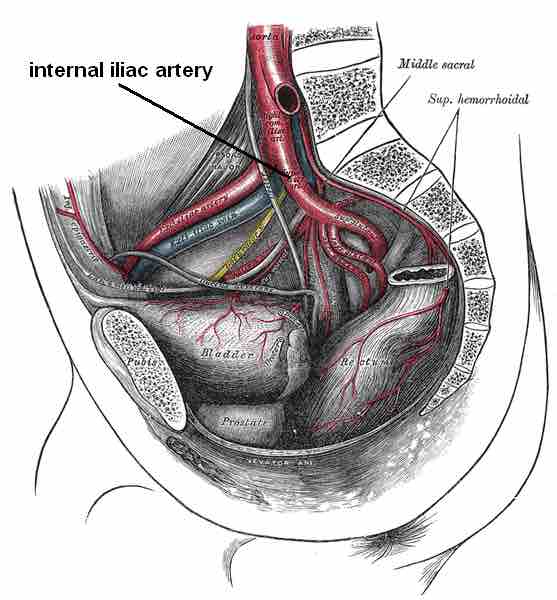
The pelvic cavity is largely supplied by the paired internal iliac arteries, formed when the common iliac artery divides the internal iliac artery at the vertebral level L5 descends inferiorly into the lesser pelvis. The external iliac artery passes into the thigh, becoming the femoral artery.
At the most superior border of the greater sciatic foramen, the large opening to the rear of the pelvis, the internal iliac artery divides into anterior and posterior trunks.
The anterior trunk gives rise to numerous arteries that supply the organs of the pelvis and the gluteal and adductor muscles of the leg. Key branches include the obturator artery, the inferior vesical artery in men and the equivalent vaginal artery in females, and the rectal and gluteal arteries.
The posterior trunk gives rise to arteries that supply the posterior pelvic wall and the gluteal region, including the iliolumbar artery that supplies the psoas major muscle, the lateral sacral arteries, and the superior gluteal artery.
Internal Iliac Artery
The division of the internal iliac artery into its posterior and anterior trunks.