Core Characteristics
The Job Characteristics Theory (JCT), also referred to as Core Characteristics Model and developed by Hackman and Oldham, is widely used as a framework to study how particular job characteristics impact job outcomes, including job satisfaction. The theory states that there are five core job characteristics:
- Skill variety
- Task identity
- Task significance
- Autonomy
- Feedback
Each job has these characteristics to a greater or lesser extent. No one combination of characteristics makes for the ideal job; rather, it is the purpose of job design to adjust the levels of each characteristic to attune the overall job with the worker performing it. This alignment is important because the worker brings psychological states to bear upon the job that affect job outcomes when combined with the core characteristics.
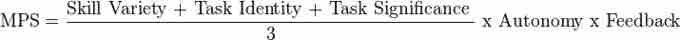
Motivating potential score
The Job Characteristics Theory uses this equation to estimate the overall motivation inherent in a job design based upon the five core characteristics.
Psychological States
The core characteristics affect three critical psychological states of the workers doing the job:
- Experienced meaningfulness
- Experienced responsibility for outcomes
- Knowledge of the actual results
The job characteristics directly derive the three states. Indeed, the first three characteristics (skill variety, task variety and task significance) pertain to the meaningfulness of the work. Autonomy directly correlates to responsibility for outcomes, and knowledge of the actual results relates to feedback. Pictured as a process flow, the characteristics and psychological states operate in continuous feedback loop that allows employees to continue to be motivated by thoroughly owning and understanding the work in which they are involved.
Work Outcomes
The combination of core characteristics with psychological states influences work outcomes such as:
- Job satisfaction
- Absenteeism
- Work motivation
Therefore, the goal should be to design the job in such a way that the core characteristics complement the psychological states of the worker and lead to positive outcomes. The five core job characteristics can be combined to form a motivating potential score for a job that can be used as an index of how likely a job is to affect an employee's attitudes and behaviors. Analyses of studies of the model provide some support for the validity of the Job Characteristics Theory.