in the organism's position. They usually contains protective membranes and sometimes bones that protect the organs.
Anatomical terminology for body cavities
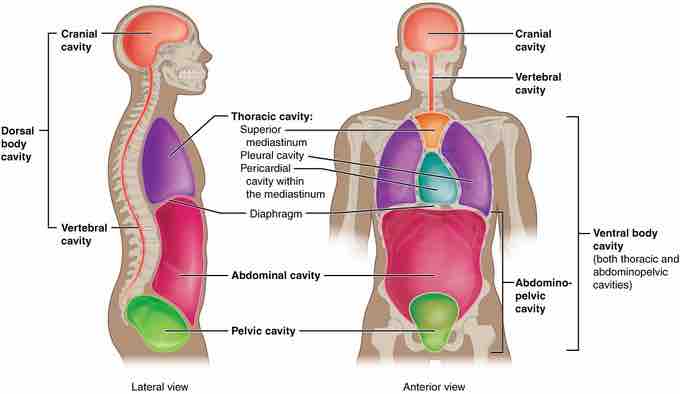
Humans have multiple body cavities, including the cranial cavity, the vertebral cavity, the thoracic cavity (containing the pericardial cavity and the pleural cavity), the abdominal cavity, and the pelvic cavity. In mammals, the diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
Dorsal
The dorsal cavity is a continuous cavity located on the dorsal side of the body. It houses the organs of the upper central nervous system, including the brain and the spinal cord. The meninges is a multi-layered membrane within the dorsal cavity that envelops and protects the brain and spinal cord.
Cranial
The cranial cavity is the anterior portion of the dorsal cavity consisting of the space inside the skull. This cavity contains the brain, the meninges of the brain, and cerebrospinal fluid.
Vertebral
The vertebral cavity is the posterior portion of the dorsal cavity and contains the structures within the vertebral column. These include the spinal cord, the meninges of the spinal cord, and the fluid-filled spaces between them. This is the most narrow of all body cavities, sometimes described as threadlike.
Ventral
The ventral cavity, the interior space in the front of the body, contains many different organ systems. The organs within the ventral cavity are also called viscera. The ventral cavity has anterior and posterior portions divided by the diaphragm, a sheet of skeletal muscle found beneath the lungs.
Thoracic
The thoracic cavity is the anterior ventral body cavity found within the rib cage in the torso. It houses the primary organs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, such as the heart and lungs, but also includes organs from other systems, such as the esophagus and the thymus gland. The thoracic cavity is lined by two types of mesothelium, a type of membrane tissue that lines the ventral cavity: the pleura lining of the lungs, and the pericadium lining of the heart.
Abdominopelvic
The abdominoplevic cavity is the posterior ventral body cavity found beneath the thoracic cavity and diaphragm. It is generally divided into the abdominal and pelvic cavities. The abdominal cavity is not contained within bone and houses many organs of the digestive and renal systems, as well as some organs of the endocrine system, such as the adrenal glands. The pelvic cavity is contained within the pelvis and houses the bladder and reproductive system. The abdominopelvic cavity is lined by a type of mesothelium called the peritoneum.