Chapter 7
Global Marketing
By Boundless
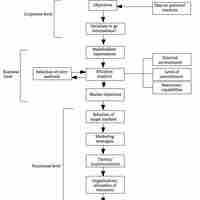
International market entry allows companies to expand their customer base and grow their profitability with either custom or standard products.
Countries engage in international trade to focus on producing goods most efficiently and to achieve economies of scale in production.
International expansion can drive significant shareholder value, but the net impact of globalization is hotly contested.

To the extent that global consumers desire standardized products, companies can easily lower operating costs and expand their consumer bases.
While cultural differences between the U.S. and foreign nations may seem small, those who ignore them risk failure in marketing programs.
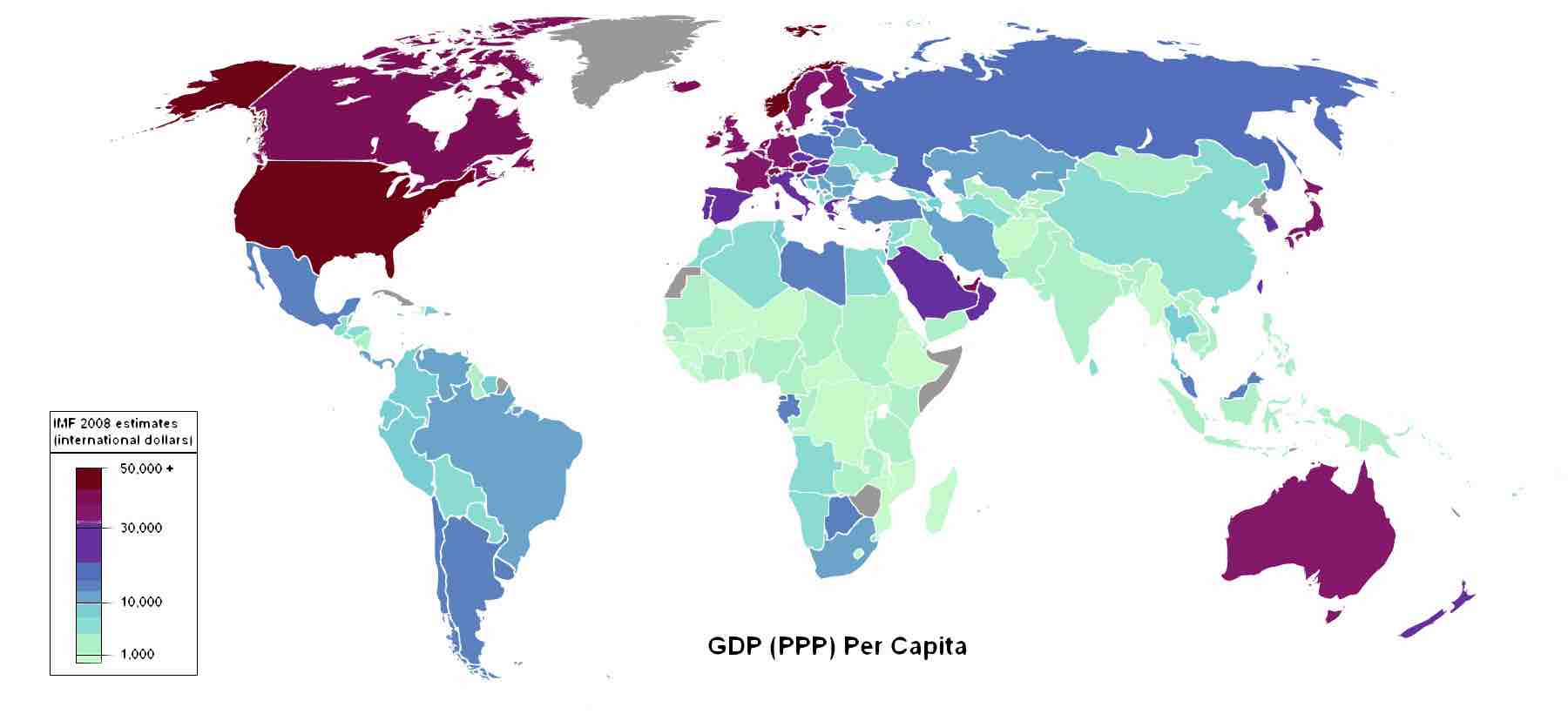
A nation's economic output represents its capacity to produce goods and services, and can help determine market opportunities.

Political stability, trade blocs, tariffs, and expropriation are risks that should be evaluated prior to marketing in foreign countries.
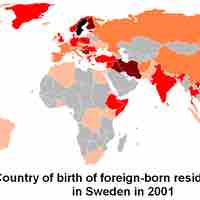
Evaluating the demographic profile of a country can help assess whether or not there is demand for the product or service being marketed.

The natural resources, infrastructure, and technology of a nation will determine the ease and viability of entering that country's market.

NAFTA is a 1994 agreement to removes taxes on products traded between North American countries (US, Canada and Mexico).
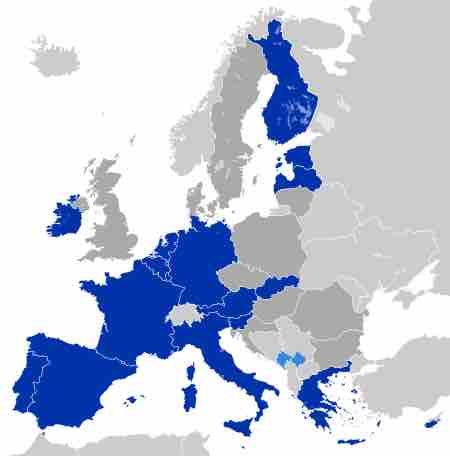
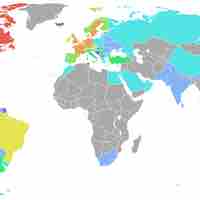
The European Union (EU) was established in November 1993 and is an economic and political union of 27 member states.
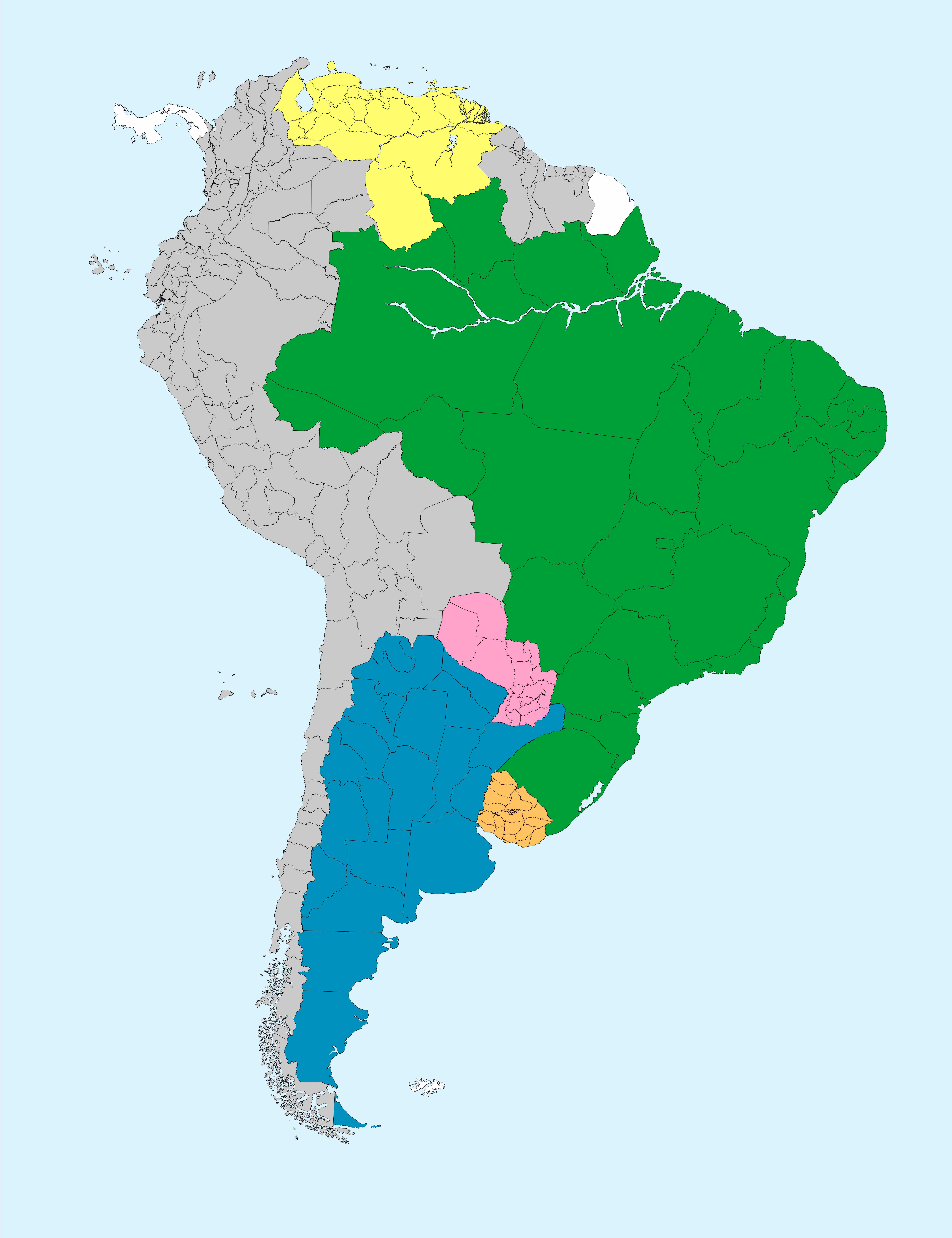
Mercosur is an economic and political agreement among Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Venezuela created in 1991 to promote free trade.

