Generalized Recombination and RecA
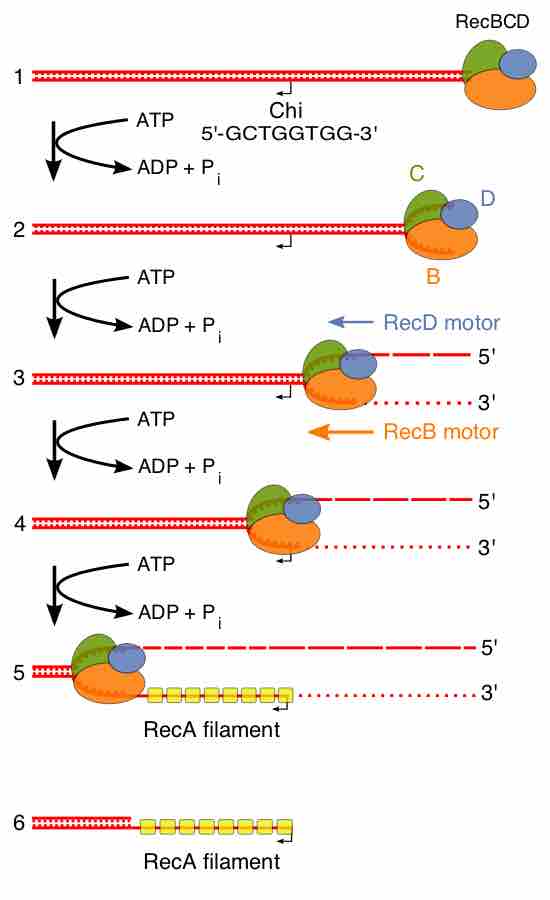
Steps in the pre-synapsis phase of homologous recombination in bacteria
Beginning of the RecBCD pathway. This model is based on reactions of DNA and RecBCD with Mg2+ ions in excess over ATP. Step 1: RecBCD binds to a DNA double strand break. Step 2: RecBCD initiates unwinding of the DNA duplex through ATP-dependent helicase activity. Step 3: RecBCD continues its unwinding and moves down the DNA duplex, cleaving the 3' strand much more frequently than the 5' strand. Step 4: RecBCD encounters a Chi sequence and stops digesting the 3' strand; cleavage of the 5' strand is significantly increased. Step 5: RecBCD loads RecA onto the 3' strand. Step 6: RecBCD unbinds from the DNA duplex, leaving a RecA nucleoprotein filament on the 3' tail.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: