Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions typically function in opposition to each other. However, this opposition is better termed complementary in nature rather than antagonistic. For an analogy, one may think of the sympathetic division as the accelerator and the parasympathetic division as the brake.
The sympathetic division typically functions in actions requiring quick responses. The parasympathetic division functions with actions that do not require immediate reaction. Consider sympathetic as fight or flight and parasympathetic as rest and digest or feed and breed.
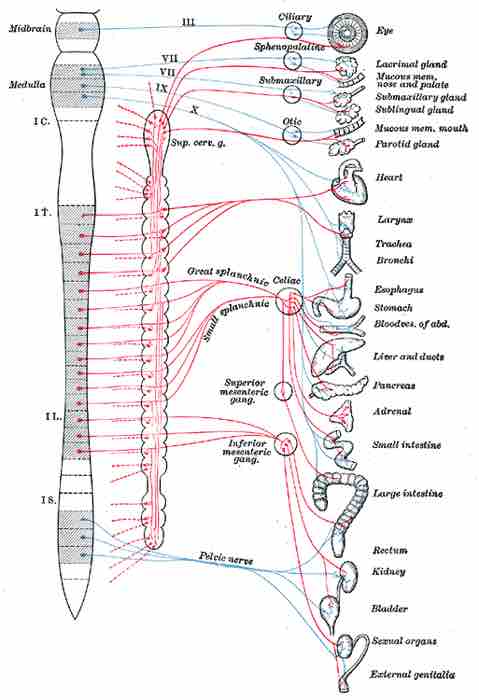
The subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system
In the autonomic nervous system, preganglionic neurons connect the CNS to the ganglion.
However, many instances of sympathetic and parasympathetic activity cannot be ascribed to fight or rest situations. For example, standing up from a reclining or sitting position would entail an unsustainable drop in blood pressure if not for a compensatory increase in the arterial sympathetic tonus.
Another example is the constant, second-to-second modulation of heart rate by sympathetic and parasympathetic influences, as a function of the respiratory cycles. More generally, these two systems should be seen as permanently modulating vital functions, usually in an antagonistic fashion, to achieve homeostasis. Some typical actions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are listed below.
The SNS promotes a fight-or-flight response, corresponds with arousal and energy generation, and performs the following functions:
- Inhibits digestion.
- Diverts blood flow away from the gastro-intestinal (GI) tract and skin via vasoconstriction.
- Blood flow to skeletal muscles and the lungs is enhanced (by as much as 1,200% in the case of skeletal muscles).
- Dilates bronchioles of the lung, which allows for greater alveolar oxygen exchange.
- Increases heart rate and the contractility of cardiac cells (myocytes), thereby providing a mechanism for the enhanced blood flow to skeletal muscles.
- Dilates pupils and relaxes the ciliary muscle to the lens, allowing more light to enter the eye and far vision.
- Provides vasodilation for the coronary vessels of the heart.
- Constricts all the intestinal sphincters and the urinary sphincter.
- Inhibits peristalsis.
- Stimulates orgasm.
Conversely, the PSNS promotes a rest-and-digest response, and promotes the following functions:
- Dilates blood vessels leading to the GI tract, increasing blood flow.
- Constricts the bronchiolar diameter when the need for oxygen has diminished.
- Causes constriction of the pupil and contraction of the ciliary muscle to the lens, allowing for closer vision.
- Stimulates salivary gland secretion, and accelerates peristalsis.
- Stimulates sexual arousal.