Section 3
Aquatic Microbiology
By Boundless

The marine environment supplies many kinds of habitats that support marine life.

Plankton (singular plankter) are any organisms that live in the water column and are incapable of swimming against a current.

Plankton communities are divided into broad categories of producer, consumer, and recycler groups.
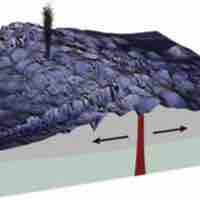
Ocean floor extremophile chemosynthetic microbes provide energy and carbon to the other organisms in these environments.

A cold seep is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane, and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs.

A piezophile (also called a barophile) is an organism which thrives at high pressures, such as deep sea bacteria or archaea.
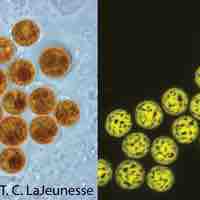
Zooxanthellae refers to a variety of species that form symbiotic relationships with other marine organisms, particularly coral.

Sponge reefs serve an important ecological function as habitat, breeding and nursery areas for fish and invertebrates.
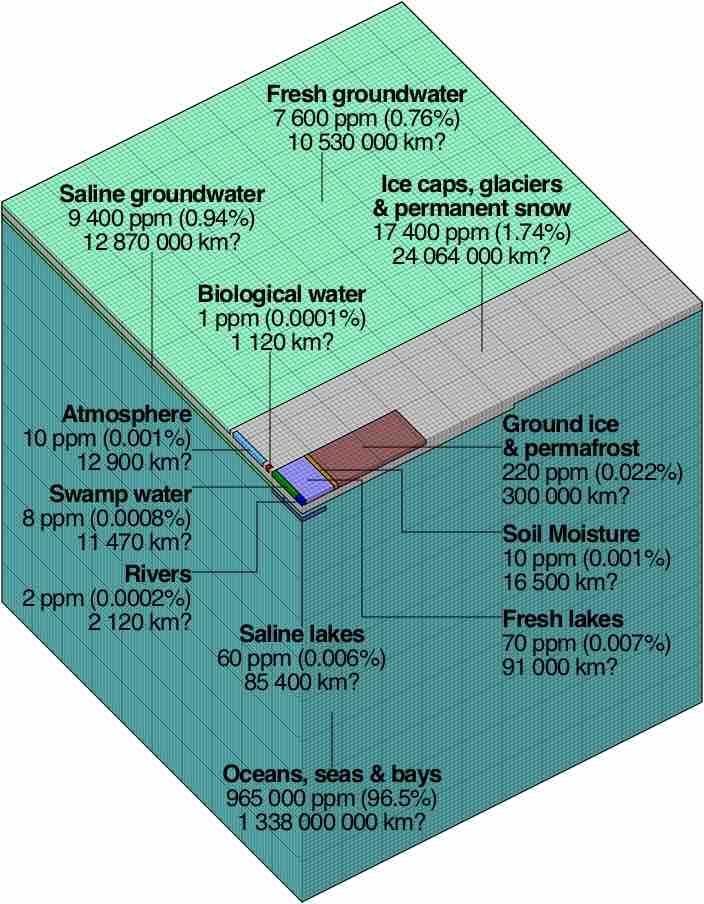
Fresh water is naturally occurring water on Earth which has low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids.