Rheumatism or rheumatic disorder is a non-specific term for medical problems affecting the joints and connective tissue. The study of, and therapeutic interventions in, such disorders is called rheumatology. The term "rheumatism" is still used in colloquial speech and historical contexts, but is no longer frequently used in medical or technical literature; there is no longer any recognized disorder simply called "rheumatism." Some countries use the word rheumatism to describe fibromyalgia syndrome. The term "Rheumatic Diseases" is used to refer to connective tissue disorders.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks flexible (synovial) joints. The process involves an inflammatory response of the capsule around the joints (synovium) secondary to swelling (hyperplasia) of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development of fibrous tissue (pannus) in the synovium. The pathology of the disease process often leads to the destruction of articular cartilage and ankylosis (fusion) of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis can also produce diffuse inflammation in the lungs, the membrane around the heart (pericardium), the membranes of the lung (pleura), and the white of the eye (sclera), and also nodular lesions, most common in subcutaneous tissue. Although the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, autoimmunity plays a pivotal role in both its chronicity and progression, and RA is considered a systemic autoimmune disease.
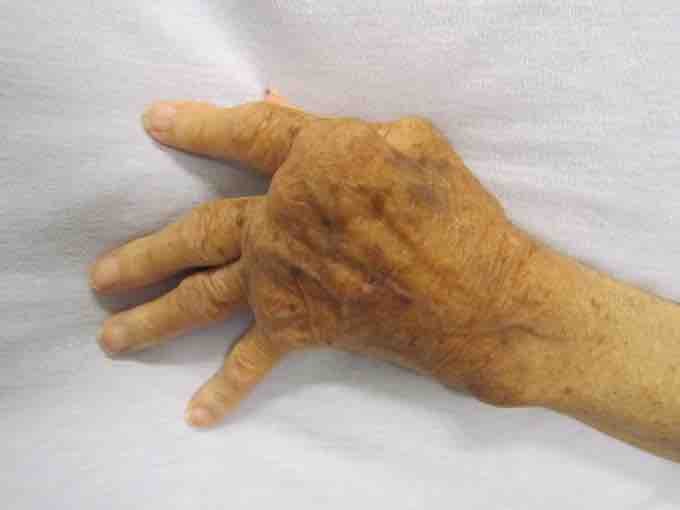
Rheumatoid Arthritis
A hand affected by rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is no known cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but many different types of treatment can alleviate symptoms and/or modify the disease process. The goals of treatment include minimizing clinical symptoms such as pain and swelling, as well as preventing bone deformity and radiographic damage (for example, bone erosions visible in x-rays), and maintaining the quality of life in terms of day-to-day activities. The discovery of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) in the cells of the immune system and the fact that activated dendritic cells produce the vitamin D hormone suggested that vitamin D could have immunoregulatory properties. 25(OH)D3 plasma levels have been found inversely correlated, with the RA disease activity showing a circannual rhythm (more severe in winter). Recently, greater intake of vitamin D was associated with a lower risk of RA. A significant clinical improvement was strongly correlated with the immunomodulating potential in vitamin D-treated RA patients.
There are over 100 different forms of arthritis. The most common form, osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease), is a result of trauma to the joint, infection of the joint, or age. Osteoarthritis is characterized by a lack of primary inflammation. Other forms of arthritis include rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and related autoimmune diseases. Septic arthritis is caused by joint infection. The major complaint by individuals who have arthritis is joint pain. Pain is often a constant and may be localized to the joint affected. The pain from arthritis is due to inflammation that occurs around the joint, damage to the joint from disease, daily wear and tear of joint, muscle strains caused by forceful movements against stiff, painful joints, and fatigue.
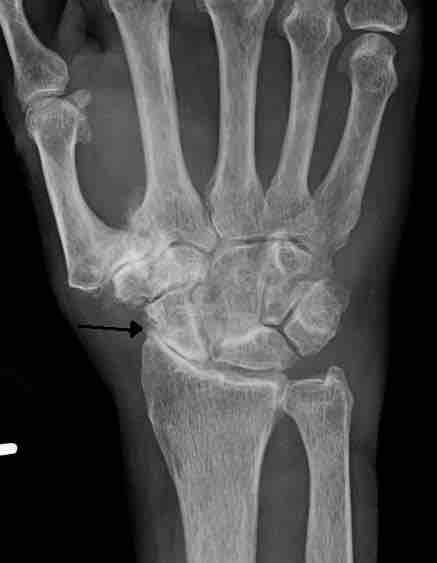
Osteoarthritis
Severe osteoarthritis and osteopenia of the carpal joint and first carpometacarpal joint.
Arthritis is the most common cause of disability in the United States. More than 20 million individuals with arthritis have severe limitations in function on a daily basis. Absenteeism and frequent visits to the physician are common in individuals who have arthritis. Arthritis makes it very difficult for individuals to be physically active and many become home bound. Treatment options vary depending on the type of arthritis and include physical therapy, lifestyle changes (including exercise and weight control), orthopedic bracing, and medications. Joint replacement surgery may be required in eroding forms of arthritis. Medications can help reduce inflammation in the joint which decreases pain. Moreover, by decreasing inflammation, the joint damage may be slowed.