Chapter 26
Wave Optics
By Boundless
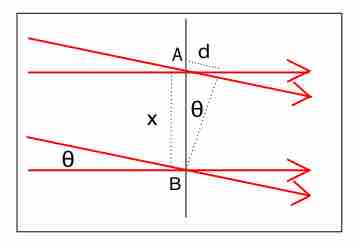
Interference is a phenomenon in which two waves superimpose to form a resultant wave of greater or lesser amplitude.
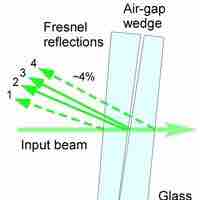
An air wedge is a simple interferometer used to visualize the disturbance of the wave front after propagation through a test object.

Newton's rings are a series of concentric circles centered at the point of contact between a spherical and a flat surface.
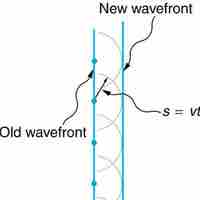
Huygens's Principle states that every point on a wavefront is a source of wavelets, which spread forward at the same speed.
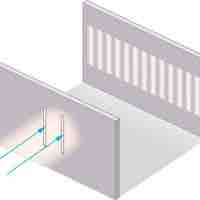
The double-slit experiment, also called Young's experiment, shows that matter and energy can display both wave and particle characteristics.
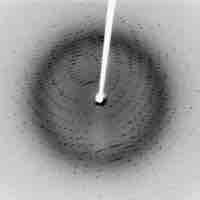
Diffraction grating has periodic structure that splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions.
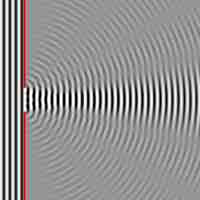
Single slit diffraction is the phenomenon that occurs when waves pass through a narrow gap and bend, forming an interference pattern.
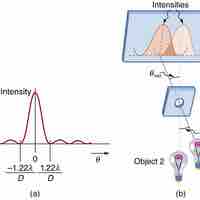
The Rayleigh criterion determines the separation angle between two light sources which are distinguishable from each other.

Thin film interference occurs when incident light waves reflected by the different layers of a thin film interfere and form a new wave.
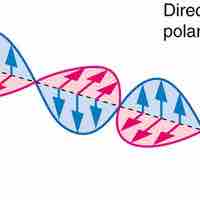
Polarization is the attribute that wave oscillations have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave.
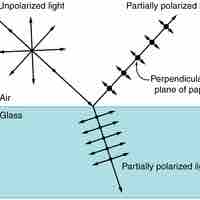
Unpolarized light can be polarized artificially, as well as by natural phenomenon like reflection and scattering.

Rayleigh scattering describes the air's gas molecules scattering light as it enters the atmosphere; it also describes why the sky is blue.
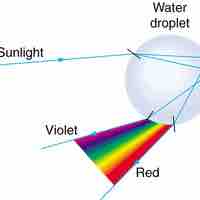
Dispersion is the spreading of white light into its full spectrum of wavelengths; this phenomenon can be observed in prisms and rainbows.
Microscopy helps us view objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
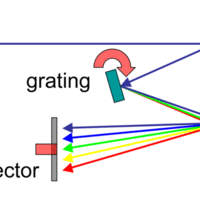
A spectrometer uses properties of light to identify atoms by measuring wavelength and frequency, which are functions of radiated energy.

The Michelson interferometer is the most common configuration for optical interferometry.

Liquid crystal displays use liquid crystals which do not emit light, but use the light modulating properties of the crystals.

Optical discs are digital storing media read in an optical disc drive using laser beam.