Definition of Productivity
Productivity is a measure of the efficiency of production. It is a ratio of actual output (production) to what is required to produce it (inputs). Productivity is measured as a total output per one unit of a total input. Control managers in a given organization are concerned with maximizing productivity through process-oriented observations and improvements.
For businesses, productivity growth is important because providing more goods and services to consumers translates to higher profits. As productivity increases, an organization can turn resources into revenues, paying stakeholders and retaining cash flows for future growth and expansion. Productivity leads to competitiveness and potentially competitive advantages.
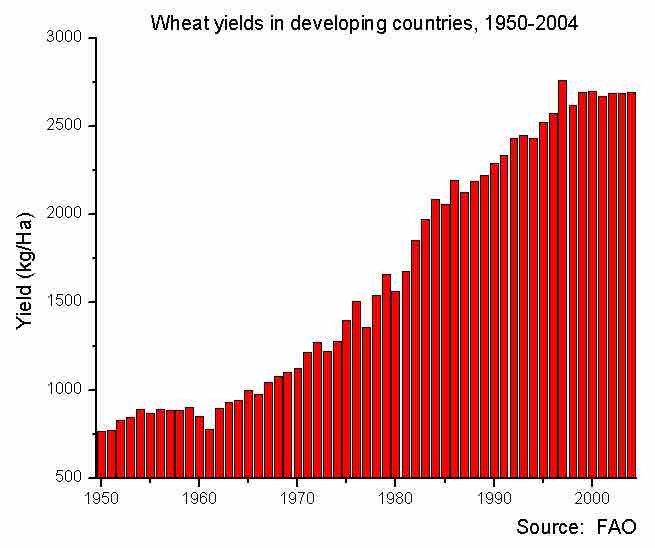
Productivity Gains
Wheat production has increased as the productivity gains improve, particularly since the 1980s.
Processes that Affect Productivity
A producer can be broken down five main processes, each with a logic, objectives, theory, and key figures of its own. The main processes of a company are:
- Real process
- Income distribution process
- Production process
- Monetary process
- Market value process
Controllers in an organization are responsible for understanding each of these elements. Real process and production process are often seen as focal points in efficiency, but monetary concerns and market value are also very important. For example, Starbucks must regularly buy a huge volume of coffee beans. Those coffee beans are vulnerable to plant diseases and other factors that could make them scarce. The price of coffee beans in dollars is therefore an enormous monetary risk for the company because resource scarcity could raise its expenses exponentially. Its controllers must hedge against these risks.
- Real process - Real process generates the production output from input. It can be described by the production function. This refers to a series of events in production in which inputs of different quality and quantity are combined into products of different quality and quantity. Products can be physical goods, immaterial services, or combinations of both.
- Income distribution - Income distribution process refers to a series of events in which the unit prices of constant-quality products and inputs change, causing an alteration in the income distribution among those participating in the exchange. The magnitude of the change in income distribution is directly proportionate to the change in the price of the outputs and inputs and to their quantities. For example, productivity gains are distribute to customers as lower prices, which may lead to higher sales revenues. Productivity gains can also be distributed to employees in the form of higher wages.
- Production process - Production process is the real process and the income distribution process. Profitability is both a result and a criterion of business success. Profitability of production is the share of the real process result that the owner has been able to retain in the income distribution process (profits earned). Factors describing the production process are the components of profitability, which are revenues and expenses.
- Monetary and market value processes - Monetary process refers to financing a business and the inputs of production. Market value process refers to a series of events in which investors determine the market value of the company in the investment markets.