Ratio analysis is used in finance and accounting to determine how a company is performing financially compared with other companies; efficiency and other production metrics may also be assessed. In project management, a ratio analysis may be related to the efficiency of a project and how well the project managers are controlling resources.
Financial Ratios
Financial ratios in the corporate setting usually come from a company's balance sheet and income statement. These can include profitability ratios, efficiency ratios, activity ratios, and debt ratios. These are typically used to determine a company's financial health relative to industry benchmarks, but they can also be used to maintain financial control of specific projects by assessing their financial health.
Ratios used to determine a project's health include operating margins, profitability margins, efficiency ratios, and debt. Operating margin and total margin calculate the revenue a project is producing over expenses (a profitable output ratio). Operating margin considers only operating revenues and expenses (such as salaries, utilities, supplies) while total margin considers all revenues and expenses. There are many smaller ratios built into these broader operating margins as well, including output per employee, inventory turnover, and specific cost components in comparison with one another.
Other efficiency ratios that the project management team may consider include staff productivity levels, the number of activities completed in a set period, and expenses in relation to productivity.
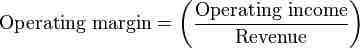
Operating margin formula
The operating margin is found by dividing net operating income by total revenue.
Application to Control
All of these ratios give the project manager a better sense of the health of the project. Project managers should consider these ratios in relation to past, present, and future projects, making sure that they are investing in a project that will produce the best value for their dollar.
The goal of process control is increased efficiency; ratio analysis uses a wide variety of point in similar projects as benchmarks to denote where efficiency can be enhanced, and underlines differences in profitability and efficiency that may sway resource allocation for the organization in the future.
The goal of any organization is profits, and ratio analysis allows organizations to see where dollars are being invested and the results on that investment in terms of profitability percentage. Project managers must justify their projects in this context to appease managerial concerns and considerations; thus ratio analysis is also useful in ensuring the viability and likelihood of renewal for a given project.