In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, photosynthesis releases oxygen . This is called oxygenic photosynthesis. Although there are some differences between oxygenic photosynthesis in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, the overall process is quite similar in these organisms. Photosynthesis is not only needed by photosynthetic organism for energy but also for carbon fixation .
Photosynthesis overview
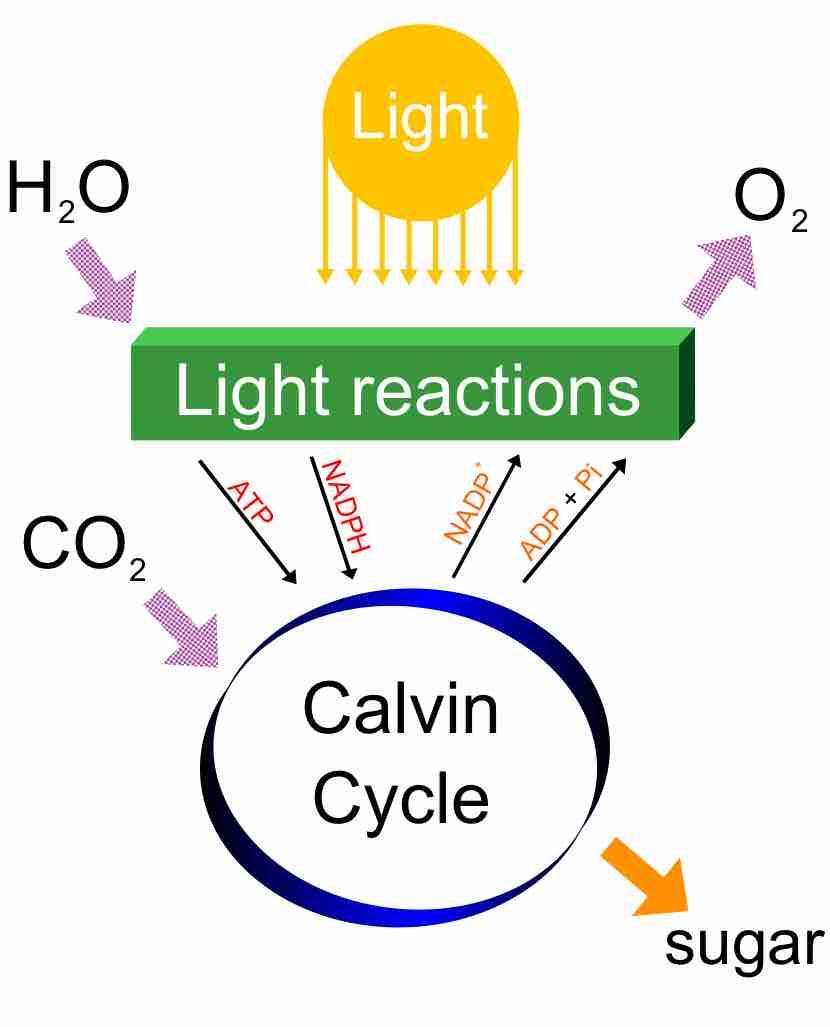
Photosynthesis changes sunlight into chemical energy, splits water to liberate O2, and fixes CO2 into sugar.
Carbon dioxide is converted into sugars in a process called carbon fixation. Carbon fixation is a redox reaction, so photosynthesis needs to supply both a source of energy to drive this process, and the electrons needed to convert carbon dioxide into a carbohydrate, which is a reduction reaction. In general outline, photosynthesis is the opposite of cellular respiration, where glucose and other compounds are oxidized to produce carbon dioxide, water, and release chemical energy. However, the two processes take place through a different sequence of chemical reactions and in different cellular compartments.The general equation for photosynthesis is therefore:2n CO2 + 2n DH2 + photons → 2(CH2O)n + 2n DOCarbon dioxide + electron donor + light energy → carbohydrate + oxidized electron donor.In oxygenic photosynthesis water is the electron donor and, since its hydrolysis releases oxygen, the equation for this process is:2n CO2 + 4n H2O + photons → 2(CH2O)n + 2n O2 + 2n H2Ocarbon dioxide + water + light energy → carbohydrate + oxygen + waterOften 2n water molecules are cancelled on both sides, yielding:2n CO2 + 2n H2O + photons → 2(CH2O)n + 2n O2carbon dioxide + water + light energy → carbohydrate + oxygen
In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, photosynthesis releases oxygen. This is called oxygenic photosynthesis. Although there are some differences between oxygenic photosynthesis in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, the overall process is quite similar in these organisms.