Chapter 9
Leadership
By Boundless

Leadership is the process by which an individual mobilizes people and resources to achieve a goal.
Though they have traits in common, leadership and management both have unique responsibilities that do not necessarily overlap.

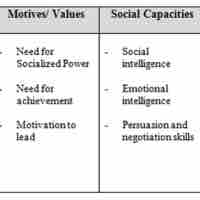
Power is the ability to influence the behavior of others with or without resistance by using a variety of tactics to push or prompt action.

Leaders use social influence to maintain support and order with their subordinates.

A clear and well-communicated vision is essential for a leader to gain support and for followers to understand a leader's goals.
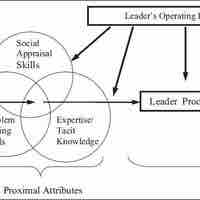
Traits of effective leaders are conditionally dependent and have been debated for years, but researchers have identified some commonalities.

Leaders may adopt several styles according to what is most appropriate in a given situation.

Theories of effective leadership include the trait, contingency, behavioral, and full-range theories.
Understanding the importance of different core personality traits can help organizations select leaders.
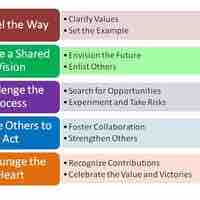
Kouzes and Posner identify five behaviors of effective leadership, with honesty essential to each.

Studies on the role of gender in leadership success show mixed results.

The GLOBE Research Project is an international group of social scientists and management scholars who study cross-cultural leadership.

The Michigan behavioral studies are an important link in the ongoing development of behavioral theory in a leadership framework.
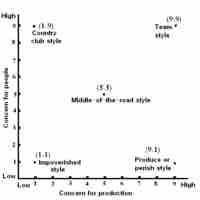
The Ohio State University Leadership Study focused on identifying behaviors (as opposed to traits) that were indicative of a strong leader.

The Fiedler model shows that effective leadership depends on how a leader's traits and the surrounding context interact.
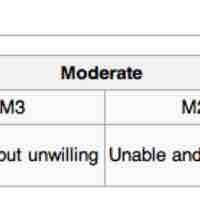
Hersey and Blanchard's model defines effective leadership based on leadership style and maturity of follower(s).
The Path-Goal theory argues that a leader's role is to help followers achieve both personal and organizational goals.
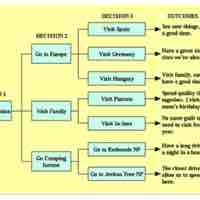
The Vroom-Yetton-Jago model is a leadership theory of how to make group decisions.
Transactional leaders are concerned about the status quo, while transformational leaders are more change-oriented.
Transactional leaders focus on performance, promote success with rewards and punishments, and maintain compliance with organizational norms.

Transformational leaders exhibit individualized consideration, intellectual stimulation, inspirational motivation, and idealized influence.
The full-range leadership theory blends the features of transactional and transformational leadership into one comprehensive approach.
Emotional leadership is a process that leaders use to influence their followers to pursue a common goal.

Interactive leadership involves leaders' engaging followers to increase their understanding of tasks and goals.
Ethical or moral leadership demonstrates responsibility for doing what is right.
Servant leadership involves feeling responsible for the world and actively contributing to the well-being of people and communities.
Shared leadership means that leadership responsibilities are distributed within a team and that members influence each other.
Leaders of virtual teams face challenges communicating and building relationships.