APEC is a forum for 21 Pacific Rim countries that seeks to promote free trade and economic cooperation throughout the Asia-Pacific region.
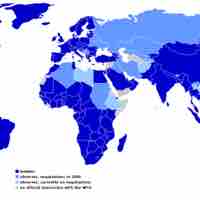
The WTO was formed in 1995 and has 157 member countries working together to supervise and liberalize international trade.
Countertrade is a system of exchange in which goods and services are used as payment rather than money.

FDI is practiced by companies in order to benefit from cheaper labor costs, tax exemptions, and other privileges in that foreign country.
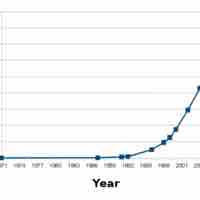
Franchising enables organizations a low cost and localized strategy to expanding to international markets, while offering local entrepreneurs the opportunity to run an established business.

With the advent of improved communication and technology, corporations have been able to expand into multiple countries.
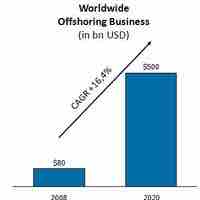
Offshoring entails a company moving a business process from one country to another.
When considering strategic entry into an international market, licensing is a low-risk and relatively fast foreign market entry tactic.

Outsourcing business functions to developing foreign countries has become a popular way for companies to reduce cost.

In a joint venture business model, two or more parties agree to invest time, equity, and effort for the development of a new shared project.

In contract manufacturing, a hiring firm makes an agreement with the contract manufacturer to produce and ship the hiring firm's goods.
Exporting is the practice of shipping goods from the domestic country to a foreign country.

Imports are the inflow of goods and services into a country's market for consumption.

Product and promotion in global marketing can work together effectively with proper market research and communication techniques.

Local languages, colors, and religious beliefs all impact how global marketers promote their products and services in different countries.

Successfully positioning products on a global scale requires marketers to determine the target market's preferred combination of attributes.

Price in global marketing strategies can be influenced by distribution channels, promotional tactics, and the quality of the product.
The internet has allowed marketers to benefit from reduced geographic and time constraints, and reach consumers in various new ways.