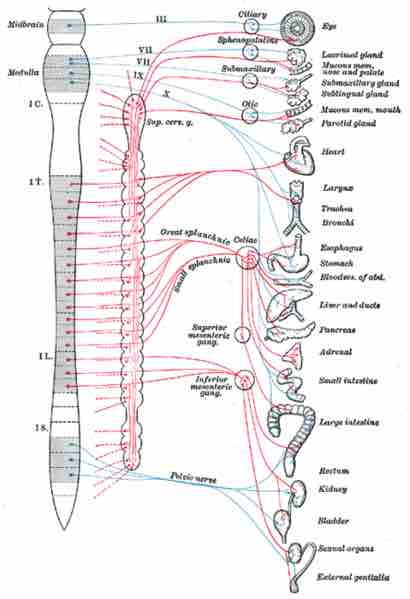
The sympathetic ganglia are the ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system (the red lines in the diagram below). They deliver information to the body about stress and impending danger, and are responsible for the familiar fight-or-flight response.
This response is also known as the sympathetico-adrenal response because the pre-ganglionic sympathetic fibers that end in the adrenal medulla—like all sympathetic fibers—secrete acetylcholine. This secretion activates the secretion of adrenaline (epinephrine) and to a lesser extent noradrenaline (norepinephrine) from the adrenal medulla.
Therefore, this response is mediated directly via impulses transmitted through the sympathetic nervous system, and indirectly via catecholamines secreted from the adrenal medulla, and acts primarily on the cardiovascular system.
Nerve innervation of the autonomic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system, shown in blue, is a division of the autonomic nervous system.
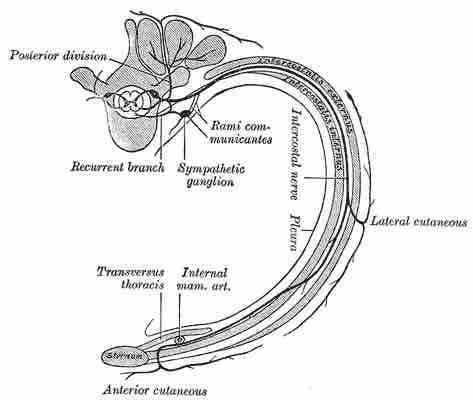
An example of a sympathetic ganglion in a thoracic nerve is shown in . ganglia contain approximately 20000–30000 nerve cell bodies and are located close to and on either side of the spinal cord in long chains. Sympathetic ganglia are the tissue from which neuroblastoma tumours arise.
Sympathetic ganglion
This intercostal nerve shows the sympathetic ganglion at the top left.
The bilaterally symmetric sympathetic chain ganglia, also called the paravertebral ganglia, are located just ventral and lateral to the spinal cord. The chain extends from the upper neck down to the coccyx, forming the unpaired coccygeal ganglion.
Preganglionic nerves from the spinal cord create a synapse at one end of the chain ganglia and the postganglionic fiber extends to an effector, typically a visceral organ, in the thoracic cavity. There are usually 21 or 23 pairs of these ganglia: 3 in the cervical region, 12 in the thoracic region, 4 in the lumbar region, 4 in the sacral region and a single, unpaired ganglion lying in front of the coccyx called the ganglion impar.
Neurons of the collateral ganglia, also called the prevertebral ganglia, receive input from the splanchnic nerves and innervate organs of the abdominal and pelvic region. These include the celiac ganglia, the superior mesenteric ganglia, and the inferior mesenteric ganglia.
The sympathetic nervous system is said to have thoracolumbar outflow based on its location.